Allow us to start our dialogue with slightly thought experiment. Think about a primitive world the place expertise limits the mode of communication and transportation to inside continents. Nations throughout the continents perform as interconnected economies and share their sources, cash, and data to develop cohesively.
Our hypothetical world has a catch. Irrespective of how far the person continents might advance inside their economies, they are going to by no means set up contact with each other.
How totally different would such a world look from our actuality? Every continent could be restricted to its pure and human sources. They’d individually resolve all of the questions on science and expertise. Each continent would progress at a special tempo, restricted by the sources at their disposal.
Our hypothetical world is an analogy for the state of Web3 at this time. Just like the continents, every ecosystem in Web3, together with Ethereum, Solana, Cardano, or Polkadot, is actually evolving as a closed financial system, every ecosystem secured by its particular person staked belongings. With the restricted alternate of knowledge and liquidity, every chain is fixing the scalability trilemma by itself.
In June 2023, Polygon proposed “The Value Layer of the Internet” as an answer that facilitates a blockchain financial system resembling a model of our hypothetical world the place continents are certainly interconnected like in actuality, evolving quickly with the worldwide alternate of information and sources. Polygon 2.0 goals to realize this threshold of worth alternate between particular person blockchains.
This up to date overview of Polygon 2.0 is all it is advisable know concerning the evolving Polygon ecosystem. We may even cowl a few of the extra vital implications of this expertise and evaluate it with Ethereum’s evolving roadmap.
What’s Polygon?
The reply to this query has advanced since Polygon was referred to as the Matic Ecosystem. Polygon started as a Proof of Stake Sidechain related to Ethereum. The sidechain would periodically attest to the mainchain with anchor factors the state may revert to towards an assault. The sidechain design didn’t inherit any safety ensures from Ethereum.
What’s Polygon As we speak?

Polygon is greater than a layer-2 scaling resolution in 2024. With the transition to Polygon 2.0, Polygon is a collection of blockchain options relevant at totally different layers of the blockchain stack. Polygon serves a number of roles at this time:
- As a blockchain ecosystem, Polygon gives three distinct platforms for constructing high-performance Dapps:
- Polygon PoS – A POS sidechain on Ethereum, quickly to evolve to zkEVM Validium (extra on that later).
- Polygon zkEVM Rollup is a Zero-knowledge proofs-powered, EVM-capable layer-2 community on Ethereum.
- Polygon Miden is a zero-knowledge proofs-powered, non-EVM layer-2 community with a novel execution setting.
- As a growth equipment, the Polygon CDK helps builders assemble customizable EVM-compatible ZK proofs powered layer-2 chains suited to their particular use case.
- Polygon ID helps construct on-chain, self-sovereign digital identification programs.
With Polygon 2.0, the crew introduces a number of infrastructural upgrades to realize the next two broad targets between the networks in its ecosystem:
- The collective demand for block house can scale linearly with demand to enhance scalability, similar to factories add new meeting strains to multiply output.
- The identical liquidity can proceed to supply all needed safety ensures to each new chain becoming a member of the community with out further safety assumptions.
Polygon 2.0 goals to determine a community of ZK-powered layer-2 chains united by a cross-chain coordination protocol, collectively branding it because the Worth Layer of the Web. So, let’s unwrap this large endeavor.
Key Options of Polygon 2.0:
- Scalability – All networks throughout the Polygon ecosystem will leverage ZK expertise to supply excessive throughput sensible contract execution and financial fuel charges.
- Interoperability – The networks would seamlessly share liquidity and data to function as a unified community, forming the idea for constructing cross-chain decentralized functions.
- Customizability – The Polygon CDK is a set of modular blockchain layers. Builders can merely plug within the desired layers and construct new interoperable chains within the Polygon ecosystem.
- Safety – All chains supply some dedication to Ethereum for safety. The Polygon POS, zkEVM, and Miden are proprietary Polygon chains, whereas CDK is obtainable to construct new ones.
Execs of Polygon
- Ethereum-enabled qualities – Polygon leverages the Ethereum mainnet for safety and finality.
