I’ve been studying about blockchain expertise since 2021. I bear in mind my fascination when studying about Polygon as one of many first Ethereum scaling options. Again then, Polygon was an Ethereum sidechain, one of many many scaling options that sprung up. The innovation frenzy was about making Ethereum sooner and extra highly effective with out sacrificing its distinctive qualities of decentralization and safety.
Sidechains are not a novel idea. They’re an extensively researched idea in Ethereum, and lots of sidechain initiatives function beneath Ethereum's umbrella right now. I might go as far as to say that in Ethereum particularly, sidechains are an outdated idea, as now we have way more environment friendly scaling options within the combine right now. Designs like Layer 2 techniques, Validium, and sovereign rollups carry out higher than sidechains.

Nonetheless, even after this idea has seemingly antiquated in Ethereum, with even Polygon, essentially the most profitable sidechain challenge, migrating to a more moderen design (learn Polygon 2.0), why are we overlaying this matter at The Coin Bureau?
It’s as a result of, to our shock, the sidechain as an idea is making a comeback. This text will break down sidechains and perceive their scalability potential. We’ll cowl the advantages that made it well-known within the final cycle and the drawbacks that led it out of favor. Lastly, we’ll talk about some current initiatives that leverage sidechains, which can give us a peek into how this design could also be making a comeback.
What’s a Sidechain?
The motivation for a sidechain stems from the scalability trilemma. The trilemma states {that a} blockchain community has to trade-off between safety, decentralization, and scalability, as it’s unattainable for a community to attain all three in a single system.
This limitation has impressed a number of blockchain designs which have employed multi-chain structure over time, and a sidechain is considered one of them.
A sidechain is a separate blockchain connected to its guardian blockchain utilizing a two-way peg. The connection permits property from the sidechain to be redeemable on the mainchain and vice versa, enabling the sidechain to function independently whereas nonetheless being anchored to the mainchain for crypto-economic ensures.
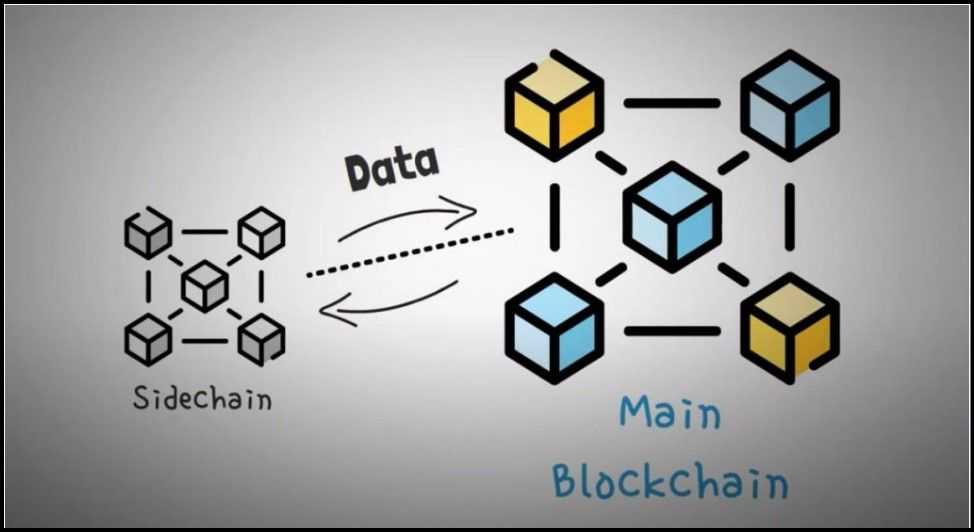
Listed below are some key ideas of sidechains:
Two-Approach Peg
An asset switch mechanism is deployed to switch property from the mainchain to the sidechain and again, primarily based on a predetermined fee and guidelines. The pegging ensures that the whole provide of the asset stays constant throughout each chains.
The interoperability of property permits transferring liquidity between the chains, a vital characteristic to leverage the sidechain's capabilities. For example, a sidechain is often sooner and cheaper to make use of than the mainchain, so it could act as a cost channel for the mainchain, the place customers settle balances periodically.
