Blockchain interoperability is the know-how that permits totally different blockchain networks to speak and share data seamlessly. Initially, this idea was of curiosity primarily to blockchain fanatics. Nevertheless, because the variety of blockchain networks and customers expanded, the necessity for these various techniques to work collectively grew to become important.
Over time, options facilitating interoperability have considerably developed. Early strategies usually concerned a number of steps that weren’t user-friendly. In the present day, with developments like chain abstraction, the panorama has remodeled. Chain abstraction simplifies interactions throughout a number of blockchains by offering a unified interface, making it simpler for customers and builders to function throughout numerous networks with out coping with the underlying complexities.
On this article, we'll discover the foundational ideas of blockchain interoperability, focus on the influence of initiatives driving this sector, and study rising tendencies shaping the way forward for interconnected Web3.
Definition of Blockchain Interoperability
TL;DR: Blockchain interoperability refers back to the capability of various blockchains to work together with one another to speak and share knowledge, data, or worth.
In our on a regular basis web expertise, we seamlessly ship emails from Gmail to Outlook, share recordsdata between Home windows and Mac techniques, and entry web sites throughout the globe whatever the internet hosting service. This easy change of knowledge is feasible due to interoperability—the power of various techniques to speak and work collectively.
Think about if this weren't the case: a fragmented web the place every service operated in isolation, unable to work together with others. Such a state of affairs would severely restrict the web's utility and comfort. Equally, for Web3 to surpass Web2, attaining seamless interoperability amongst numerous blockchain networks is essential.
Why Can’t Blockchains Interoperate?
Whereas the thought of various blockchains working collectively sounds perfect, a number of technical challenges forestall this from occurring naturally.
Blockchains are Remoted Ecosystems
Every blockchain operates as a self-contained community of nodes. These nodes collaborate by a peer-to-peer community, sharing important transaction data to achieve consensus and validate new blocks. They keep a state database containing all sensible contract knowledge, account balances, and different related data mandatory for impartial block development.
Nevertheless, each blockchain has its separate community of nodes and state datasets. Consequently, nodes on one blockchain are unaware of actions outdoors their system, together with these on different blockchains, the standard Web2 Web, or the actual world. This isolation ensures safety and integrity inside every blockchain however poses a big barrier to cross-chain communication.
Blockchains are Trustless Techniques
Within the blockchain realm, "trustless" implies that the system operates with no need to position belief in an exterior occasion or knowledge. All transactions and knowledge are verified by predefined consensus mechanisms. We should transmit on-chain knowledge from the supply chain to the vacation spot to attach two remoted blockchain ecosystems.
Nevertheless, since blockchains are trustless, one blockchain can not merely "trust" data from one other chain with out verification. Furthermore, it lacks entry to the required state and transaction knowledge to authenticate this exterior data. Subsequently, any interoperability answer should introduce a belief part—a system that may successfully vouch for the accuracy of knowledge originating from outdoors the community.
In subsequent sections, we'll discover blockchain bridges, that are designed to deal with this very problem.
Major Targets of Blockchain Interoperability
Primarily based on our dialogue thus far, the principle targets of blockchain interoperability embody:
- Establishing a System for Sharing Block Info Between Blockchain Networks: Creating mechanisms that enable totally different blockchains to change knowledge seamlessly.
- Guaranteeing the Shared Info is Appropriate and Full: Implementing safeguards to ensure that knowledge transferred between chains stays untampered and uncensored.
- Making a System of Liquidity Move Between Chains Whereas Eliminating Dangers Like Double Spending: Facilitating the motion of belongings throughout blockchains with out the danger of the identical asset being spent greater than as soon as.
- Permitting Sensible Contracts from One Chain to be Known as from One other Chain: Enabling sensible contracts on totally different blockchains to work together broadens the scope of decentralized purposes.
Attaining these objectives is crucial for constructing a cohesive and environment friendly blockchain ecosystem, which can pave the best way for the subsequent technology of decentralized purposes and providers.
The Evolution of Interoperability in Blockchain
Blockchain interoperability has developed by distinct phases, every pushed by particular limitations and calls for that impressed new options. The development from atomic swaps to intents and chain abstraction displays how the business has constantly tailored to allow extra seamless and environment friendly cross-chain interactions.
Atomic Swaps (2013–2017): The First Step Towards Cross-Chain Transactions
Downside: Early blockchains had been siloed ecosystems (as we realized beforehand), that means belongings couldn’t transfer between chains with out intermediaries (like CEXs, which isn’t perfect for privateness). The necessity for decentralized cross-chain transactions led to the event of atomic swaps.