- Developer pleasant – In depth EVM help permits straightforward developer onboarding within the Polygon ecosystem.
- The Polygon additionally leverages Ethereum’s sturdy liquidity and decentralization it has cultivated over time.
Cons of Polygon
- Untested – Polygon 2.0 defines an entire system overhaul. The efficiency of those upgrades has but to be examined by customers in the actual world.
A Temporary Historical past of Polygon
The Polygon community wouldn’t have come about if it weren’t for the NFT undertaking CryptoKitties. In 2017, it was essentially the most talked-about undertaking on the Ethereum blockchain and throughout the crypto group. Its recognition triggered horrible community congestion on the Ethereum blockchain and merchants needed to pay exorbitant charges. Jaynti Kanani, an information scientist in India working for Housing.com, seen this challenge and noticed a chance for enchancment. He contacted Sandeep Nailwal, a blockchain developer, and Anurag Arjun, a enterprise guide, for assist. They drafted a white paper and referred to as their undertaking MATIC community, with Mumbai as their operations middle.
Later, in April 2019, the Polygon crew offered about 1.9 billion MATIC tokens to boost funds for growing the undertaking by the Binance launchpad in an IEO (Preliminary Change Providing). The MATIC community efficiently launched in Q2 of 2020.
In February 2021, the crew rebranded itself as Polygon. The rebrand represents a shift within the crew’s focus from growing Plasma chains to increasing the undertaking’s providers, together with utilizing a number of scaling options. Mihailo Bjelic joined the crew along with his software program engineering experience throughout this transition.
Since then, the undertaking's power has grown by leaps and bounds. Its mission is to be the highest aggregator of Ethereum-compatible blockchains by offering them with superior interoperability functionality whereas processing transactions made on the Ethereum community to assist pace up the method.
In October 2023, Kanani mentioned he stepped down from “the day-to-day grind” of working at Polygon. He won’t contribute “from the sidelines.”
Polygon 2.0
