Decentralised Finance (DeFi) has come to embody one of the crucial intriguing, versatile and thrilling segments of the digital asset house. With its ecosystem rising at such an exponential fee, DeFi has firmly established itself as a natively disruptive expertise that seeks to completely refashion the monetary establishment and revolutionise the best way people conceptualise worth.
All through its historic growth, blockchain expertise has given start to a wide range of completely different monetary purposes, worth propositions, crypto belongings and different infrastructures. Whereas blockchain has most positively spearheaded among the most fascinating technological improvements of the final decade, to this present day its design stays fairly remoted and enclosed.

Public blockchains, resembling Bitcoin and Ethereum as an illustration, are constructed as digital ledgers which can be open-source, clear and visual to all. Nonetheless, regardless of on-chain information being absolutely clear, a blockchain’s infrastructure is actually designed to be a self-contained, siloed ecosystem.
There may be, after all, good cause for this as one of the crucial very important components of blockchain expertise resides in its means to protect community safety. In actual fact, to take care of the consensus that underpins the safety and accuracy of a shared ledger, solely miners who meticulously comply with the principles of every community are allowed to confirm and write transactions to the blockchain.
This technique is certainly efficient, nonetheless, the siloed nature of blockchain is considerably stunting the expansion and progress of the DeFi ecosystem, locking DeFi contributors right into a single, enclosed community when truly, given its permissionless and disintermediated functionalities, it ought to permit customers to achieve entry to a wider array of alternatives.
At a time when the DeFi Lego-like composability of decentralised Purposes (dApps) is altering the face of monetary infrastructures as we now have all the time recognized them, it’s extra necessary than ever for impartial blockchains to speak and share information with each other.

Whereas tasks resembling Polkadot, Kusama, Avalanche and Cosmos are experimenting with the idea of cross-chain interoperability and community composability, DeFi customers fairly merely would love to have the ability to transfer belongings from one chain to a different, use dApps interchangeably and leverage different DeFi companies extra effectively. Thus, there appears to be a widespread want for blockchain intercommunication and whereas blockchain infrastructures have remained fairly remoted till very lately, one of the crucial optimum options will be present in cross-chain bridges.
About Cross-Chain Bridges
Cross-Chain Bridges allow interoperability and intercommunication between vastly completely different networks, such Bitcoin and Ethereum as an illustration, and between one guardian blockchain and its baby chain, often known as a sidechain, which both operates underneath completely different consensus guidelines or inherits its safety from the guardian blockchain, as is the case for Polkadot and Kusama parachains.

Cross-chain bridges permit for the switch of belongings, tokens, information or ever sensible contract directions from one chain to a different and between utterly impartial platforms, enabling customers to:
- Deploy digital belongings on one blockchain to dApps on one other.
- Conduct quick, low-cost transactions of tokens hosted on non-scalable blockchains.
- Implement and execute dApps throughout multiple platform.
Want For Cross-Chain Interoperability
Crypto lovers, traders and institutional entities are all rising more and more conscious of the problems posed by chain maximalism, the dangers of Balkanisation, and of the general closure inherent in most blockchain networks.
This sentiment is primarily pushed by the truth that blockchain, at coronary heart, was all the time designed to unravel among the complexities, bottlenecks and limitations which have traditionally characterised conventional monetary buildings. Nonetheless, for almost all of blockchain contributors, it’s close to to unimaginable to seamlessly execute trades and effectively transfer belongings throughout the digital asset house with out encountering some form of technical hurdle.