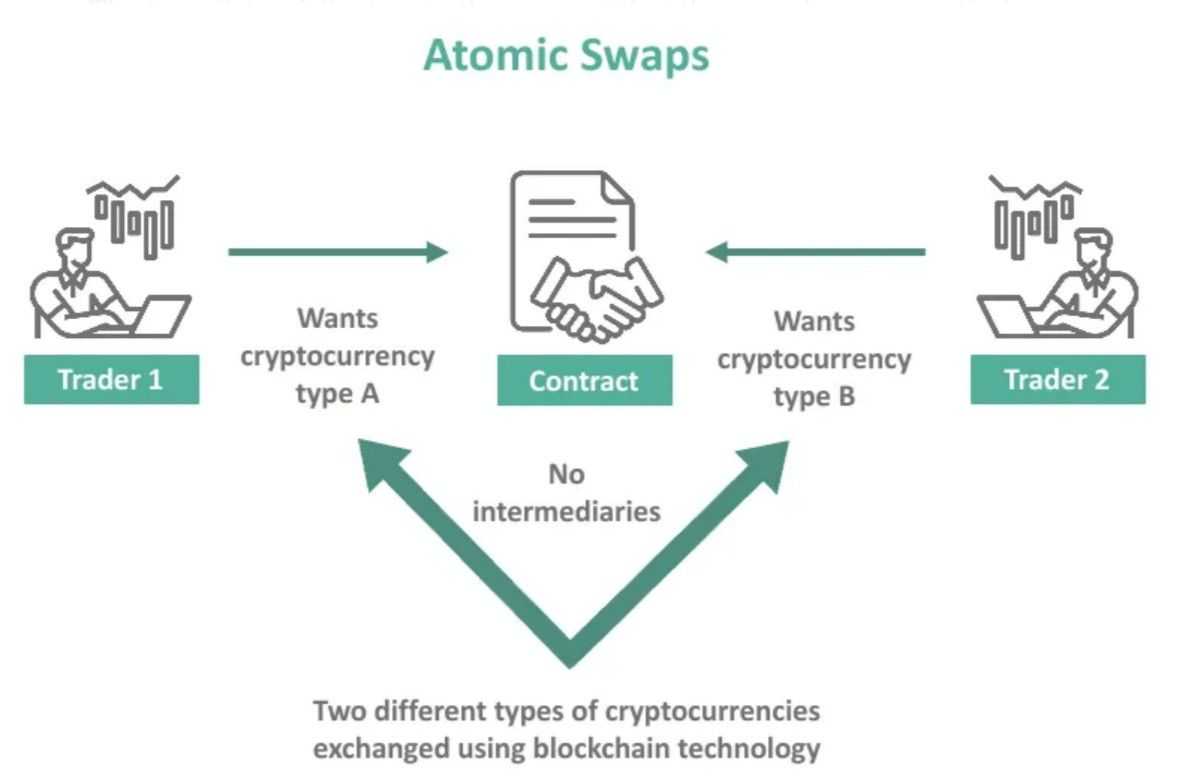
Innovation Achieved: Atomic swaps used hashed time-locked contracts (HTLCs) to allow trustless peer-to-peer asset exchanges between two chains. This mechanism ensured that both each events obtained their belongings or the transaction was canceled.
An HTLC contract works like an escrow between two events. The receiving occasion needed to acknowledge receiving funds inside a particular time, or the contract would cancel your entire change and return the belongings to their authentic addresses.
New Issues and Calls for:
- Restricted usability: Atomic swaps had been complicated, requiring individuals to be on-line concurrently, limiting their purposes.
- Low effectivity: They solely labored for belongings that supported the identical hashing and scripting mechanisms.
- No general-purpose interoperability: Atomic swaps allowed asset transfers however didn’t allow sensible contract interactions throughout chains.
Cross-Chain Bridges (2017–2020): Facilitating Asset and Knowledge Transfers
Downside: Atomic swaps labored just for primary asset exchanges, however DeFi’s rise launched the necessity for extra fluid asset transfers and sensible contract interactions throughout blockchains. Whereas atomic swaps had been restricted to peer-to-peer cross-chain interplay, bridges enabled peer-to-contract change, permitting customers to switch funds cross-chain reasonably than an change.
Innovation Achieved:
- Liquidity-backed bridges (e.g., Wrapped Bitcoin) allowed belongings to be locked on one chain and minted as derivatives on one other. Wrapped Bitcoin enabled customers to lock BTC in a particular tackle and mint its artificial spinoff on one other, sensible contracts-enabled chain like Ethereum, enabling BTC-based DeFi methods whereas the lock maintained Bitcoin’s intrinsic worth.
- Mild-client-based bridges (e.g., Interledger, Cosmos IBC) enable safe cross-chain messaging by Merkle proofs and on-chain verification. A light-weight shopper is a node that tracks solely a community’s block headers as a substitute of your entire block, making it conscious of community exercise. Mild purchasers can observe a cross-chain request and ship the information to the vacation spot chain.