In 2023, Polygon introduced that its MATIC token will start a multi-year transition to the POL token as part of the Polygon 2.0 Initiative. It’s a roadmap to organically combine all of the layers and networks working in unique environments with restricted interoperability within the Polygon ecosystem.
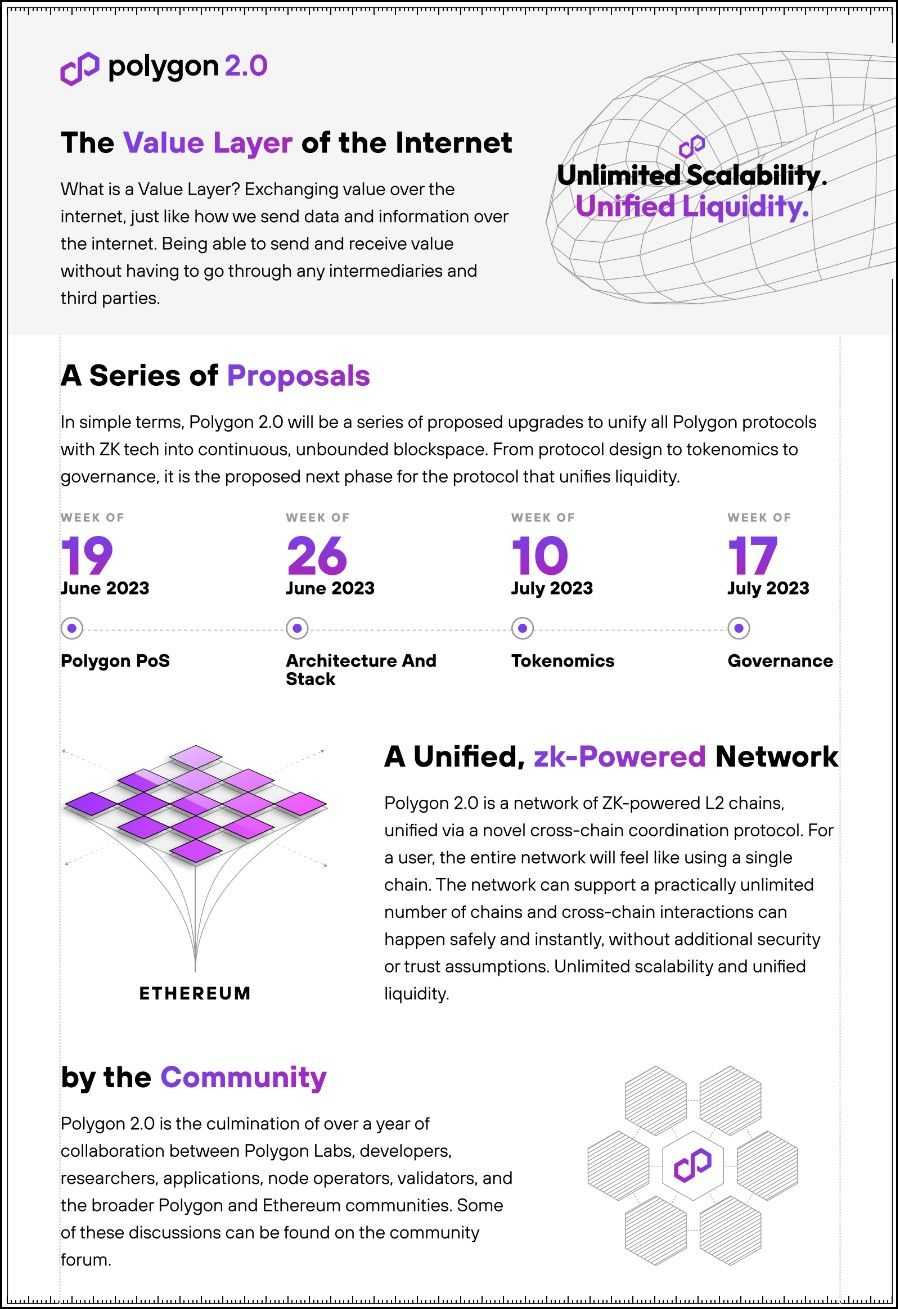
The Polygon Ecosystem Token (POL) will steadily change the MATIC token over the subsequent 4 years. The transfer goals to cement the zkEVM skeletal structure on Polygon as the usual for environment friendly and economical building of safe networks appropriate with Ethereum.
Three Polygon Enchancment Proposals (PIPs) kicked off the transition to Polygon 2.0:
PIP-17 POL Token
PIP-17 describes POL and the associated contracts that deal with emission and token migration. POL will enable for a one-to-one migration of the present MATIC token with an preliminary provide of 10B and a yearly emission of two% distributed between validator staking rewards and a group treasury. The POL token will be capable to help an ecosystem of ZK-based Layer 2 chains by enabling staking, possession, and governance.
PIP-18 Polygon 2.0 Part 0
PIP-18 gives a high-level define for the improve. Part 0 is designed in order that no motion will should be taken from customers and builders already on Polygon PoS and Polygon zkEVM chains. PIP-18 will implement adjustments to the Ethereum contracts on the next chains:
- Initiation of the improve from MATIC to POL.
- Improve from MATIC to POL because the native fuel token for Polygon PoS.
- Improve from MATIC to POL because the staking token for Polygon PoS.
- Launch of the Staking Layer and migration of Polygon public chains.
PIP-19 Replace PoS Native Token to POL
PIP-19 will improve the native fuel token on Polygon PoS from MATIC to POL in a approach that helps backward compatibility. The PIP upgrades the native MATIC Bridge Contract. The MATIC token will change from a declare on the Bridge's MATIC to 1 on the Bridge's POL. The improve won’t change any of the contracts on Polygon PoS, however contracts on Ethereum anticipating MATIC from the MATIC Bridge could also be affected.
For extra particulars concerning the improve to Polygon 2.0, examine the POL Whitepaper and Polygon 2.0 Roadmap.
What’s the Polygon Community?