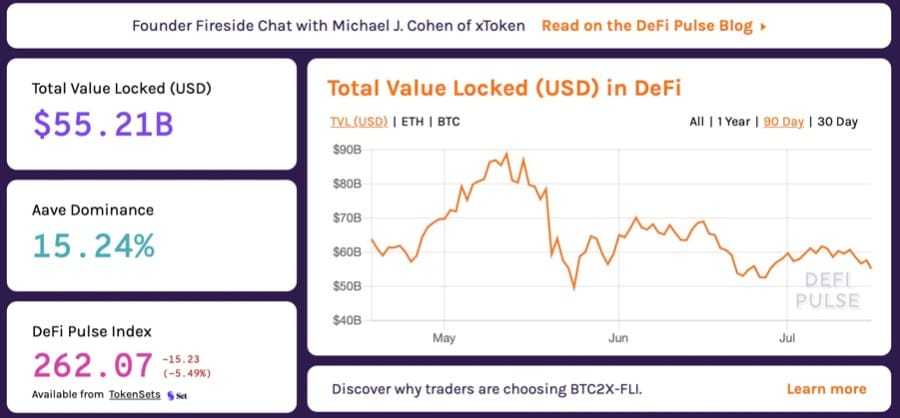
With Decentralised Finance skyrocketing because the starting of 2020, the demand for cross-chain composable techniques within the DeFi house is at the moment at an all-time-high. In essence, this is because of the truth that immediately’s DeFi networks stay siloed and remoted inside their very own ecosystems and can’t trustlessly talk with one another to trade significant quantities of worth.
We construct too many partitions and never sufficient bridges – Isaac Newton (1643-1727)
The answer to this primarily resides in cross-chain interoperability because it permits tasks to successfully cooperate with each other and break the boundaries separating their respective infrastructures.
Nonetheless, many of the present options that present cross-blockchain communication are both too difficult, dangerous, overloaded or will probably embrace a 3rd social gathering medium. Having a 3rd social gathering act as escrow throughout a cross-chain switch totally deprives blockchain of its innate decentralised philosophy and inherently defeats the aim of its expertise altogether.
To treatment this, cross-chain bridges present the mandatory underlying structure for blockchain tasks to soundly develop their interoperability options and reliably work together with different chains, whereas obviating the necessity for a 3rd social gathering medium.
How Cross-Chain Bridges Work
As beforehand talked about, a cross-chain bridge is a connection that permits the switch of tokens, belongings and information from one chain to a different. Each chains can have completely different protocols, guidelines and governance fashions, however the bridge supplies an intercommunicative and appropriate approach to interoperate securely on each side.

Not all cross-chain bridges are the identical as, in reality, there are fairly a couple of designs in existence, however they’ll typically be divided into two important segments:
- Centralised Cross-Chain Bridges, based mostly on third social gathering belief.
- Decentralised and Trustless Cross-Chain Bridges, based mostly on cryptographic-mathematical belief.
Extra centralised bridges depend on some form of central authority or system to perform, which means that customers are required to put their belief in a 3rd social gathering mediator to make use of a selected utility or service. Utilizing a centralised bridge can enchantment to these customers who’ve maybe simply entered the crypto house and haven’t but developed the skillset or the arrogance required to maneuver their capital throughout completely different chains on their very own.
Whereas there are positively some advantages to utilizing centralised bridges, resembling ease of use and relative automation, most crypto aficionados want to have interaction in cross-chain operations on their very own accord and customarily look to extra decentralised and trustless choices.

Among the many hottest trust-based, centralised bridge options is the initiative that allows Bitcoin holders to leverage the advantages of the Ethereum blockchain by way of Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC). On this centralised bridge system, customers deposit X quantity of BTC via companions known as ‘merchants’ right into a pockets managed by a trusted, centralised custodian which shops Bitcoin safely after which mints Wrapped BTC (WBTC) tokens of equal worth on Ethereum.
This will doubtlessly become fairly useful for Bitcoin holders as Wrapped BTC, in contrast to native BTC, is an ERC-20 token that may be utilised as collateral in a wide range of DeFi protocols, resembling Aave, Compound, MakerDAO and Uniswap.

However, decentralised cross-chain bridges are these by which customers aren’t required to put their belief in a single entity or centralised authority, however fairly their belief is positioned within the mathematical reality of the underlying blockchain’s codebase. In blockchain techniques, mathematical reality is achieved by many laptop nodes reaching a typical settlement, or consensus, in accordance with the principles written into the code. This enables for the creation of an open, decentralised and clear system that just about completely depends on the blockchain’s foundational infrastructure and removes lots of the points ingrained in centralised ecosystems, that are topic to potential corruption and malicious behaviour.