Impartial Operation
A sidechain isn’t depending on its guardian for normal operation, permitting it to undertake a distinct design. The independence to make use of completely different consensus guidelines, block creation processes, and blockchain design means it might provide distinctive advantages and options to its guardian chain. Having distinctive capabilities {that a} typical guardian chain like Ethereum is incapable of is the primary USP of sidechains.
Safety
A sidechain might keep a two-way peg as a safety characteristic as effectively. In case of anomalies within the sidechain, the peg will allow customers to redeem their property on the secure mainchain. The mainchain might also assist reinforce the sidechain's safety utilizing numerous mechanisms, which we’ll cowl later within the article.
How Sidechains Function
A sidechain primarily operates as an unbiased blockchain with some particular ensures or connections with one other, sometimes bigger chain. There is no such thing as a normal for a way sidechains function. As an alternative, a sidechain is a spectrum of chains that share some design ideas. Let's discover what these ideas are.
Asset Switch Between Mainchain and Sidechain
Asset switch between a mainchain and a sidechain is a basic mechanism that allows the interoperability of those two blockchain networks. This course of sometimes includes locking the asset on the mainchain and creating or releasing an equal asset on the sidechain, and vice versa. Right here's an in depth take a look at how this switch mechanism works and its implications for blockchain ecosystems:
Locking and Minting Belongings
- Locking the Asset on the Mainchain: To switch property to the sidechain, the person initiates a switch of that asset to a devoted sensible contract on the mainchain.
- Locking the Asset: The sensible contract locks the asset, and the mainchain information this transaction.
- Issuance on the sidechain: The sidechain observes the mainchain exercise continuously. When a sensible contract notices this locking occasion, successfully proving that the property are locked within the designated location, it mints an equal quantity of property. It sends it to the person's handle on the sidechain.
These property pegged to a token on one other chain are known as artificial property. Artificial property are a vital ingredient of cross-chain asset transfers. For property like ETH, its provide is out of our management; if burned, we lose such property completely. Artificial property make sure the motion of canonical crypto property throughout chains with out necessitating its burn on the supply chain.
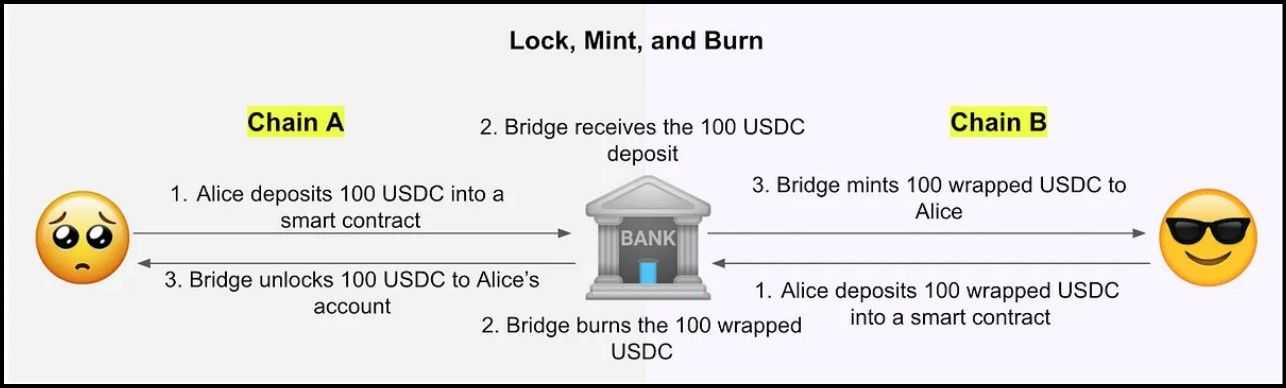
Redeeming Artificial Belongings
Redeeming the unique asset on the supply chain includes reversing the locking course of. So, the artificial asset is shipped again to the sensible contract that created it, which then burns it, creating an occasion on the sidechain. Then, the sensible contract on the supply chain picks on this occasion and releases the unique asset to its earlier handle.
Sensible Contracts and Performance
Sidechains provide a versatile platform for deploying superior sensible contracts and functionalities past the constraints of mainchains. Sidechains drive scalability and effectivity enhancements throughout blockchain ecosystems by enabling extra advanced transactions and revolutionary functions.