In English, “poly” is usually used to speak about one thing multi-faceted. Whereas a pentagon has 5 sides and a hexagon has six, a polygon has an arbitrary variety of sides; that is the ethos of the Polygon community, a blockchain undertaking with a number of sides to serve the Ethereum community.
The Polygon Community is a sequence of zk-powered layer-2 blockchain networks on Ethereum. The Community refers to a collective entity comprising community members from Ethereum and Polygon layer-2s always interacting with each other, lastly materializing on the Ethereum mainnet for safety and finality.
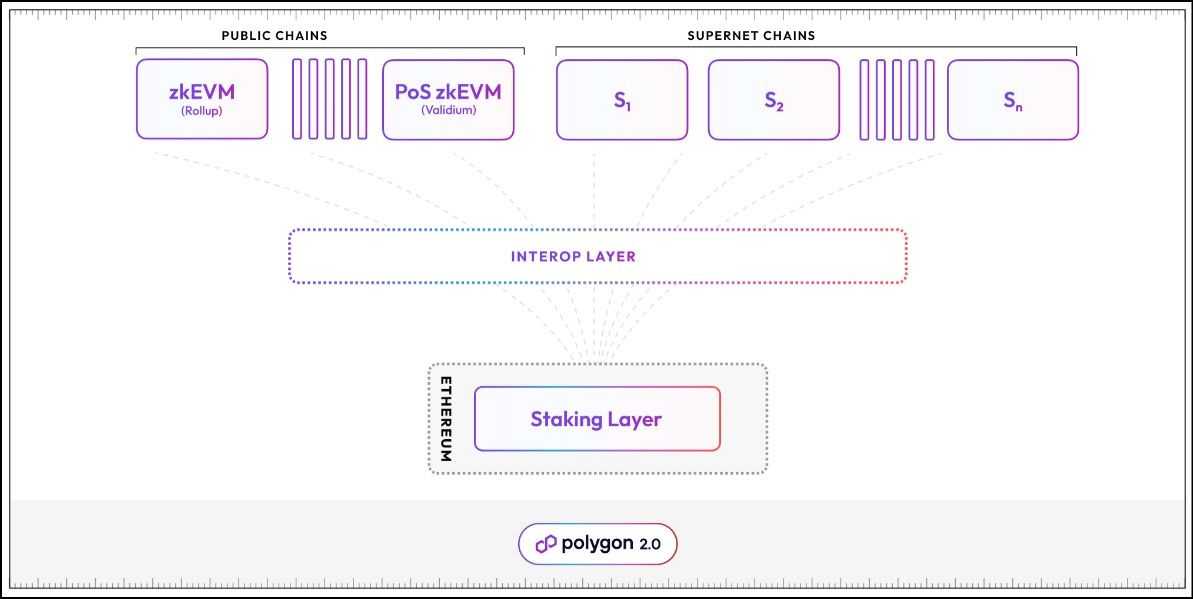
The Polygon Community layer-2 contains Public and ‘Supernet Chains’:
- Polygon constructed the Public Chains. It contains the Polygon zkEVM Rollup and PoS zkEVM Validium (also called Polygon PoS Chain earlier than the two.0 improve).
- The third-party chains developed with the Polygon Chain Improvement Package are dubbed Supernet Chains.
The Staking Layer exists on Ethereum as a Proof of Stake protocol constructed on Polygon’s native POL token. It’s a community of 100 validators who serve many roles. Their roles might range with every rollup to whom validators supply decentralization and safety.
The Interop Layer exists between the layer 2 and the staking layer. It permits seamless interoperability and composability between all Polygon layer-2s.
Due to this fact, the scope of ‘The Polygon Network’ has broadened in Polygon 2.0. It has advanced from a cluster of unbiased Ethereum scalability options to a unified community of a number of scalability and interoperability options on Ethereum.
Heimdall Node
Heimdall nodes work with Polygon’s stake supervisor contract on Ethereum to coordinate validator choice and updation. Heimdall nodes are liable for checkpointing. These nodes create a checkpoint by aggregating layer 2 blocks right into a single Merkel root and periodically publishing it to Ethereum. As soon as a checkpoint enters the Ethereum block data, it achieves Ethereum-secured finality.