Cross-chain bridges will be constructed to serve a wide range of functions, and never simply asset transfers. Certainly, they aren’t solely able to enabling tokens on one community to be utilised on one other, however they may also be carried out to trade any kind of knowledge, together with sensible contract calls, decentralised identifiers and off-chain data resembling inventory market worth feeds by way of oracles.
Cross-Chain Bridge Structure
When a consumer transfers belongings from blockchain A to blockchain B via a decentralised cross-chain bridge, these belongings aren’t technically ‘sent’ or relocated elsewhere. In actual fact, this switch is kind of the phantasm as belongings on blockchain A usually are not transferred, however fairly briefly locked on blockchain Some time the identical quantity of equal tokens is unlocked on blockchain B. Belongings on blockchain A can then unlock when the equal quantity of tokens on blockchain B turns into locked once more.
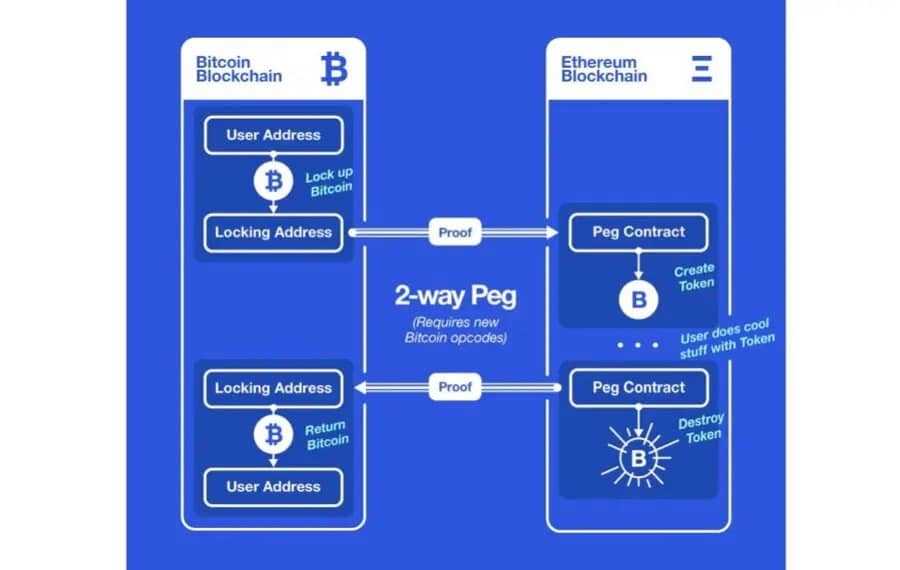
Many blockchain tasks within the house have began implementing and creating their very own interoperability options via this aforementioned system attributable to its effectiveness and decentralised nature. The idea for this cross-chain interoperable structure, known as a two-way peg (2-WP) system, dates again to the very early days of Nakamoto, and whereas this technique does theoretically work it truly comes with some inherent dangers.
Any decentralised cross-chain bridge system depends closely on assumptions of belief and honesty between the 2 actors concerned within the cross-chain bridge. If these assumptions fail to carry, then it’s potential that belongings on each blockchain A and blockchain B unlock on the identical time, inflicting a malicious double spend. To counter this, tasks resembling Clover Finance, a Substrate-based parachain seeking to ahead its personal in-house 2-WP mechanism, permit for a seamless and safe cross-chain communication system to be put in place by way of trustless 2-WPs.