- Versatile Sensible Contracts: Sidechains can help a extra complete array of programming languages and customized requirements, permitting builders to implement subtle sensible contracts tailor-made to particular use circumstances. They facilitate multi-stage transactions and integration with oracles, important for functions like decentralized finance (DeFi), the place contracts should reply to real-world knowledge.
- Pace and Effectivity: Sidechains considerably improve transaction speeds by decreasing block instances and implementing scalable options like sharding. This leads to sooner confirmations and decrease transaction charges, making them helpful for high-frequency buying and selling, gaming, and micropayments. For instance, whereas Bitcoin's mainchain processes block each 10 minutes, sidechains just like the Liquid Community obtain a lot faster block instances.
- Experimentation and Innovation: Builders use sidechains to pilot new applied sciences and protocols with out risking the mainchain's stability. This sandbox setting fosters innovation, enabling the testing of novel consensus algorithms and interoperability options. Sidechains additionally help customized DeFi platforms and superior privateness options, offering safe environments for decentralized exchanges and confidential transactions.
In conclusion, sidechains empower blockchain ecosystems with enhanced capabilities, driving the adoption of blockchain expertise by making it extra accessible, scalable, and versatile. As they evolve, sidechains will proceed to play a vital position in increasing blockchain's potential and fostering cross-chain interoperability.
Consensus Mechanism
Sidechains can use a distinct consensus mechanism from the mainchain. For example, whereas the mainchain may use Proof of Work (PoW), the sidechain might use Proof of Stake (PoS) or different consensus algorithms to validate transactions and create blocks. This flexibility permits for experimentation with completely different applied sciences and efficiency optimizations that may not be possible on the mainchain.
Safety and Checkpointing
The mainchain performs a vital position in reinforcing the safety of a sidechain in a blockchain ecosystem. Though sidechains are designed to function independently, they will leverage the robustness and safety features of the mainchain in a number of methods. Right here's a complete rationalization of how the mainchain helps to bolster the safety of the sidechain:
Anchoring
Anchoring includes periodically recording the state of the sidechain onto the mainchain. Anchors can embrace essential data like the newest block hashes or different state knowledge. The anchoring course of offers a verifiable reference level on the mainchain, which may validate the state of the sidechain.
Anchoring sidechain states on the mainchain exposes any malicious makes an attempt to change its historical past by evaluating it to information saved within the mainchain. This linkage acts as a deterrent towards fraud and helps in battle decision.
Checkpointing
