Web3 is evolving quickly, unlocking quite a few avenues to deploy one’s assets successfully and generate earnings. Taking part in blockchain consensus protocols stands out as a foundational technique to have interaction with decentralized networks. Two predominant consensus mechanisms have emerged: Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). Partaking with PoW is often known as crypto mining whereas taking part in PoS is called crypto staking.
Each mining and staking are important for sustaining the safety and integrity of blockchain ecosystems. Nevertheless, they require distinct methods, assets, and ability units. Mining usually calls for substantial computational energy and vitality consumption, whereas staking entails locking cryptocurrency holdings to help community operations.
Understanding the nuances between these two approaches is essential for people aiming to optimize their participation within the crypto area. This text explains the dynamics of crypto mining and staking, analyzing the related abilities, assets, methods, and dangers. By offering a complete comparability, we intention to equip readers with the information wanted to find out which technique aligns finest with their objectives and affords essentially the most worthwhile outcomes.
What’s Crypto Mining?
Crypto mining is the method by which contributors, generally known as miners, interact in Proof of Work (PoW) consensus methods to validate transactions and safe blockchain networks. On this position, miners compete to resolve advanced mathematical puzzles, and the primary to take action earns the fitting so as to add a brand new block to the blockchain. This course of validates transactions and introduces new items of the native cryptocurrency into circulation, rewarding the profitable miner.
The time period "mining" parallels conventional mining, the place people expend assets—reminiscent of electrical energy and computational energy—to extract priceless commodities, on this case, digital forex.
Examine What’s Bitcoin Mining on the Coin Bureau for deeper insights into mining. You'd additionally do effectively to go over our high picks for the very best cloud-based crypto mining platforms checklist.
A number of distinguished blockchain networks make the most of mining as their consensus mechanism:
- Bitcoin: The pioneering cryptocurrency that launched the PoW consensus, counting on mining to validate transactions and safe its decentralized ledger.
- Litecoin: Typically thought-about the silver to Bitcoin's gold, Litecoin employs a PoW system with quicker block technology occasions and a special hashing algorithm.
- Ethereum Traditional: A continuation of the unique Ethereum blockchain, Ethereum Traditional maintains a PoW consensus mechanism to uphold its decentralized community.
Examine the checklist of the Greatest Crypto to Mine on the Coin Bureau.
How Crypto Mining Works
The crypto mining course of entails a number of key steps:
- Fixing Complicated Mathematical Puzzles: Miners make the most of specialised {hardware} to carry out speedy computations, aiming to resolve intricate mathematical issues. The primary miner to search out the proper resolution positive aspects the fitting so as to add the following block to the blockchain.
- Deciding on and Validating Transactions: Miners choose transactions to incorporate within the new block from the pool of unconfirmed transactions, generally known as the mempool. They confirm the legitimacy of those transactions, guaranteeing that the sender has ample funds and that there is no such thing as a double-spending.
- Establishing the New Block: As soon as transactions are validated, miners compile them into a brand new block, which features a reference to the earlier block, making a steady chain.
- Propagating the Block to the Community: After setting up the block, the miner broadcasts it. Different nodes then confirm the block's validity, guaranteeing it adheres to the community's consensus guidelines.
- Incomes the Newly Mined Cryptocurrency: Upon profitable validation by the community, the miner receives a reward within the type of newly minted cryptocurrency and any transaction charges related to the transactions included within the block.