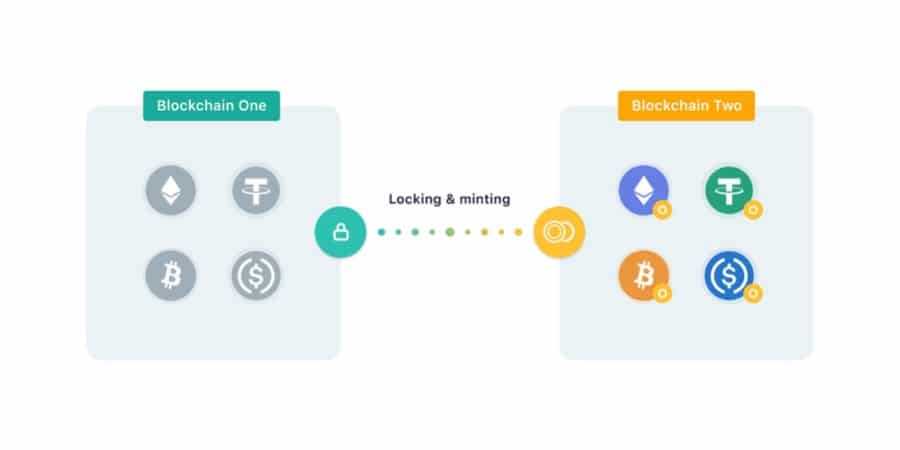
One other pertinent instance of a decentralised blockchain bridge is the Ren Protocol. The Ren Digital Machine (RenVM) is supported by a big, decentralised community of laptop nodes that set up consensus in a way just like the Ethereum community.
The RenVM spreads data and information throughout many units, and leverages multi-party computation (MPC) to create shared cryptographic signatures that allow its community to lock digital belongings on one blockchain and permit customers to mint equal belongings on one other blockchain.
Thus, the RenVM mechanism permits customers to mainly ‘transfer’ belongings and information from blockchain A to blockchain B with out help from any third social gathering entity.
Sidechain Bridges
Earlier than diving into sidechain bridges, it’s constructive to briefly analyse what sidechains are, as it’ll assist to raised contextualise the performance and significance of a sidechain bridge as a complete.
Sidechains are impartial blockchains with their very own consensus mechanisms, particular person nodes and infrastructures. Sidechains profit from the decentralisation and safety of the underlying important blockchain and preserve the pliability to carry out extremely specialised use instances. Primarily, sidechains are synonymous with scalability as they permit the underlying blockchain to dilute and unfold out a few of its workload throughout a parallel ecosystem of sidechains, thus making its complete system extra environment friendly.
Polkadot and Kusama parachains represent maybe essentially the most related instance of a sidechain, as they too profit from the safety, reliability and Layer-0 scalability of the Polkadot Relay Chain, and possess impartial, highly-specialised capabilities. Particularly within the Polkadot ecosystem, sidechains must be consistently tied-in with the central Relay Chain however may also set up cross-chain communication with different parachains as properly. In fact, so as to take action, a sidechain-specific bridge is required.
Not like a bridge that hyperlinks two utterly completely different blockchains, a sidechain bridge connects a guardian blockchain to its baby. As a result of the guardian and baby function underneath completely different consensus guidelines, communication between them requires a bridge.
For example, the builders of the favored blockchain-based sport Axie Infinity created a devoted Ethereum-like sidechain, known as Ronin, to permit the sport to scale past what was potential on the Ethereum mainnet. Ronin’s Ethereum bridge allows customers to deposit ETH, ERC-20 tokens and NFTs into sensible contracts, which Ronin’s validators decide up and relay to the sidechain.