Checkpointing is just like anchoring however usually includes saving extra detailed data, like full blocks or transaction histories, from the sidechain onto the mainchain. These checkpoints function safe backup factors that the sidechain can reference in case of disputes or anomalies.
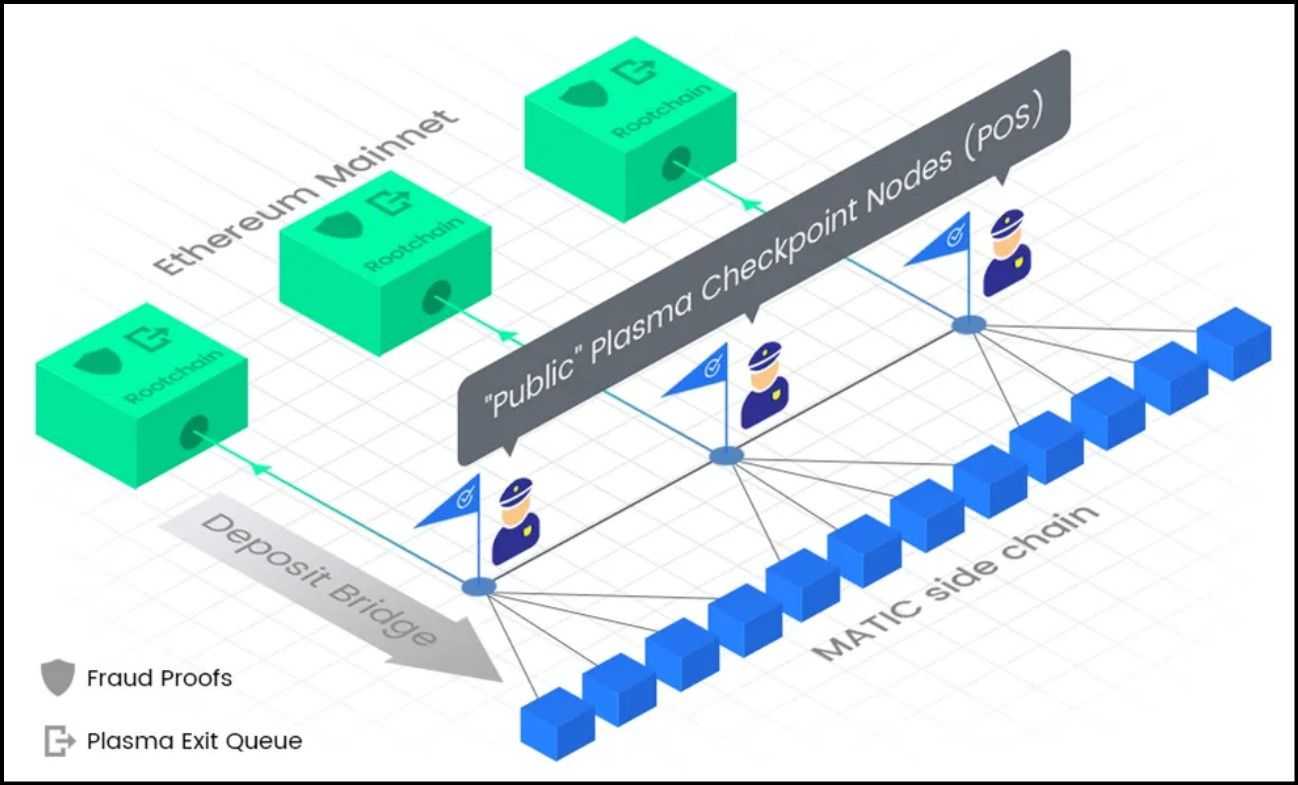
Checkpointing on the mainchain provides an extra layer of safety by offering a dependable and tamper-proof document of the sidechain's operations. It additionally assists within the rollback course of if malicious exercise is detected.
Cross-Chain Consensus Mechanisms
Some sidechains additionally deploy cross-chain consensus mechanisms the place validators or miners from the mainchain are concerned in securing the sidechain. Listed below are two examples of cross-chain consensus mechanisms:
- Merge Mining: It permits miners to concurrently safe the primary and facet chains utilizing the identical computational work. The method helps the sidechain inherit some safety properties of the mainchain.
- Federated Validators: In a federated mannequin, a gaggle of pre-approved validators (usually the identical entities that validate the mainchain) is tasked with sustaining the sidechain. This mannequin depends on the reputational and operational belief of the federated validators. Since these validators are sometimes a part of the mainchain's ecosystem, they’ve a vested curiosity in sustaining integrity and safety.
Conclusion
The safety reinforcement offered by the mainchain to sidechains is multifaceted and demanding to the dependable operation of sidechains. Whether or not by way of anchoring, cross-chain consensus, validation, redundancy, or financial incentives, the mainchain gives strong mechanisms that improve the general safety and trustworthiness of sidechains. This symbiotic relationship permits sidechains to innovate and scale whereas leveraging the foundational safety properties of their mainchains.
Sidechains vs. Parachains
A parachain is an application-specific knowledge construction that may be validated by the validators of the Relay Chain, working in parallel to reinforce transaction processing and scalability throughout the Polkadot and Kusama networks. Whereas sometimes structured as blockchains, parachains aren’t restricted to this kind.
They profit from the community's general safety and may talk with different parachains by way of the XCM format. Parachains are managed by collators, who keep the parachain's full node, retain vital data, and produce new block candidates for Relay Chain validation. The incentivization of collators varies by parachain and doesn’t essentially require staking or proudly owning the native token until specified by the parachain.
Key variations between sidechains and parachains embrace:
- Design Function: Sidechains offload particular transactions from a primary chain, whereas parachains function alongside a primary chain inside a bigger community.
- Integration: Sidechains are extra unbiased from the primary chain, whereas parachains are tightly built-in with the Polkadot community, leveraging its governance system and cross-chain interoperability.