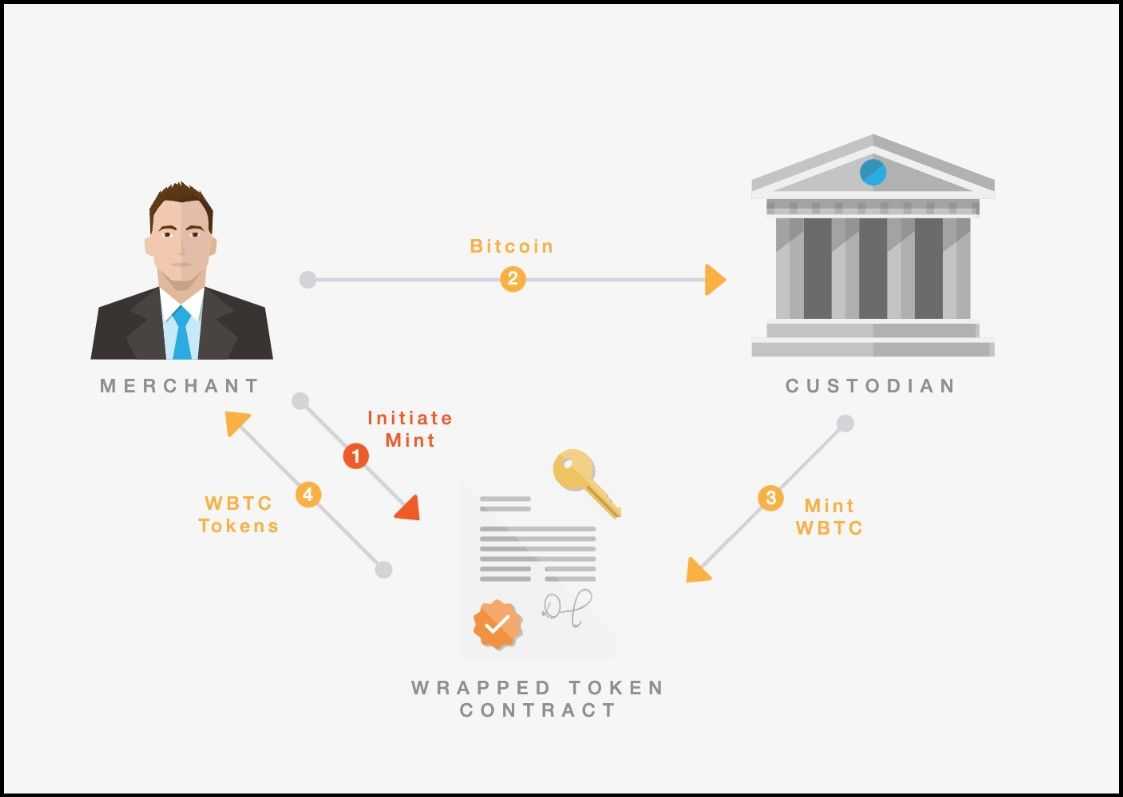
New Issues and Calls for:
- Centralization dangers: Many bridges relied on trusted events or federations to handle locked belongings, creating honeypots for hacks. Bridges used mechanisms like multi-sig contracts to safe bridge contracts holding large liquidity, attracting hackers and colluders.
- Safety vulnerabilities: Bridges grew to become prime targets for exploits, shedding billions in hacks.
- Excessive latency and prices: Verifying cross-chain transactions in a decentralized manner was computationally costly and gradual.
Cross-Chain Messaging Protocols (2020–2022): Introducing Sensible Contract Composability
Downside: Transferring liquidity throughout chains wasn’t sufficient. Customers demanded sensible contract interoperability, the power to entry sensible contracts on one chain by calling them from one other.
Innovation Achieved:
- Generalized messaging protocols (e.g., LayerZero, Axelar, Wormhole) allowed sensible contracts to speak throughout chains utilizing relayers, oracles, and multi-party validation.
- Cross-chain DApps: Normal objective messaging enabled cross-chain DApps. Builders not wanted to fork DApps to help a number of networks.
New Issues and Calls for:
- Fragmented liquidity: Every rollup or cross-chain bridge had its personal liquidity swimming pools, creating inefficiencies.
- Lack of Requirements: Similar tokens (like stablecoins) on a community arriving kind totally different bridges weren’t fungible, fragmenting liquidity and creating market inefficiency.
- Lack of user-friendly experiences: Customers should manually bridge belongings and work together with a number of networks, resulting in poor UX.
- Safety trade-offs: Some messaging protocols compromised on decentralization or relied on exterior relayers.
Intent-Primarily based Interoperability (2022–Current): Automating Cross-Chain Execution
Downside: Cross-chain interactions remained user-initiated and handbook, requiring customers to bridge belongings and execute transactions throughout totally different chains. This complexity hindered mass adoption.