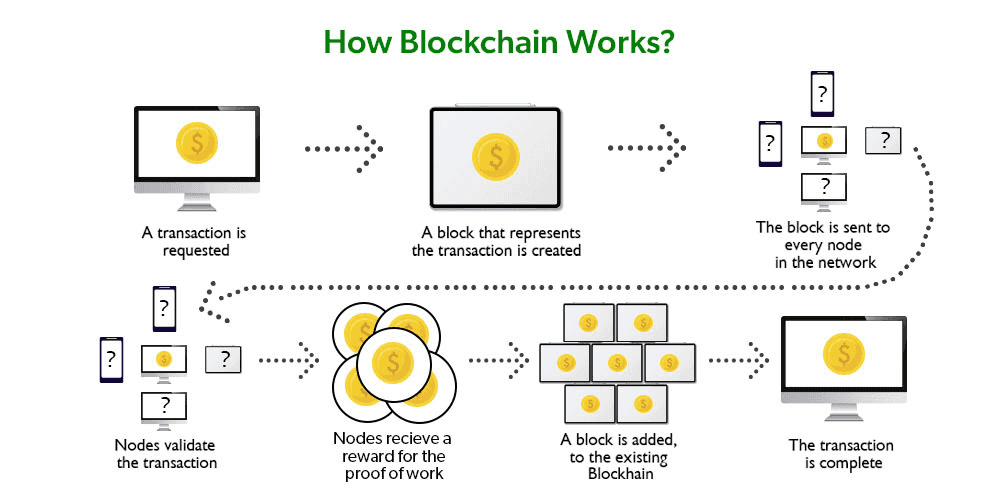
This mining course of is prime to the operation of PoW blockchains, guaranteeing safety, decentralization, and the continual addition of recent blocks to the chain.
Crypto Mining Useful resource Necessities
Partaking in crypto mining requires substantial funding in assets to make sure environment friendly and worthwhile operations. Key necessities embody:
- Specialised {Hardware}: Mining operations primarily make the most of two sorts of {hardware}:
- Graphics Processing Items (GPUs): Initially standard for mining as a result of their versatility and availability.
- Software-Particular Built-in Circuits (ASICs): Goal-built gadgets providing superior efficiency and vitality effectivity for particular mining algorithms.

- Steady and Excessive-Velocity Web Connection: A dependable web connection is essential for well timed communication with the blockchain community, guaranteeing immediate transaction validation and block propagation.
- Electrical energy Provide: Mining {hardware} consumes important quantities of electrical energy. Entry to inexpensive and constant energy is important to take care of profitability and stop operational disruptions.
- Supporting Infrastructure:
- Computer systems: To handle mining operations and monitor efficiency.
- Cooling Techniques: Efficient cooling options are essential to dissipate warmth generated by mining tools, stopping overheating and {hardware} harm.
- Electrical Tools: Correct wiring, energy distribution items, and surge protectors are very important to deal with {the electrical} load safely.
- Bodily House: Ample area is required to deal with the mining setup, contemplating components like air flow, noise ranges, and safety.
- Technical Experience: A strong understanding of mining software program, {hardware} upkeep, and troubleshooting is helpful for environment friendly operations.
The excessive useful resource calls for and complexity of crypto mining underscore the necessity for cautious planning and consideration earlier than embarking on such ventures.
What’s Crypto Staking?
Crypto staking entails utilizing Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus methods as a validator node. On this position, stakers lock up a certain quantity of cryptocurrency to help community operations, together with validating transactions and securing the blockchain. This course of is essential for setting up new blocks throughout consensus, executing transactions, and updating the blockchain's state. Profitable validators earn block rewards within the items of the community's native cryptocurrency, distributed proportionally primarily based on the quantity staked.
The time period "staking" displays committing cryptocurrency as collateral to realize the fitting to take part within the consensus course of. This dedication incentivizes trustworthy conduct, as validators who act maliciously or fail to carry out their duties could face penalties, reminiscent of having a portion of their staked property slashed. Many blockchain networks favor PoS as a result of its considerably decrease vitality necessities than Proof of Work (PoW) methods.
A number of distinguished blockchain networks make use of staking:
- Ethereum 2.0: Transitioned from PoW to PoS to boost scalability and scale back vitality consumption.
- Solana: Makes use of a PoS mechanism mixed with Proof of Historical past to attain excessive throughput and low latency.
- Cosmos: Employs PoS to allow interoperability between a number of blockchains inside its ecosystem.
- Cardano: Constructed on a PoS protocol, Ouroboros emphasizes safety and sustainability.
Examine Coin Bureau's checklist of the Greatest Crypto Staking Cash.