- Customization: Sidechains have restricted customization and performance, usually restricted to sure sorts of transactions. In distinction, parachains are extremely customizable and optimized for particular use circumstances, providing larger flexibility and energy for builders.
New Sidechain Options
Sidechains initially gained traction as an answer to Ethereum's scalability points, providing a option to offload transactions from the congested mainchain and course of them extra effectively on a separate, parallel chain. This method instantly boosted transaction speeds and diminished prices, making sidechains widespread throughout Ethereum's progress surge. Tasks like Polygon epitomized this success, turning into outstanding gamers within the blockchain house.
Nonetheless, because the blockchain panorama developed, so did the expertise to scale Ethereum. Extra superior mechanisms like rollups have emerged, overshadowing sidechains concerning effectivity and safety. Rollups course of transactions off-chain however submit minimal knowledge on-chain, leveraging Ethereum's safety whereas dramatically rising throughput. This shift in focus is evidenced by Polygon's transition from its authentic sidechain mannequin to adopting the Validium framework in its Polygon 2.0 roadmap, signaling a broader business transfer in the direction of these extra subtle scaling options.
Bitcoin's Resurgence
In the meantime, the Bitcoin community has skilled a resurgence in sidechain growth, because of its Segregated Witness (SegWit) and Taproot upgrades. These upgrades have unlocked new capabilities, making Bitcoin smarter and extra versatile. SegWit improved transaction effectivity and capability, whereas Taproot enhanced Bitcoin's scripting capabilities, enabling extra advanced transactions and privateness options. These developments have opened the door for growing Layer 2 options on Bitcoin, lots of which leverage sidechain expertise. By integrating Bitcoin's robust safety and decentralization with sidechain functionalities, these new options goal to deliver scalable, sensible contract-like capabilities to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
New Sidechains on Bitcoin
The SegWit and Taproot upgrades have basically remodeled Bitcoin's capacity to help extra subtle functions and scaling options. Right here's how these upgrades set the stage for the brand new wave of Bitcoin-based sidechains:
SegWit (Segregated Witness)
- Transaction Effectivity: SegWit separates signature knowledge from transaction knowledge, decreasing the dimensions of transactions and permitting extra transactions to suit into every block. This not solely will increase the transaction throughput but in addition lowers charges and mitigates the danger of malleability assaults.
- Flexibility: By altering the way in which knowledge is saved, SegWit makes it simpler to construct extra layers on prime of Bitcoin, facilitating the creation of extra advanced sidechain architectures.
Taproot
- Enhanced Scripting Capabilities: Taproot introduces extra superior scripting talents, enabling advanced conditional funds and the flexibility to mix a number of transactions right into a single, extra non-public transaction.
- Privateness Enhancements: Transactions that make the most of Taproot appear to be another transactions on the blockchain, enhancing privateness and decreasing the visibility of advanced sensible contract executions.
Leveraging these upgrades, a number of Bitcoin-based L2 options have emerged, every using distinctive sidechain mechanisms to increase Bitcoin's performance:
Rootstock (RSK)
- Merge Mining: Rootstock employs a merge-mining technique, the place Bitcoin miners can concurrently mine each Bitcoin and RSK blocks utilizing the identical computational energy. This course of permits RSK to inherit Bitcoin's safety whereas working its sidechain.
- Sensible Contracts: Rootstock helps Ethereum-compatible sensible contracts, bringing the pliability and programmability of Ethereum to the Bitcoin community. This integration permits builders to deploy decentralized functions (Dapps) on a platform secured by Bitcoin's strong mining infrastructure.
Liquid Community
- Federated Sidechain: The Liquid Community operates as a federated sidechain, the place a consortium of trusted entities (functionaries) oversees the community's operations. This mannequin offers sooner transactions and extra environment friendly asset transfers whereas sustaining excessive safety.
- Confidential Transactions: Liquid enhances Bitcoin's capabilities by providing confidential transactions, the place the transaction quantities are hidden from public view, thus enhancing privateness with out compromising the safety and transparency of the community.
Stacks
- Distinctive Consensus Mechanism: Stacks introduces a novel consensus mechanism known as Proof of Switch (PoX), which anchors its sidechain to Bitcoin by requiring members to switch Bitcoin as proof of labor. This connection ensures that Stacks advantages from Bitcoin's safety whereas working independently.