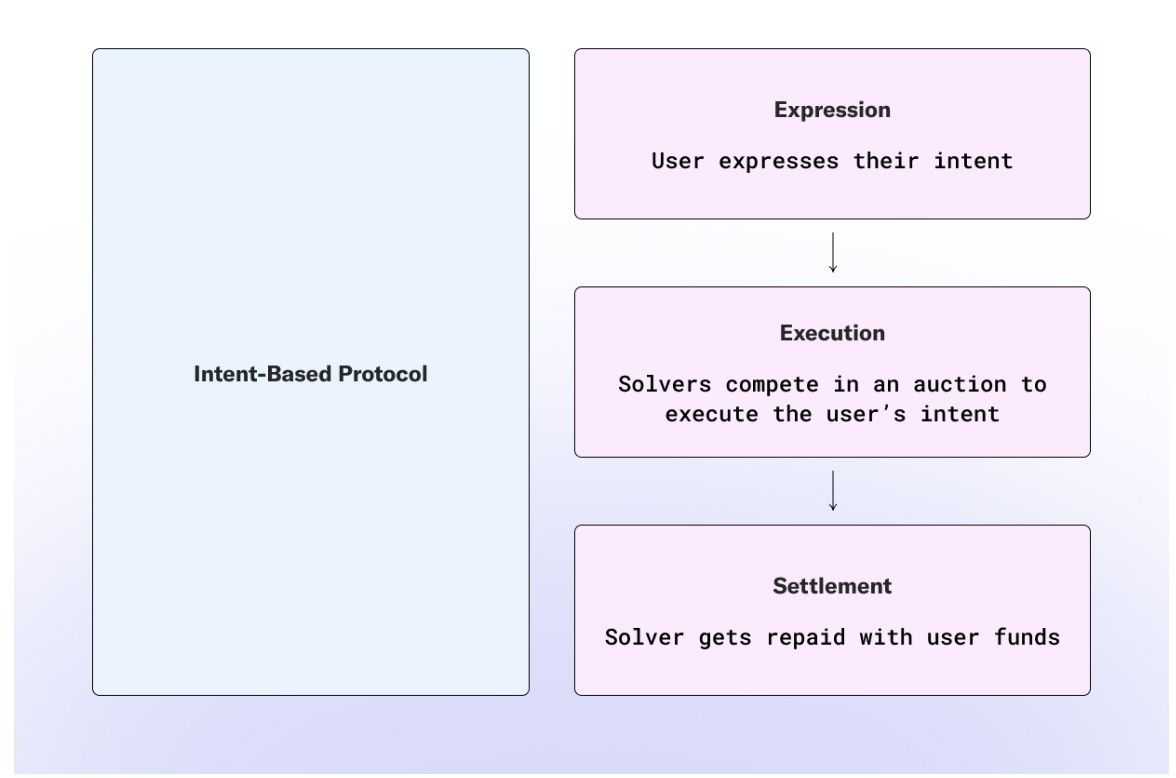
Innovation Achieved:
- Intent-based architectures (e.g., Anoma) shifted the paradigm from customers signing each transaction to customers expressing what they need to obtain (intent), and decentralized solvers would execute the transaction most optimally.
- Composable interoperability (e.g., Hyperlane, Chainlink CCIP) allowed chains to speak on the sensible contract stage, making interoperability extra seamless.
New Issues and Calls for:
- Standardization challenges: No common commonplace exists for the way intents needs to be expressed and executed throughout chains.
- Belief assumptions: Some intent-based techniques introduce new middlemen (solvers), requiring belief in off-chain computation.
- Effectivity constraints: Guaranteeing quick execution and MEV resistance stays an space of energetic improvement.
Chain Abstraction (Rising Development, 2024+): Erasing Blockchain Boundaries
Downside: Even with intents, customers nonetheless must know what chain they work together with. The finish aim of interoperability is full chain abstraction—the place customers work together with purposes with out worrying about which blockchain they’re on.
Innovation Achieved:
- Omnichain execution layers (e.g., Omni Community, Particle Community) intention to make chains interoperable on the base layer, eradicating the necessity for bridges completely.
- AI-driven solvers automate complicated cross-chain transactions in a manner that’s invisible to customers.
Subsequent Challenges:
- Safety trade-offs: Chain abstraction options depend on relayers and third-party execution layers, requiring sturdy safety measures.
- Scalability: Dealing with seamless execution throughout a number of chains with low latency stays a technical problem.
- Ecosystem adoption: For chain abstraction to succeed, wallets, apps, and builders should combine these options.
Conclusion: The place Are We Headed?
The evolution of blockchain interoperability has constantly adopted a cycle of demand, innovation, and new challenges:
- Atomic Swaps launched primary trustless swaps however lacked flexibility.
- Cross-Chain Bridges enabled transfers however had been safety dangers.
- Messaging Protocols & Rollups improved interoperability however led to liquidity fragmentation.
- Intent-based techniques automated cross-chain execution however nonetheless required consumer information of chains.
- Chain Abstraction is now eliminating blockchain obstacles, making interactions chain-agnostic.
The endgame of blockchain interoperability is a completely unified ecosystem during which customers work together with DApps with out figuring out which blockchain they’re on—simply because the Web abstracts away underlying community protocols at this time.
Core Parts of Blockchain Interoperability
Attaining seamless interplay between various blockchain networks includes a number of key parts, every addressing particular challenges to make sure environment friendly and safe cross-chain operations. Let's examine these core parts and perceive their roles in fostering blockchain interoperability.

Orchestration Tasks
Position: Orchestration initiatives facilitate seamless interactions throughout a number of blockchain networks, enabling customers to execute cross-chain operations with out delving into the underlying complexities.
Subcomponents:
- Account Abstraction: This strategy simplifies consumer interactions by decoupling the complexities of blockchain accounts from the end-user expertise. Tasks like Avocado and Turnkey give attention to creating extra intuitive interfaces, permitting customers to handle belongings throughout totally different chains with out dealing with a number of personal keys or understanding the intricacies of every blockchain.
- Pockets Abstraction: Pockets abstraction goals to unify the administration of belongings throughout numerous blockchains. Platforms corresponding to OneBalance, Particle Community, Arcana Community, and Orb Labs present options that enable customers to entry and handle their holdings on totally different chains by a single pockets interface, enhancing consumer expertise and lowering friction.
- Orchestration Frameworks: Tasks like Klaster, Mild, Agoric, and Li.Fi develops frameworks that coordinate and handle cross-chain transactions. They make sure that a consumer's intent to carry out operations throughout a number of blockchains is executed effectively and securely, dealing with the complexities of communication and transaction validation between networks.
