Bitcoin hacking is a major issue that exchanges, businesses, and regulators face.
In spite of this, there have been many advances in cybersecurity which are able counter some of these threats. To see how far we’ve come, you only have to look at the number and size of hacks in the past.
This article will examine seven of the most significant Bitcoin hacks that have occurred in recent years. I will tell you how these hacks occurred, how the industry responded and what we learned from it.
Eight of the biggest bitcoin hacks
It is important to note that the hacks are based upon the amount of Bitcoins stolen. The dollar value of the hacks could have been different at the time, depending on the Bitcoin price.
In fact, many of these hacks occurred because the Bitcoin that had been stolen was not properly guarded. This could be a direct consequence of the lower price of Bitcoin at that time.
With that being said, let's jump in!
1. Mt. Mt.
Mt. Gox hack, which saw 850,000 BTC vanish in February 2014. The company later found 200,000 BTC. However, 650,000 BTC are still unaccounted for. Mt. Gox, the largest Bitcoin exchange on the planet, handled over 70% of the trading volume.

Mt. Gox filed for bankruptcy three weeks after the attack. The theft was approximately 7% of Bitcoin at the time. Further investigation revealed that Bitcoin had been slowly taken from the exchange since late 2011.
The majority of people thought the perpetrators wouldn’t be caught but, to their surprise and dismay, someone was eventually found. Alexander Vinnik had been arrested in Greece and accused in 2017 of being one the operators of BTC e. This is the exchange where most of the Mt. This is the exchange through which most of the coins from Mt.
2. Bitfinex
A large Bitcoin exchange is also a target for hackers. Hackers targeted Bitfinex in August 2016, stealing roughly 120,000 BTC through an attack against the exchange’s multi-signature wallet. Ironically, this multi-signature attack was successful because multi-sig makes a wallet more secured.
Exchanges employ multisignature wallet schemes whereby more than one signature is needed to approve a transaction. One of the best-known configurations is 2 of 3. The 2 of 3 configuration means that the transaction can be signed using any two private keys.
There were many questions about how a hacker could exploit this configuration. Many people began to blame BitGo for Bitfinex’s use of a wallet provided by BitGo. But the vulnerability was a combination a few factors unique to Bitfinex.
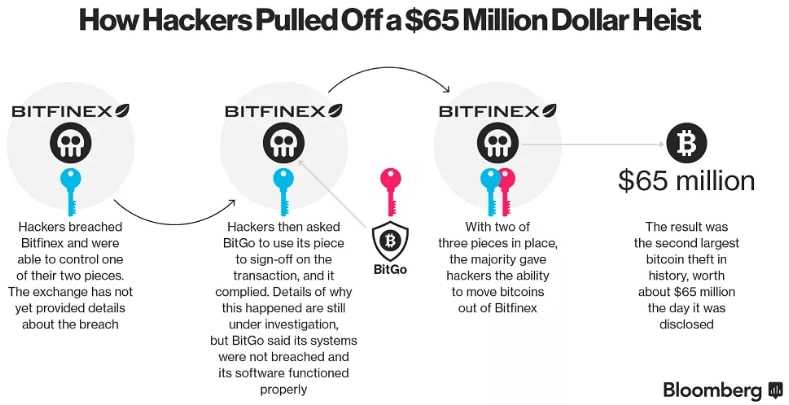
Bitfinex recovered from the hack by using a creative solution. They took 36% of customer balances, and replaced them with a redeemable BFX token. Bitfinex bought the redeemable BFX tokens back with trading fees over the eight-month period, making everyone happy and allowing the business to continue. Bitfinex, today, remains one of Bitcoin’s largest exchanges.
3. Bitcoinica
Bitcoinica may be a name that you don’t remember, but they are ranked number three in this ranking, after losing roughly 101,000 BTC over three separate heists. Each of these three heists could have placed Bitcoinica on the third place by itself. The first hack happened in March 2012. Hackers were able socially engineer their way into cloud hosting provider Linode’s network.
Linode was hosting Bitcoinica’s infrastructure and hackers made off with 43,000 BTC. The identity of the hacker has not been revealed, although some suspect it was a Linode worker. The second hack also occurred as a result of shared hosting, when Bitcoinica’s Rackspace server was targeted in April 2012. Another 38,000 BTC were stolen. After the Rackspace loss, the Bitcoinica website was taken offline. But the losses didn’t stop there.
In July, 40,000 BTC held by Mt.Gox disappeared. There was a report that the BTC had been recovered, but it’s still not confirmed. The liquidation of the funds and distribution to previous clients were supposed to occur over a period of several months after an August 2012 Receivership. However, there appears to be no such distribution yet.
4. Allinvain
Hackers aren’t only interested in exchanges. Allinvain, the pseudonym for a Bitcointalk forum member who in June 2011 posted about a hack where 25,000 Bitcoins were stolen from his PC. Allinvain was an early Bitcoin miner and had accumulated 25,000 BTC between 2010 and 2011. He was able identify the address to which the BTC were transferred but was never able recover any of the coins.