- Sensible Contract Layer: Stacks offers a separate layer that allows sensible contract performance, permitting builders to construct decentralized functions that may work together with the Bitcoin blockchain by way of Readability, a safe sensible contract language designed particularly for Stacks.
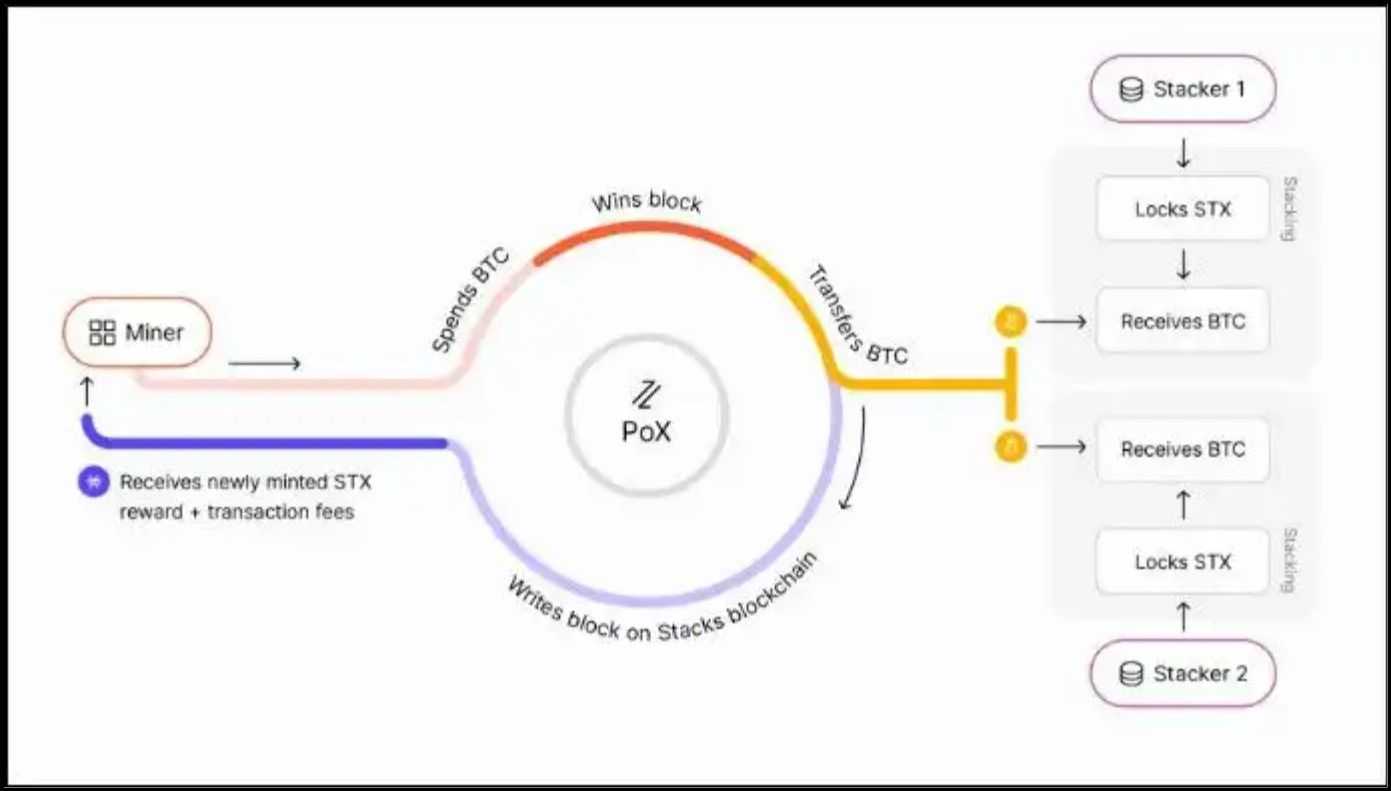
The SegWit and Taproot upgrades have considerably enhanced Bitcoin's capability to help subtle Layer 2 options, together with sidechains that leverage Bitcoin's unparalleled safety and decentralization. Rootstock, Liquid Community, and Stacks exemplify how these developments develop Bitcoin's capabilities, ushering in a brand new period of scalable, sensible contract-enabled functions. As blockchain expertise evolves, sidechains will seemingly play a pivotal position in bridging the hole between scalability and decentralization.