Orderflow Sources and Auctions
Position: These initiatives handle the circulation of transactions throughout totally different blockchains, guaranteeing environment friendly liquidity distribution and optimum execution of cross-chain operations.
Key Tasks:
- Socket: Facilitates seamless asset transfers between blockchains, guaranteeing liquidity is effectively managed throughout networks.
- UniswapX: An extension of the Uniswap protocol, UniswapX permits cross-chain swaps, permitting customers to commerce belongings throughout totally different blockchains seamlessly.
- Router Protocol: Supplies infrastructure to facilitate cross-chain communication, enabling the change of belongings and knowledge between heterogeneous blockchains.
- Throughout+: Focuses on environment friendly bridging options, permitting fast and cost-effective transfers between Layer 2 networks and Ethereum.
- deBridge: Affords a decentralized platform for cross-chain interoperability, enabling the switch of arbitrary knowledge and belongings between numerous blockchains.
- Anoma: Goals to supply a generalized framework for asset-agnostic, privacy-preserving transfers and interactions throughout a number of blockchains.
Solvers and Solver Networks
Position: Solvers are entities or algorithms that discover optimum paths and strategies to execute cross-chain transactions, guaranteeing effectivity and minimizing prices. Solver networks are collaborative platforms the place a number of solvers work collectively to reinforce transaction execution.

Key Tasks:
- Solver Networks: Platforms like Enso and Khalani create environments the place a number of solvers can function, offering various methods for transaction execution and bettering general effectivity in cross-chain operations.
- Solvers: Entities corresponding to Wintermute and Amber focus on liquidity provision and market-making throughout numerous blockchain networks. They make sure that cross-chain transactions have the required liquidity and are executed at optimum costs.
Token Requirements
Position: Standardized token protocols guarantee consistency and compatibility of tokens throughout totally different blockchain networks, facilitating seamless transfers and interactions.
Notable Requirements:
- ERC-7281 (Shared Safety Vaults)
- Defines a cross-chain shared safety vault mechanism, permitting a number of chains to collectively safe belongings and supply staking-based safety fashions.
- Interoperability Position: Facilitates cross-chain safety sharing, enabling belongings and protocols to leverage unified safety swimming pools throughout blockchains.
- ERC-7683 (Cross-Chain Order Move Auctions – COFA)
- Standardizes a cross-chain transaction execution mechanism by introducing decentralized order circulation auctions.
- Interoperability Position: Helps optimize cross-chain execution by permitting solvers to bid for transaction achievement, guaranteeing cost-effective and environment friendly asset transfers throughout blockchains.
- ERC-4337 (Account Abstraction for Sensible Wallets)
- Allows sensible contract wallets to function like externally owned accounts (EOAs) by eradicating the necessity for personal key-controlled accounts.
- Interoperability Position: Simplifies cross-chain consumer experiences by permitting sensible wallets to operate seamlessly throughout totally different blockchains with out requiring modifications to consensus guidelines.
- EIP-3074 (Transaction Sponsorship & Batch Execution)
- Permits EOAs to delegate transaction execution to sensible contracts, enabling meta-transactions and sponsored transactions.
- Interoperability Position: Improves cross-chain composability by lowering fuel charges and enabling seamless relayed transactions throughout L1s and L2s.
- EIP-7022 (Execution Layer-Triggerable Validator Withdrawals)
- Extends validator withdrawal capabilities by enabling execution layer-triggered exits, eradicating dependence on the consensus layer.
- Interoperability Position: Enhances cross-chain validator coordination, enabling smoother interactions between Ethereum staking and restaking techniques built-in throughout a number of chains.
These requirements contribute to Ethereum's cross-chain interoperability by lowering friction in safety, execution, asset motion, and consumer interactions throughout blockchain ecosystems.
Settlement and Infrastructure Tasks
Position: These initiatives present the foundational infrastructure for cross-chain communication, transaction settlement, and sensible contract interoperability.
Key Tasks:
- LayerZero: Affords an omnichain interoperability protocol that permits decentralized purposes to speak throughout a number of blockchains effectively.
- Hyperlane: Supplies a platform for safe cross-chain messaging, permitting sensible contracts on totally different blockchains to work together seamlessly.
- Axelar: Delivers a decentralized community and instruments to facilitate safe cross-chain communication, enabling builders to construct interoperable purposes.
- Wormhole: A cross-chain messaging protocol that connects a number of blockchains, permitting the switch of belongings and data between them.
- Omni Protocol: Focuses on offering a unified interface for cross-chain interactions, simplifying the event of interoperable purposes.
- Astria: Develops infrastructure to help cross-chain settlement and communication, enhancing the scalability and interoperability of blockchain networks.
- Polygon Agglayer: A part of the Polygon ecosystem, Agglayer goals to combination liquidity and facilitate seamless transactions throughout numerous Layer 2 options and Ethereum.
- Optimism Superchain: An extension of the Optimism Layer 2 answer, the Superchain focuses on making a cohesive community of rollups that may interoperate seamlessly, enhancing scalability and consumer expertise.
By integrating these parts, the blockchain ecosystem strikes nearer to attaining true interoperability, the place belongings and knowledge can circulation freely throughout various networks, unlocking new prospects for decentralized purposes and providers.