How Crypto Staking Works
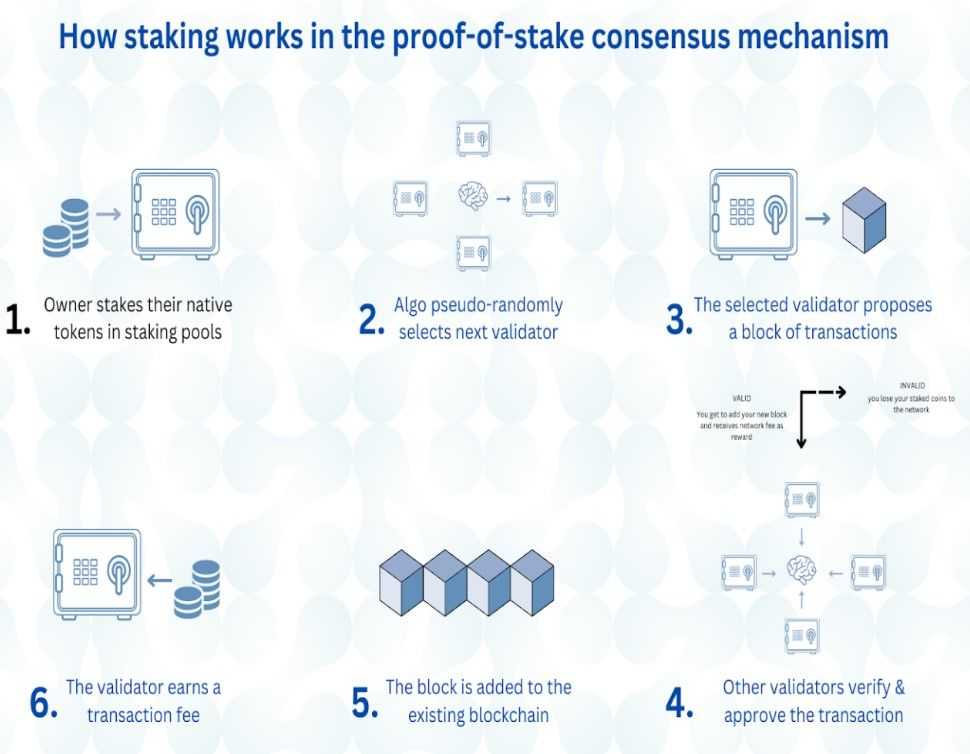
The staking course of entails a number of key steps:
- Changing into a Validator: Contributors stake a specified quantity of cryptocurrency to grow to be validator nodes, committing their property to help community safety and operations.
- Number of Leaders: The protocol randomly selects a validator to suggest a brand new block, with the likelihood of choice proportional to the quantity staked relative to the whole stake within the community.
- Block Proposal: The chosen validator assembles a brand new block by processing and verifying transactions, guaranteeing they’re reliable and cling to community guidelines.
- Block Validation: Different validators evaluate the proposed block, verifying its accuracy and validity. They then vote to simply accept or reject the block primarily based on consensus guidelines.
- Incomes Rewards: Upon efficiently validating and together with the block into the blockchain, the proposing validator receives rewards within the type of newly minted cryptocurrency. Moreover, transaction charges collected throughout the block are distributed amongst validators, offering additional incentives for participation.
Check with Coin Bureau’s Information to Staking Crypto for deeper insights into crypto staking.
This staking mechanism secures the community and affords contributors the chance to earn passive earnings via their contributions to the blockchain's integrity and performance.
Crypto Staking Useful resource Necessities
Taking part in crypto staking calls for considerably fewer assets in comparison with mining, making it a extra accessible possibility for people and establishments alike. Beneath are the important thing necessities for staking:
- Primary Pc {Hardware}: Not like crypto mining, staking doesn’t require specialised {hardware} like GPUs or ASICs. A normal laptop or server with fundamental specs can run staking operations successfully.
- Steady and Excessive-Velocity Web Connection: A dependable web connection is essential to take care of constant communication with the blockchain community and keep away from downtime, which may result in penalties or missed rewards.
- Minimal Electrical energy Consumption: Staking operations devour far much less electrical energy in comparison with mining. The facility wanted to run a fundamental laptop is roughly 99% decrease than the electrical energy necessities of Proof of Work mining rigs.
- Ample Bodily House: Staking setups require minimal area, usually housing a single laptop or server in a well-ventilated space, making staking extra sensible for residence setups than the in depth area wanted for mining farms.