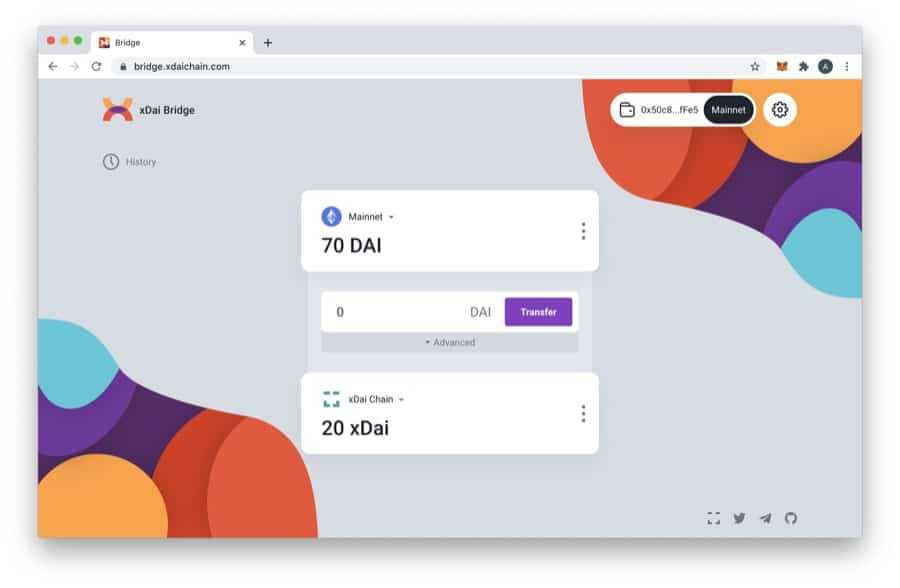
One other well-known instance of an Ethereum-based sidechain bridge is xDai. Equally to Ronin, xDai is secured by a set of validators distinct from the miners who preserve the principle Ethereum blockchain. Two bridges, the xDAI Bridge and the OmniBridge, join the xDai chain to the Ethereum mainnet, permitting straightforward switch of tokens.
Furthermore, sidechains are set to play an important position within the growth technique of the Ethereum community with the roll-out of its sharding capabilities with ETH 2.0. In actual fact, Ethereum 2.0 will introduce elevated scalability to the ETH community by bundling many sidechain transactions right into a single transaction secured on the principle Beacon Chain.
Think about that Ethereum has been break up into hundreds of islands. Every island can do its personal factor. Every of the island has its personal distinctive options and everybody belonging on that island i.e. the accounts, can work together with one another AND they’ll freely take pleasure in all its options. In the event that they need to contact different islands, they must use some form of protocol. – Vitalik Buterin at Devcon 2018 – LinkedIn
Constructing Bridges On Polkadot
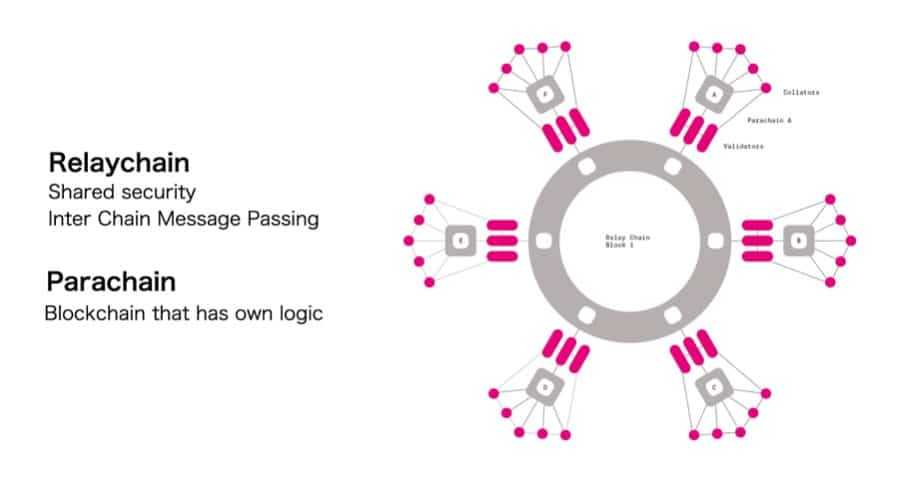
Polkadot was designed to be a ‘blockchain of blockchains’ with the assumption that each one future blockchain infrastructures would require interoperability to perform effectively. Polkadot permits sovereign Layer-1 blockchains, known as parachains, to be absolutely intercommunicative and cross-chain composable, whereas benefitting from the safety, scalability and Layer-0 performance of the Polkadot central Relay Chain.