Advantages of Blockchain Interoperability
A New Period of Blockchain Interoperability with Chain Abstraction
Blockchain interoperability has come removed from easy token swaps and cross-chain bridges. With the onset of chain abstraction, interoperability is not nearly shifting belongings between networks—it’s about making blockchain boundaries invisible to customers and builders. This new paradigm permits purposes to operate seamlessly throughout a number of chains, fixing challenges as soon as thought-about insurmountable.
In the present day, interoperability frameworks like generalized messaging layers, intent-based execution fashions, and common sensible contracts have redefined what’s potential within the blockchain area. Issues corresponding to community congestion, liquidity fragmentation, complicated account administration, and developer silos are being tackled in ways in which had been inconceivable only a few years in the past. Let’s discover the important thing advantages.
1. Lowered Congestion on the Ethereum Mainnet
One of many largest challenges in blockchain scalability has been Ethereum’s community congestion, which ends up in excessive fuel charges and gradual transaction occasions. Up to now, customers had no selection however to compete for block area on Ethereum, inflicting charges to skyrocket in periods of excessive demand (e.g., NFT minting booms or DeFi liquidations).
With cross-chain interoperability, transactions can now be offloaded to Layer 2 options (e.g., Arbitrum, Optimism, Starknet) or various chains (e.g., Polygon, Avalanche) whereas nonetheless sustaining Ethereum's safety ensures. Moreover, cross-rollup messaging protocols like LayerZero, Axelar, and Hyperlane enable sensible contracts on Ethereum to work together with contracts on different chains with out requiring customers to manually bridge belongings.
Instance: As a substitute of executing all DeFi trades on Ethereum, customers can swap belongings on Arbitrum whereas settlement happens on Ethereum, lowering congestion on the mainnet whereas sustaining safety.

2. Defragmenting Liquidity and Eliminating Liquidity Silos
Liquidity fragmentation has been a persistent problem in DeFi. As a result of belongings are sometimes locked in remoted swimming pools throughout totally different chains, customers face inefficiencies, slippage, and value discrepancies when swapping belongings.
Interoperability options corresponding to Omnichain Liquidity Protocols (e.g., THORChain, Stargate) allow liquidity to maneuver freely throughout chains, guaranteeing deeper and extra environment friendly buying and selling markets. Cross-chain DEXs (e.g., Squid, LI.FI, Router Protocol) enable customers to swap belongings natively between chains with out counting on centralized exchanges or conventional bridges.
Instance: A dealer seeking to swap ETH on Ethereum for USDC on Solana can now achieve this in a single transaction utilizing cross-chain DEXs, with out manually bridging belongings and swapping them individually.
3. Simplified Account Administration with Account Abstraction and Pockets Abstraction
Managing wallets throughout a number of blockchains has historically been a nightmare for customers. Totally different chains require totally different wallets, and customers should manually change networks, retailer a number of seed phrases, and keep in mind which chain holds which belongings.
With account abstraction (ERC-4337) and pockets abstraction, customers can work together with a number of blockchains from a single sensible contract pockets with out worrying about chain-specific complexities. Moreover, interoperable wallets (e.g., Rabby, Squid, and Particle Pockets) enable customers to execute transactions throughout chains from a single interface.
Instance: A consumer holding belongings on Ethereum, BNB Chain, and Avalanche can use a sensible contract pockets to execute transactions with out switching networks manually or remembering a number of personal keys.
4. Lowering the Must Preserve A number of Gasoline Tokens for Totally different Networks
A serious UX ache level in crypto is holding totally different fuel tokens (ETH for Ethereum, MATIC for Polygon, AVAX for Avalanche, and many others.) to pay for transactions on totally different chains. This provides pointless complexity, particularly for brand new customers.
Gasoline abstraction options now enable customers to pay fuel charges in any token and even have fuel prices sponsored by third-party relayers. Tasks like Biconomy, Pimlico, and Gelato allow gasless transactions and cross-chain fuel funds, making blockchain interactions frictionless.
Instance: A consumer sending USDC on Optimism can pay fuel charges in USDC as a substitute of needing ETH, simplifying the consumer expertise.
5. Defragmenting Developer Mindshare Throughout Totally different Networks
Up to now, blockchain builders needed to select a particular community to construct on, resulting in tooling, liquidity, and adoption fragmentation. Builders engaged on Ethereum had been usually remoted from these constructing on Solana, Avalanche, or Cosmos.
With interoperability options like cross-chain sensible contract frameworks (e.g., Agoric, Hyperlane, Axelar VM, Omni Community, and Particle Community), builders can write purposes as soon as and deploy them throughout a number of blockchains with out re-engineering them for every community.
Instance: A DeFi protocol can now launch a single sensible contract that interacts seamlessly with Ethereum, Solana, and Cosmos, guaranteeing a unified consumer base and liquidity pool throughout chains.
Conclusion: The Future is Chain-Agnostic
Blockchain interoperability has developed from easy asset bridges to full-stack execution layers that summary away blockchain variations completely. As we transfer towards chain abstraction, customers will not must care about which chain they’re utilizing, which fuel token they want, or the way to handle a number of wallets. Ecosystem silos will not restrict builders and might construct purposes that work seamlessly throughout chains.