- Cryptocurrency Holdings: A prerequisite for staking is proudly owning the native cryptocurrency of the community you propose to take part in. The quantity staked usually determines the validator’s probabilities of being chosen to suggest blocks and earn rewards.
- Technical Data: Whereas extra intensive than mining, understanding blockchain mechanics, staking software program, and pockets administration is helpful to make sure environment friendly and safe staking operations.
In conclusion, the useful resource necessities for crypto staking are minimal in comparison with mining. This decrease barrier to entry, coupled with its eco-friendly nature, makes staking an interesting selection for these seeking to contribute to blockchain networks and earn rewards with out important investments in {hardware} or electrical energy. Examine our Information to Staking Ethereum to start out staking ETH.
Key Variations Between Staking and Mining
Crypto mining and staking signify two basically totally different approaches to blockchain consensus, every with distinctive traits and implications for contributors. Beneath are the important thing variations between the 2 strategies:
1. Consensus Techniques
- Proof of Work (PoW): Mining is the spine of PoW methods. Miners compete to resolve advanced mathematical puzzles, guaranteeing community safety and transaction validation.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Staking helps PoS methods, the place validators lock cryptocurrency to take part in consensus, securing the community via financial dedication relatively than computational energy.
2. Power Consumption
- Mining: Power consumption is a major expense, as mining operations require substantial electrical energy to energy GPUs, ASICs, and cooling methods. Entry to low cost and dependable electrical energy is essential for profitability.
- Staking: Staking is way extra energy-efficient, consuming solely the electrical energy wanted to run a fundamental laptop setup. This decreased vitality demand aligns with environmental sustainability objectives.
3. Setup and Upkeep
- Mining: Organising a mining operation entails buying pricey {hardware}, reminiscent of GPUs or ASICs, and sustaining a purpose-built area with satisfactory air flow and cooling. Mining {hardware} experiences put on and tear, decreased effectivity over time, and eventual obsolescence as expertise advances.
- Staking: Staking requires solely a fundamental laptop or server, leading to minimal setup and upkeep prices. The {hardware} used for staking undergoes little depreciation, making it simpler to maintain in the long run.

4. Threat of Loss
- Mining: The first threat in mining is the sunk value of assets, together with vitality and {hardware}. Contributors face important monetary losses if mining rewards don’t cowl these bills.
- Staking: Stakers threat dropping a portion of their staked cryptocurrency in the event that they fail to behave according to community protocols (e.g., downtime or malicious exercise) via a course of generally known as slashing.
5. Incomes Potential
- Mining: Rewards rely on {hardware} efficiency and community issue. As extra miners be a part of, competitors will increase, and profitability could decline, particularly with periodic block rewards halving (e.g., Bitcoin halving occasions).
- Staking: Rewards are proportional to the quantity staked and decided by the blockchain’s guidelines. PoS networks usually supply predictable returns, though they fluctuate with community circumstances.
6. Technical Data and Delicate Abilities
- Mining: Profitable mining requires superior technical experience to arrange, optimize, and troubleshoot {hardware}. Understanding electrical energy administration and cooling methods can also be important.
- Staking: Staking calls for familiarity with wallets and staking protocols however is much less technically intensive. Validators profit from fundamental information of community operations and blockchain mechanisms.
7. Accessibility and Obstacles to Entry
- Mining: Excessive preliminary prices, together with {hardware} acquisition and infrastructure setup, create a major barrier to entry. Mining can also be much less accessible in areas with excessive electrical energy prices or regulatory restrictions.
- Staking: Staking has a low barrier to entry, requiring solely cryptocurrency holdings and a appropriate pockets. Some platforms, like exchanges, additional simplify the method with staking-as-a-service.
8. Environmental Affect
- Mining: Mining’s energy-intensive nature contributes to its excessive environmental influence, usually criticized for its carbon footprint.
- Staking: PoS networks are lauded for low vitality necessities, providing a sustainable various to PoW.
9. Financial Decentralization
- Mining: Mining usually turns into centralized in areas with low cost electrical energy or dominated by large-scale operations, probably undermining decentralization.
- Staking: Whereas staking additionally poses centralization dangers (e.g., giant token holders dominating), networks usually implement mechanisms to encourage decentralization, reminiscent of reward caps.