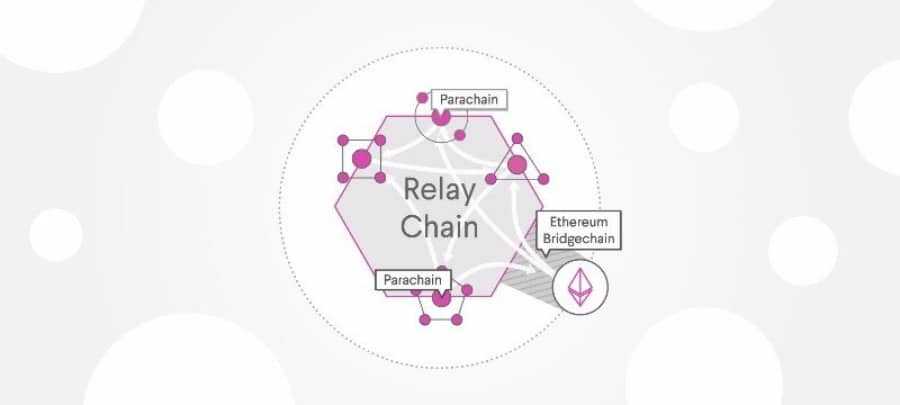
As well as, Polkadot permits its parachain buildings to attach with exterior networks resembling Bitcoin and Ethereum via cross-chain bridges. These Polkadot bridges will be carried out in numerous methods, with some being constructed as frequent good utility bridges for your complete Polkadot neighborhood, and others as a for-profit bridge design run by specialised groups.
Some of the intriguing and value-rich functionalities that include Polkadot’s cross-chain bridge structure is the flexibility to bridge and seamlessly interconnect two exterior and separate chains resembling Bitcoin and Ethereum. For example, via its parachain bridge system, Polkadot might permit the switch of belongings from Bitcoin to Ethereum in a totally decentralised method. So as to obtain this, Polkadot leverages its in-house cross-chain bridge design known as Cross-Chain Message Passing (XCMP).
XCMP Bridge
As talked about earlier, parachains take their identify from the idea of parallelised chains that run parallel to the central Relay Chain inside the Polkadot ecosystem, on each the Polkadot and Kusama Networks. As a result of their parallel nature, parachains are additionally in a position to parallelise transaction processing and ship new ranges of scalability to each Polkadot and Polkadot-based tasks.
They’re absolutely linked to the Relay Chain and benefit from the safety offered by the Polkadot framework. Nonetheless, to be able to talk and share information with different techniques, parachains leverage a mechanism known as Cross-Chain Message Passing (XCMP).
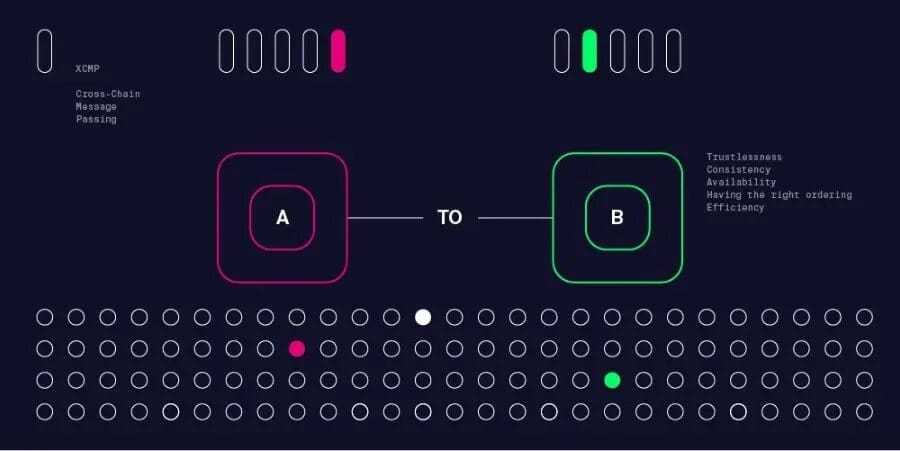
Polkadot’s XCMP bridge is a protocol that lets its in any other case remoted parachain-sidechain networks ship messages and information between one another in a safe and utterly trustless method. This Cross-Chain Message Passing system is firstly initiated by opening up a channel between the 2 parachains.