Hacking was possible because allinvain stored his wallet recovery seed on an infected computer. This is probably one of biggest hackers. "no-nos" It was probably done out of convenience when it came to the security of cryptocurrency. Allinvain was less concerned at that time because Bitcoin only cost a few cents.
This story is not widely known, but was the very first major hack. Every cryptocurrency user should learn this lesson about operational security.
5. Bitfloor
Bitfloor suffered a loss of 24,000 BTC in September 2012, which is just behind the allinvain attack. Bitfloor, the fourth-largest U.S. cryptocurrency exchange at the time, would never recover after the hack. The exchange had left all of its funds in an a "hot wallet" Its servers.
Hackers were able to gain access to client accounts using backup keys because the funds were held in a “hot wallet”. The company promised to reimburse any lost funds after shutting down the exchange for a few days. However, this never happened. The exchange shut down in April 2013, less that a year after the hack. It cited the bank closing its accounts as the cause.
Today, leaving all of your coins in an exchange's hot wallets is unheard of. Exchanges use cold storage in large quantities due to the lessons learned from hacks like this one and others. This is where the vast majority (usually 90% plus) of the exchange's coin reserves are kept offline in a secure location. This would have prevented the Bitfloor Hack.
6. Bitstamp
The Bitstamp Exchange is ranked six, with a loss in BTC of 19,00 BTC. This occurred in January 2015. This hack happened due to social engineering. The hacker repeatedly tried to contact Bitstamp’s customer service representatives, as well as other Bitstamp staff, via Skype or email. He was attempting to get them to open malware infected files by pretending to be journalists and other industry professionals.

Eventually, the hacker managed to get a worker to open the file infected. This gave him access to Bitstamp’s network. They were then able access a hot-wallet on a web server and steal 19,000 BTC.
The U.K. Police have stated that they have a lead on the identity of the attacker. However, since the attacker was not physically present in Britain, they were unable to act. Bitstamp, the oldest Bitcoin exchange, continues to be a reputable company.
7. Cryptsy
Cryptsy, another US-based exchange was also one of the largest in 2015. In December of 2015, the exchange closed due to insolvency. The exchange's founder, Paul Vernon (aka "Big Vern"() claimed that insolvency resulted from a hacker who had previously been unreported.
The founder claimed the hack happened in early 2015, and that the exchange lost 13,000 BTC. It also lost 300,000. The exchange was believed to have been hacked by a developer working on the exchange who had embedded a trojan in the code that would give him remote access.
There were however many users who suspected foul-play by the founder and they brought a lawsuit against him. The plaintiffs won the case, and the judge ordered Paul Vernon repay them $8.2m damages. Big Vern vanished before the ruling, and many believe that he is hiding somewhere in Asia.
We can’t know for sure if this was an insider job but we can agree that it is not a good idea to hire an anonymous developer to create critical code for a cryptocurrency exchange. It’s a bad idea.
8. Binance
This hack was relatively recent and took place on May 7, 2019. The perpetrators of this hack were able get away with a sum total of 7,000 Bitcoin worth approximately $40m.
Binance Exchange, for those who don’t know, is one of largest cryptocurrency exchanges worldwide. It handles daily volumes of over $2 billion (at the time of this writing). Before that incident, Binance Exchange had never experienced any security breaches.
This was not a breach that resulted in the hackers gaining access to Binance's internal systems. The hackers were slowly collecting a variety of API keys, 2FA code and other information.
The social engineering and other attack vectors they used were well known. Phishing is one of them, as are computer viruses. Hackers can use this information to initiate withdrawal requests on client accounts.
They were very patient and began mass withdrawals on May 7th. They structured their transactions so that they could circumvent Binance’s internal risk limits. The 7,000 BTC were sent to the address below in a single transaction.
Thankfully though, this only impacted Binance's Hot Wallet funds. The total Bitcoin held by Binance is less than 2%, and the majority of it is stored in cold wallets. Binance immediately stopped all withdrawals and deposits after they discovered the transaction.
Given the Binance "SAFU" Fund, all users who were affected by the hack received their accounts reimbursed. Binance covered all costs of the hack. No users were affected.
The conclusion of the article is:
These Bitcoin hacks are painful to read, but it’s incredibly useful to learn the reasons behind them. These incidents led to a number of improvements in crypto security.
Hacks are still happening, but at a much smaller scale than in the old days. Even if the hacker were to be able exfiltrate a large amount of coins today it would make it nearly impossible to launder them. Cyber security and law enforcement analysts have developed the most advanced auditing tools for blockchains that can track stolen coins.
This does not mean, however, that your home is not vulnerable to hacking and breaches on a daily basis.
This list of 7 of the biggest Bitcoin hacks in history should only serve to remind you of the importance of keeping your private keys, and wallet, safe and secure.