Conclusion
Whereas mining and staking are important to the safety and operation of blockchain networks, their differing useful resource necessities, dangers, and rewards make them appropriate for several types of contributors. Mining is finest fitted to these with entry to low cost electrical energy, technical experience, and a willingness to handle advanced setups. Staking, nonetheless, is right for contributors looking for an eco-friendly, low-maintenance option to earn rewards via lively community participation.
Benefits of Crypto Mining
Crypto mining has the next benefits:
- Excessive Incomes Potential:
- Giant-scale mining operations can generate important earnings by leveraging economies of scale.
- Small-scale miners can earn disproportionate rewards in the event that they achieve fixing the computational puzzle first. For instance, efficiently mining a Bitcoin block rewards 3.125 BTC at current, a considerable incentive.
- Community Safety:
- PoW mining contributes to the strong safety of networks like Bitcoin.
- Manipulating the blockchain turns into prohibitively costly because of the huge computational energy and vitality required, guaranteeing excessive assault resistance.
- Customizability:
- Miners have full management over their {hardware} setup, permitting them to optimize their rigs for effectivity and efficiency.
- Geographic flexibility allows miners to determine operations in areas with decrease electrical energy prices or favorable laws, bettering profitability.
- Financial Incentives for Innovation: The mining business drives computing and vitality effectivity developments. Developments in ASIC expertise and renewable vitality integration usually originate from mining calls for.
- Potential for Scaling: Miners can develop operations incrementally by including extra {hardware}, permitting for scalability primarily based on accessible assets and market circumstances.

Benefits of Crypto Staking
Crypto Staking has the next benefits:
- Power Effectivity and Eco-Pleasant:
- Staking requires much less vitality than mining, making it an environmentally sustainable consensus mechanism.
- Staking aligns with the worldwide push towards greener applied sciences and reduces the carbon footprint of blockchain networks.
- Accessibility:
- Staking eliminates the necessity for costly {hardware}, making it accessible to extra contributors.
- Liquid staking additional lowers the entry barrier, permitting customers to earn rewards with out locking up property totally.
- Regular and Predictable Rewards:
- Rewards in PoS methods are usually constant and proportional to the quantity staked, providing extra predictable returns.
- This stability appeals to contributors looking for dependable earnings from their crypto holdings.
- Extra Decentralized:
- PoS networks usually obtain better decentralization than PoW networks, as staking doesn’t require large-scale operations or centralized entry to assets like electrical energy.
- Mechanisms like capped rewards for giant stakers additional improve decentralization.
- Predictable Working Prices:
- Not like mining, staking has low and constant working prices, because it primarily entails sustaining a fundamental laptop setup.
- This predictability makes monetary planning less complicated for particular person contributors.
- Person-Pleasant Participation:
- Staking can usually be achieved via easy pockets interfaces or platforms that present staking-as-a-service, requiring minimal technical information.
- Native staking help in lots of wallets provides to the benefit of use.
- Versatile Staking Choices: PoS ecosystems supply numerous staking fashions, together with delegated staking, the place customers delegate their stake to a validator with out operating a node.
Conclusion: Why Staking is Extra Economical for People
Staking is a extra sensible and economical possibility for particular person contributors than mining. Its low useful resource necessities, predictable working prices, and regular rewards make it accessible to a broader viewers, together with these with restricted technical experience or monetary capital.
Whereas mining affords excessive incomes potential and community safety contributions, its excessive prices, vitality calls for, and technical complexities make it difficult for particular person miners to compete with industrial-scale operations. Conversely, staking's simplicity and eco-friendliness align effectively with the wants of particular person customers searching for sustainable and decentralized methods to take part in blockchain ecosystems.
Challenges and Dangers of Mining and Staking
Listed here are some challenges and dangers related to crypto mining:
- Excessive Upfront Prices: Mining requires a major preliminary funding in specialised {hardware}, reminiscent of GPUs or ASICs, and infrastructure like cooling methods and electrical setups.
- Excessive Upkeep and {Hardware} Depreciation:
- Mining {hardware} experiences put on and tear, decreasing effectivity over time.
- Steady developments in mining expertise usually render older {hardware} out of date, forcing miners to reinvest recurrently.