Within the close to future, the blockchain expertise can be as seamless because the web, the place customers work together with purposes with out worrying concerning the underlying community.
Challenges to Blockchain Interoperability
Whereas blockchain interoperability has made vital strides, it nonetheless faces a number of technical, structural, and safety challenges that hinder seamless cross-chain interactions. Because the blockchain ecosystem grows extra complicated, these challenges turn into much more pronounced.

Technical Limitations: The Belief Assumption Downside
Blockchain networks had been by no means initially designed to speak with one another, and forcing cross-chain interoperability all the time introduces some extent of belief.
Even in probably the most decentralized interoperability fashions—corresponding to light-client bridges or zero-knowledge proofs for cross-chain messaging—there isn’t a such factor as good trustlessness. Each interoperability answer should make trade-offs:
- Bridges depend on exterior relayers, validators, or multi-party computation to verify cross-chain transactions.
- Messaging protocols rely on exterior oracles or quorum-based consensus.
- Cross-chain sensible contracts introduce assault vectors the place one community’s safety assumptions don’t align with one other.
Instance: The Wormhole bridge hack ($320M misplaced) occurred due to a wise contract vulnerability in verifying cross-chain messages. Even trust-minimized options stay uncovered to safety flaws.
In the end, each interoperability mechanism introduces a belief mannequin that should be evaluated, and whereas decentralization and cryptographic safety have improved, actually trustless interoperability stays elusive.
Lack of Requirements: Fragmentation Throughout Solvers and Abstraction Layers
The present panorama of solver networks, intent-based execution fashions, and interoperability frameworks is very fragmented, creating compatibility points throughout totally different options.
- Intent-based protocols like Anoma and CowSwap depend on solvers, however no common manner exists to outline or execute intents throughout networks.
- Cross-chain messaging protocols (e.g., Axelar, LayerZero, Hyperlane) all have totally different architectures, making interoperability protocol-dependent.
- Liquidity fragmentation throughout omnichain DEXs like THORChain, Squid, and Stargate means cross-chain swaps require protocol-specific routes.
This lack of standardization hinders composability and forces builders to decide on between siloed interoperability options.
Instance: A DeFi protocol constructing a cross-chain software should determine whether or not to combine with LayerZero’s OFT commonplace, Axelar GMP, or Hyperlane. Integration choices lock initiatives into particular frameworks since no common messaging commonplace exists.
With out extensively adopted interoperability requirements, solvers, relayers, and abstraction layers will stay fragmented, limiting effectivity and adoption.
Ever-Rising Community Webs: The Scaling Downside of Interoperability
The variety of blockchains, consensus mechanisms, token requirements, and execution layers is rising quicker than ever, making it more and more troublesome to keep up a unified interoperability community.
Key elements driving this complexity:
- The rise of appchains (e.g., Cosmos SDK, Avalanche Subnets, Polkadot parachains) is growing the variety of sovereign networks that want interoperability.
- New consensus mechanisms (e.g., Transfer-based blockchains like Aptos and Sui) introduce architectural variations that complicate cross-chain integration.
- EVM and non-EVM ecosystems (e.g., Solana, Cosmos, Close to, and Bitcoin) require completely totally different interoperability options.
Instance: Cross-chain messaging protocols that help Ethereum-based rollups should completely rework their structure to help non-EVM blockchains like Solana or Cosmos.
As extra chains, rollups, and app-specific blockchains emerge, conserving tempo with new integrations and guaranteeing safe, scalable interoperability will stay a steady problem.
Different Challenges: Sensible Contract Dangers and Safety Threats
Along with the structural challenges of interoperability, a number of apparent dangers persist:
- Sensible Contract Vulnerabilities: Cross-chain bridges, messaging protocols, and liquidity swimming pools all depend on sensible contracts that may be exploited (e.g., Ronin Bridge Hack – $600M).
- Financial Assaults: Cross-chain arbitrage, sandwich assaults, and MEV (Maximal Extractable Worth) dangers improve as belongings transfer throughout chains.
- Oracle Manipulation: Cross-chain oracles introduce further belief assumptions and may be manipulated in low-liquidity environments.
Whereas interoperability unlocks a chain-agnostic future, these safety and structural challenges should be addressed earlier than cross-chain networks can attain full effectivity and reliability.
Way forward for Blockchain Interoperability: A Blockchain-Agnostic Web3
The final imaginative and prescient for blockchain interoperability is to make Web3 utterly blockchain-agnostic—the place customers not must know, and even care, which blockchain they work together with whereas performing on-chain actions.
On this future, all blockchains interconnect so effectively that belongings, purposes, and sensible contracts function as if they’re a part of a single unified system. This implies:
- Excellent liquidity defragmentation: No extra scattered liquidity swimming pools throughout totally different chains—capital flows seamlessly throughout networks, guaranteeing probably the most environment friendly execution for customers.
- Excellent cross-chain composability: Functions throughout totally different blockchains operate as in the event that they exist on the identical community, eliminating handbook bridging, fragmented ecosystems, and network-switching complexity.
- Invisible blockchain interactions: Customers will merely signal transactions by sensible wallets, and solvers will execute them optimally throughout any blockchain with out requiring the consumer to decide on a community or pay charges in a number of fuel tokens.