Bor Node
Bor is the block manufacturing layer of the Polygon POS chain. Bor nodes are a subset of validators periodically shuffled by Heimdall validators. Block producers mixture transactions to create the PoS Chain blocks.
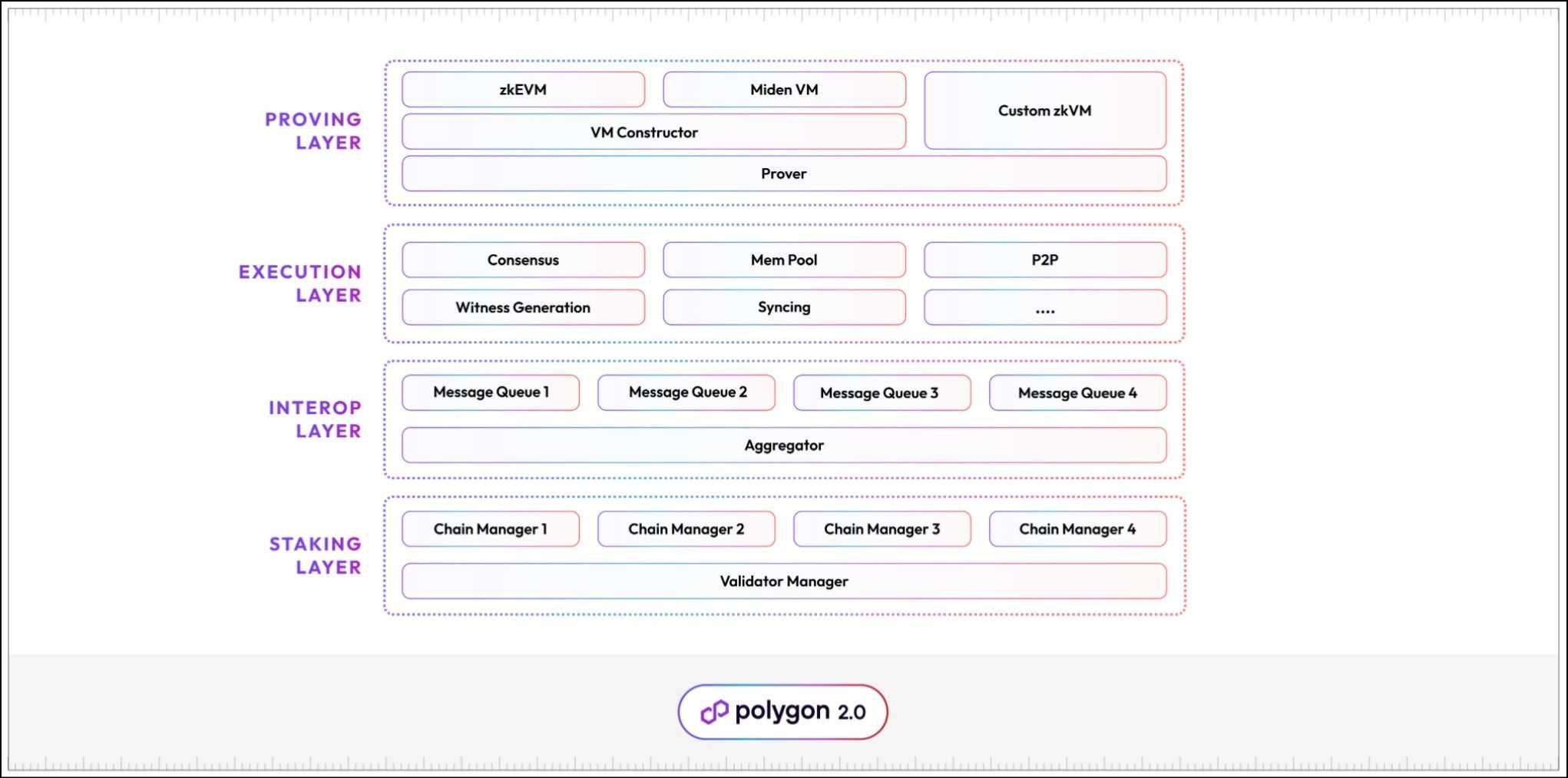
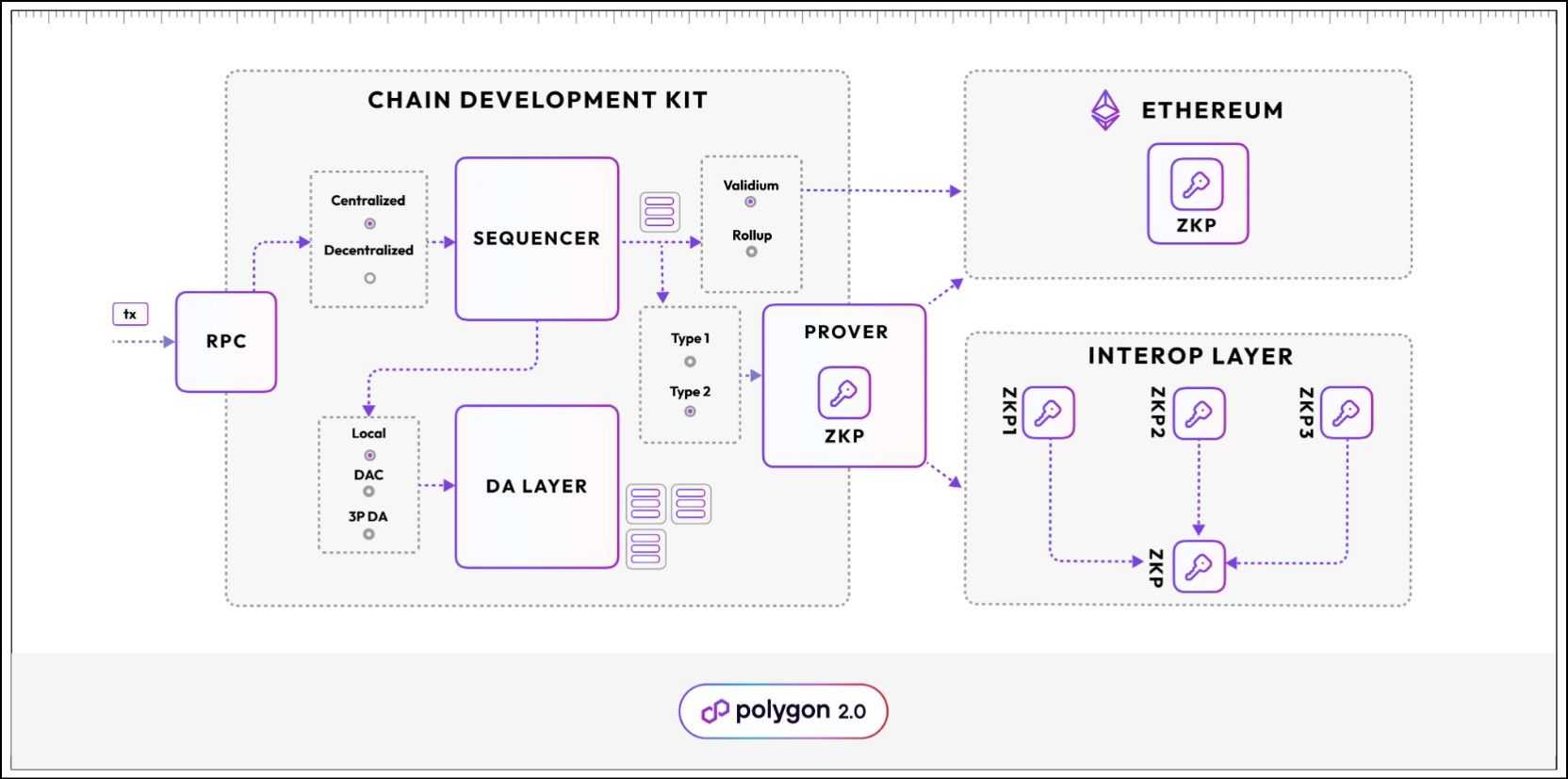
The Polygon 2.0 Structure
The up to date structure of Polygon 2.0 represents an intensive restructuring of all Polygon merchandise. The Ethos behind the brand new structure is undoubtedly modularity. The Polygon Community stack abstracts the community’s core capabilities in 4 distinct protocol layers. Each layer-2 chain on Polygon is a collective occurring of those layers interacting with each other. The 4 layers are:
- Staking Layer
- Interop Layer
- Execution Layer
- Proving Layer
To know this structure intuitively, allow us to deal with the way it implements Polygon zkEVM, a ZK-powered layer-2 chain. The zkEVM is a ZK-proofs-based rollup. Zero Data proofs in rollups are a particular kind of validity proof that proves the provision of sure information to the Ethereum chain with out revealing the precise information. Right here’s how they work:
- A sequencer on layer 2 orders, executes, and batches a number of transactions collectively to calculate the brand new state of the layer 2 chain.