- Reducing Profitability in Bitcoin Mining: Bitcoin’s halving occasions, which halves the block rewards roughly each 4 years, result in declining profitability for miners except offset by rising market costs or decreased operational prices.
- Dominance of Giant-Scale Operations:
- Giant-scale operations and mining swimming pools more and more dominate mining with entry to economies of scale, low cost electrical energy, and bulk {hardware} purchases.
- Particular person miners usually wrestle to compete on this panorama.
- Excessive Power Consumption:
- Mining operations devour huge quantities of electrical energy, making vitality prices one of the important bills.
- This dependency on inexpensive vitality usually ties mining operations to areas with low vitality costs, which can not all the time align with favorable regulatory environments.
- Environmental Issues and Regulation:
- The environmental influence of mining’s vitality consumption has drawn criticism, resulting in stricter laws in some areas.
- Sudden coverage modifications can disrupt mining operations.
- Market Volatility: Fluctuations in cryptocurrency costs can straight influence mining profitability, leaving miners susceptible to market downturns.

Listed here are some dangers and challenges related to crypto staking:
- Locked Funds Scale back Liquidity: Staked funds are sometimes locked for a particular interval, limiting liquidity and stopping customers from accessing their property throughout emergencies or market alternatives.
- Threat of Slashing:
- Validators threat having their staked cryptocurrency slashed for community violations reminiscent of downtime or malicious conduct.
- Not like mining, the place useful resource funding is the first threat, slashing straight impacts the validator’s monetary property.
- Rewards Dependence on Transaction Charges:
- In lots of PoS networks, staking rewards are partially derived from block transaction charges.
- Low community exercise can scale back the general reward pool, impacting validators’ earnings.
- Excessive Upfront Staking Necessities:
- Some networks require contributors to stake substantial quantities of cryptocurrency to grow to be validators, making a monetary barrier to entry.
- For instance, Ethereum 2.0 requires a minimal of 32 ETH to run a validator node.
- Penalties for Downtime:
- Validators who fail to take care of constant uptime or meet community necessities could face slashing penalties or lose eligibility for rewards.
- Mining doesn’t penalize downtime, making staking comparatively riskier on this regard.
- Dependency on Community Well being:
- The worth and safety of staked funds rely on the general well being and adoption of the PoS blockchain.
- Poor governance or vulnerabilities within the protocol can jeopardize staked property.
- Centralization Dangers: Staking via centralized platforms or companies could expose contributors to third-party dangers, together with mismanagement or hacking of custodial funds.
- Market Volatility Affect on Rewards: Whereas staking rewards are predictable, the worth of these rewards is tied to the market worth of the staked cryptocurrency, making earnings susceptible to cost fluctuations.
Conclusion
Each mining and staking include their dangers that contributors should rigorously consider. Mining calls for important upfront investments and is burdened by ongoing operational bills, whereas staking locks up property and carries dangers of penalties for poor community conduct. Nevertheless, the vitality effectivity and decrease upkeep necessities of staking make it extra interesting to people, whereas mining’s excessive prices and aggressive panorama usually favor industrial-scale operations.
Selecting Between Mining and Staking
When deciding between crypto mining and staking, contributors should assess their circumstances and preferences to find out which method aligns finest with their objectives and assets. Beneath is a breakdown of key components and supreme circumstances for every technique.
Elements to Think about
- Funds:
- Mining: Requires important capital funding in specialised {hardware} (e.g., GPUs, ASICs), cooling methods, and infrastructure. Moreover, ongoing electrical energy prices are a significant expense.
- Staking: Has a relatively low entry value. Most staking setups want solely a fundamental laptop or a pockets and the cryptocurrency to be staked. Liquid staking options additional scale back obstacles by permitting smaller contributions.
- Objectives:
- Mining: Higher fitted to long-term investments and people prepared to tackle substantial preliminary prices with the expectation of serious returns over time, notably in large-scale operations.
- Staking: Preferrred for people looking for regular, predictable rewards and passive earnings. Staking additionally appeals to these seeking to help eco-friendly blockchain options.
- Technical Experience:
- Mining: Calls for hands-on experience in organising, managing, and sustaining mining {hardware}, in addition to information of energy administration and troubleshooting.