This channel have to be recognised by each the sender and the recipient parachain, and it’s a one-way channel. Moreover, a pair of parachains can have at most two channels between them, one for sending messages and one other for receiving them.
To ensure that the bridge to be established, a deposit in DOT is required which is able to then be returned as soon as the bridge closes once more. Thus, via the XCMP channel, two separate parachains can create an intercommunicative construction for them to switch worthwhile information and belongings between one another and attain unprecedented ranges of cross-chain bridge interoperability.
Cross-Chain Bridges: The Future Of DeFi
Cross-chain bridges can primarily be conceptualised because the foundational infrastructure that may gas all future blockchain techniques, as they permit for the creation of dynamic, interoperable and interchangeable blockchain layers.
Interoperability and cross-chain composability between separate blockchains, together with guardian chains and sidechains, open up an enormous ocean of alternatives for customers and permit community contributors to entry the advantages of every chain with out jeopardising the safety and benefits of the principle chain.
Consequently, this produces some thrilling use instances for cross-chain bridges within the ever-changing realm of Decentralised Finance, giving crypto lovers the choice to maneuver belongings throughout the house in a permissionless, disintermediated vogue whereas leveraging the functionalities of each the principle and secondary chains.
 Cross-Chain Interoperability Encapsulates The Future Of DeFi and Of Blockchain Networks
Cross-Chain Interoperability Encapsulates The Future Of DeFi and Of Blockchain Networks
Bridges are proving more and more worthwhile in DeFi protocols, as they allow DeFi customers to switch digital belongings from a blockchain that holds appreciable token worth however that can’t maximise dApps of its personal, like Bitcoin, to at least one that has developed a well-established DeFi ecosystem, like Ethereum.
Thus, on this situation, it’s only because of cross-chain bridges that Bitcoin can profit from the functionalities of DeFi by changing into Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC), an ERC-20 token, on the Ethereum blockchain. That is definitely useful for native BTC holders as they’re now in a position to commerce and transfer their Wrapped BTC across the DeFi house and reap the rewards of the perfect chains within the ecosystem.

Moreover, as beforehand talked about, DeFi bridges improve community scalability by permitting important chains to attach with their secondary chains and distribute a few of their transaction load throughout their ecosystem.
Essentially the most optimum instance of that is maybe the Polkadot parachain community, via which the Polkadot important chain can dilute its work load by way of its sidechain system rising its transactional throughput and efficiency total. Given the apparent advantages inherent in cross-chain bridge options, Ethereum is at the moment creating the infrastructure essential to assist its personal DeFi sidechain bridges, that are set to roll-out with Ethereum 2.0.
Conclusion
Scalability, effectivity and innovation are the secret and, with cross-chain bridges, DeFi simply acquired means simpler. In actual fact, it’s only a matter of time earlier than increasingly more dApps, blockchain-based tasks and crypto traders come to the realisation that, with out cross-chain bridges, the DeFi purposes that we, the customers, love and utilise essentially the most wouldn’t truly be that possible an choice.
Because the inherent connection linking one blockchain to a different, cross-chain bridges present tasks with the infrastructure required to achieve interoperability in a decentralised method and permit for the seamless implementation of cross-blockchain composability.
The idea of a cross-chain bridge within the digital asset house dates again to the very early days of Bitcoin, when the worth proposition of an progressive, permissionless peer-to-peer community first emerged. Since then, blockchain bridges have flourished to such an extent that they’re proving to be essential for the general growth of the DeFi ecosystem and its Lego-like liquidity buildings.
Finally, the demand for cross-chain bridges within the house stays extremely excessive, as they firstly improve the community efficiency of many DeFi protocols on the market and, secondly, as a result of they may very properly become the definitive, common catalyst for blockchain adoption.