With improvements in chain abstraction, solver networks, AI-driven execution layers, and unified liquidity fashions, the way forward for interoperability isn’t just cross-chain compatibility—it’s making Web3 as seamless because the web, the place blockchain boundaries disappear completely.
Conclusion
Blockchain interoperability started as a systemic drawback that wanted fixing. Initially, the main focus was on fixing a basic want—shifting liquidity from one chain to a different with out counting on centralized intermediaries.
Nevertheless, as blockchain ecosystems expanded, interoperability developed past simply asset transfers. In the present day, it performs an important function in fixing deep-rooted UX challenges, making Web3 extra accessible, environment friendly, and seamless. As a substitute of simply bridging tokens, interoperability now tackles points like simplified account administration, cross-chain composability, and liquidity fragmentation—all important for mass adoption.
For Web3 to succeed, blockchains should turn into so intuitive that even our grandparents can use decentralized purposes with out confusion. This implies eliminating technical obstacles, abstracting community complexities, and guaranteeing customers by no means have to consider which blockchain they’re on. Interoperability is essential to that imaginative and prescient, bringing us nearer to a future the place Web3 is as easy to make use of because the web itself.
Often Requested Questions
Which Expertise Allows Interoperability Between Totally different Blockchains?
Blockchain interoperability is enabled by applied sciences corresponding to cross-chain bridges, messaging protocols, intent-based execution fashions, and chain abstraction.
What’s Blockchain Interoperability, and Why is it Necessary?
Blockchain interoperability refers back to the capability of various blockchains to speak, share knowledge, and switch belongings seamlessly. It is essential as a result of the blockchain ecosystem is very fragmented, with every community working in isolation.
Interoperability permits extra environment friendly liquidity circulation, cross-chain sensible contract execution, and enhanced consumer expertise, making decentralized purposes extra sensible and scalable, finally positioning Web3 as a viable various to Web2.
What Are Examples Of Blockchain Interoperability?
Examples of blockchain interoperability embody:
- Atomic Swaps – Trustless peer-to-peer asset exchanges (e.g., BTC-ETH swaps utilizing HTLCs).
- Cross-Chain Bridges – Wrapped belongings and liquidity-backed bridges (e.g., Wrapped Bitcoin, Polygon Bridge).
- Generalized Messaging Protocols – Cross-chain sensible contract interactions (e.g., LayerZero, Axelar, Wormhole).
- Intent-Primarily based Protocols – Automating cross-chain execution (e.g., Anoma, Hyperlane).
- Chain Abstraction – Eradicating blockchain obstacles utterly (e.g., Omni Community, Particle Community).
What Promotes Interoperability And Trustless Connections Between Blockchains?
Interoperability and trustless connections between blockchains are promoted by:
- Mild Consumer-Primarily based Bridges – (e.g., Cosmos IBC, Interledger) that use Merkle proofs and on-chain verification.
- Cross-Chain Messaging Protocols – (e.g., LayerZero, Axelar, Hyperlane) enabling trust-minimized communication.
- Zero-Data Proofs (ZKPs) and Rollups – (e.g., zkSync, Starknet) enhancing trustless verifications.
- Decentralized Solvers & Validators – (e.g., Wintermute, Khalani) for trust-minimized transaction execution.
- ERC Requirements – (e.g., ERC-7281, ERC-7683) guaranteeing compatibility throughout blockchains.
What are the Trendy Developments in Blockchain Interoperability?
Trendy interoperability tendencies give attention to chain abstraction, cross-chain liquidity aggregation, and modular interoperability frameworks. Chain abstraction simplifies cross-chain interactions, permitting customers to transact throughout blockchains with no need to handle a number of wallets.
Liquidity aggregation, seen in initiatives like UniswapX and Router Protocol, optimizes cross-chain swaps. Modular options, corresponding to LayerZero and Hyperlane, allow versatile, customizable cross-chain messaging, making interoperability extra adaptable and scalable.
Which Multi-Chain Community Focuses On Interoperability Between Blockchains?
A number of multi-chain networks give attention to interoperability, together with:
- Cosmos (IBC Protocol) – Facilitates cross-chain messaging utilizing Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC).
- Polkadot (Relay Chain & Parachains) – Makes use of a shared safety mannequin for cross-chain interoperability.
- LayerZero – Allows omnichain interoperability throughout EVM and non-EVM chains.
- Axelar Community – Supplies safe cross-chain communication and decentralized sensible contract execution.
- THORChain – Facilitates native cross-chain swaps with out wrapped belongings.
What’s the Position of Solvers in Attaining Interoperability?
Solvers act as liquidity facilitators and transaction optimizers in cross-chain operations. They analyze a number of blockchains to search out probably the most environment friendly paths for executing transactions. Tasks like Wintermute and Amber operate as solvers, guaranteeing that trades and transfers happen at the very best charges with minimal slippage. Solver networks, corresponding to Enso and Khalani, allow a number of solvers to collaborate, bettering transaction execution and lowering inefficiencies in interoperability.
What Is Interoperability In Ethereum?
Interoperability in Ethereum refers to its capability to speak and share knowledge with different blockchain networks. Ethereum interoperability options allow cross-chain sensible contract interactions, liquidity transfers, and asset bridges between Ethereum and different blockchains.