- Staking: Affords plug-and-play choices through staking platforms and wallets, making it extra accessible to contributors with restricted technical abilities.
- Power and Environmental Issues:
- Mining: Requires entry to low cost and dependable electrical energy, with a excessive environmental influence as a result of important vitality consumption.
- Staking: Extremely energy-efficient, making it a most popular possibility for environmentally aware contributors.
- Threat Tolerance:
- Mining: Dangers embody {hardware} obsolescence, excessive operational prices, and fluctuating profitability.
- Staking: Dangers contain slashing penalties, community dependency, and locked funds, typically decrease than mining dangers.
Greatest Use Instances
Mining:
Mining is finest fitted to contributors who:
- Have entry to inexpensive electrical energy and a steady energy provide.
- Personal or can purchase high-performance {hardware} reminiscent of ASICs or GPUs.
- Have the technical experience to optimize {hardware} efficiency and preserve mining rigs.
- Are ready for long-term investments with excessive preliminary prices however the potential for important rewards.
- Function in areas with favorable regulatory environments for mining actions.
Staking:
Staking is right for contributors who:
- Search passive earnings with minimal upkeep necessities.
- Favor an eco-friendly method to taking part in blockchain networks.
- Have decrease upfront capital however maintain the required cryptocurrency for staking.
- Need regular and predictable rewards with out the complexity of operating hardware-intensive operations.
- Worth liquid staking choices permit participation with smaller quantities or entry to funds with out strict locking intervals.
- Favor a decrease threat profile, with fewer operational bills and decreased publicity to vitality prices.
Closing Ideas
Crypto mining and staking are two basic strategies for taking part in blockchain networks and supporting their operations. All through this text, we explored their definitions, processes, benefits, and dangers, highlighting how every method serves a definite position within the decentralized ecosystem.
Because the spine of Proof of Work methods, mining affords excessive incomes potential and important contributions to community safety however comes with substantial upfront prices, technical necessities, and environmental issues. However, staking offers an energy-efficient and accessible various in Proof of Stake methods, providing regular rewards with decrease useful resource calls for. Nevertheless, it entails dangers like slashing and locked funds.
Elements reminiscent of price range, objectives, technical experience, and environmental priorities are essential for people deciding between the 2. Mining is right for these with entry to inexpensive electrical energy and superior {hardware} whereas staking fits these looking for passive earnings and a low-maintenance, eco-conscious technique.
In the end, selecting between mining and staking relies on private circumstances and aims. By offering a complete comparability, this text aimed to equip readers with the information wanted to resolve which method aligns finest with their objectives and assets within the Web3 area.
Continuously Requested Questions
What are the Variations Between Crypto Mining and Staking?
Crypto mining entails utilizing computational energy to resolve mathematical puzzles in Proof of Work methods, whereas staking requires locking cryptocurrency in Proof of Stake methods to validate transactions. Mining calls for excessive electrical energy utilization and specialised {hardware}, whereas staking is energy-efficient and accessible with fundamental laptop setups. Rewards in mining rely on {hardware} efficiency whereas staking rewards are proportional to the quantity staked.
Is Staking Extra Worthwhile Than Mining?
Staking usually offers regular and predictable rewards, making it interesting for passive earnings seekers. Mining, whereas probably extra worthwhile in large-scale operations, requires important funding and has fluctuating returns influenced by vitality prices and community issue. Profitability relies on particular person assets and circumstances, with staking typically being extra economical for small-scale contributors.
What are the Dangers of Crypto Staking?
Key dangers in staking embody locked funds, decreasing liquidity; slashing penalties for downtime or malicious conduct; and dependency on the community’s well being and governance. Moreover, staking rewards can fluctuate with transaction charge accumulation and community exercise. Nevertheless, in comparison with mining, staking dangers are typically decrease and simpler to handle.
Why is Mining Power Intensive?
Mining makes use of specialised {hardware} like GPUs and ASICs, which devour giant quantities of electrical energy to resolve advanced mathematical puzzles. Cooling methods additional add to vitality utilization. This excessive vitality demand is a significant operational value and has environmental implications, usually making mining possible solely in areas with low cost electrical energy.