Closing Ideas
All through this text, we’ve explored the transformative position of sidechains within the blockchain ecosystem. Initially, sidechains gained reputation throughout the Ethereum community as an answer to scalability points, permitting for sooner and cheaper transactions. Nonetheless, as extra superior applied sciences like rollups have emerged, Ethereum's reliance on sidechains has diminished, prompting even main initiatives like Polygon to transition to newer frameworks.
In the meantime, Bitcoin’s ecosystem has seen a resurgence in the usage of sidechains following the numerous SegWit and Taproot upgrades. These enhancements have enabled Bitcoin to help extra advanced and environment friendly Layer 2 options. We examined how platforms like Rootstock, Liquid Community, and Stacks are leveraging these upgrades to reinforce Bitcoin's capabilities, providing scalable and safe environments for superior functions and sensible contracts.
Sidechains proceed to be an important innovation within the blockchain house, offering distinctive benefits by way of scalability, safety, and performance. They symbolize a vital bridge between the necessity for high-speed, low-cost transactions and the foundational ideas of decentralization and safety. As blockchain expertise evolves, sidechains will seemingly play a vital position in increasing the horizons of what decentralized networks can obtain. Staying knowledgeable about these developments is vital for anybody excited about the way forward for blockchain, as sidechains provide a glimpse into the potential for extra versatile and highly effective blockchain options.
Steadily Requested Questions
What are Sidechains?
A sidechain is a separate blockchain that runs in parallel to a primary blockchain (mainchain), permitting property and knowledge to maneuver between them. Sidechains allow sooner and cheaper transactions by offloading exercise from the congested mainchain. They use mechanisms like two-way pegs to lock property on the mainchain and launch or create equal property on the sidechain. This technique permits for larger scalability and adaptability with out compromising the safety of the mainchain.
How are Sidechains and Rollups Completely different?
Sidechains and rollups each goal to reinforce blockchain scalability, however they function in a different way. Sidechains are unbiased blockchains with their very own consensus mechanisms and may function semi-autonomously from the mainchain. Rollups, alternatively, course of transactions off-chain and periodically submit compressed knowledge again to the mainchain, counting on the mainchain’s safety for transaction validity. Rollups are typically safer as a result of they inherit the mainchain’s safety immediately, whereas sidechains want their very own safety measures.
How Does Bitcoin Facilitate Sidechains?
SegWit (Segregated Witness) and Taproot are Bitcoin upgrades that improved transaction effectivity and enhanced scripting capabilities. SegWit separates signature knowledge from transaction knowledge, rising transaction throughput and reducing prices. Taproot permits for extra advanced and personal transactions by enabling sensible contract-like functionalities. These upgrades create a extra versatile setting for growing sidechains, which may now provide superior options corresponding to sensible contracts and sooner, extra non-public transactions on prime of Bitcoin’s safe base.
What Are Some Notable Bitcoin Sidechains?
Distinguished examples of sidechains embrace Rootstock (RSK), the Liquid Community, and Stacks. Rootstock employs merge mining, permitting Bitcoin miners to safe each Bitcoin and RSK. It helps Ethereum-compatible sensible contracts, integrating them with Bitcoin’s safety. The Liquid Community operates as a federated sidechain, providing quick, confidential transactions overseen by trusted functionaries. Stacks makes use of a Proof of Switch mechanism, anchoring its operations to Bitcoin whereas enabling a separate layer for sensible contract performance, enhancing Bitcoin’s capabilities with out altering its base layer.
Why Have Sidechains Misplaced Reputation in Ethereum?
Sidechains had been initially widespread on Ethereum for enhancing scalability and decreasing transaction prices. Nonetheless, the rise of rollups has shifted focus away from sidechains. Rollups present a extra environment friendly resolution by processing transactions off-chain and posting compressed knowledge again to the mainchain, leveraging Ethereum’s safety immediately. They provide higher scalability and safety than sidechains, which function with their very own consensus mechanisms and safety fashions. Because of this, even initiatives like Polygon are transferring in the direction of adopting rollup-based options of their growth roadmaps.