- The sequencer generates a ZK-proof, a sort of validity proof that each one the transactions included within the newest block are legitimate.
- The sequencer posts the ZK-proof to the rollup sensible contract on Ethereum, together with the state dedication and related transaction information. A state dedication is often a hash of the most recent block, which ensures that the state can’t be tampered with later.
- ZK-rollups additionally put up the minimal quantity of transaction information required to calculate the rollup state to the Ethereum chain.
- Now, any validator on the Ethereum chain has entry to the next details about the rollup:
- ZK-proofs of all of the transactions included within the rollup state.
- A state dedication of the rollup state.
- Related transaction information to calculate the rollup state.
- The above-mentioned data is sufficient to calculate a snapshot of the rollup state on Ethereum. The ZK-proofs paired with the state commitments can show the inclusion of transactions within the rollup state. On the identical time, the obtainable transaction information can confirm the proper calculation of the rollup state.
- The Ethereum community lends safety and finality by together with this information in its blockchain.
The supply of transaction information on the Ethereum community is named ‘Data Availability.’ By making transaction information obtainable to Ethereum nodes, they make fewer safety assumptions concerning the rollup state, thus offering extra sturdy safety. The draw back to enhanced safety is that transaction information incurs vital storage prices, growing the price of ZK rollups.
FYI: ZK-Rollups are nonetheless cheaper than Optimistic rollups, which require much more information on the Ethereum principal chain, together with full transaction (not the naked minimal) historical past and transaction signatures.
Now that we clearly perceive how zkEVM works, we’ve got the knowledge to unpack the Polygon 2.0 structure. Let’s dive in!
The Staking Layer
The Staking Layer is carried out on Ethereum. It’s a PoS-based protocol working on Polygon’s native POL token. The Staking layer gives decentralization to the layer 2 chains within the Polygon ecosystem with a standard, decentralized validator pool with a restaking mannequin.
The Staking Layer is split into two elements:
- The Validator supervisor sensible contract retains monitor of the frequent validator pool that may be leveraged by all Polygon chains.
- The Chain supervisor contract manages the validators' units of particular person chains.
Validators stake POL to affix the validator set on Ethereum, offering decentralization to all the layer 2 ecosystem. Validator staking on Ethereum is important for the next:
- Stopping Sybil assaults, the place the identical individual runs a number of node identities.
- Creates incentives for the validators.
- Permits slashing and punishments of malicious validators.
As soon as the validator stakes POL to enter the validator pool, they’re eligible to affix the validation actions of any chain. That is the place the community’s restaking capabilities kick in. The validators have the next incentive schemes:
- Protocol rewards – The staking protocol emits predefined quantities of POL and distributes them to all energetic validators.
- Transaction charges – Validators accumulate transaction charges from the chains they select to validate.
- Extra rewards – Particular person chains can introduce extra rewards by their token emissions to draw extra validators to their community.
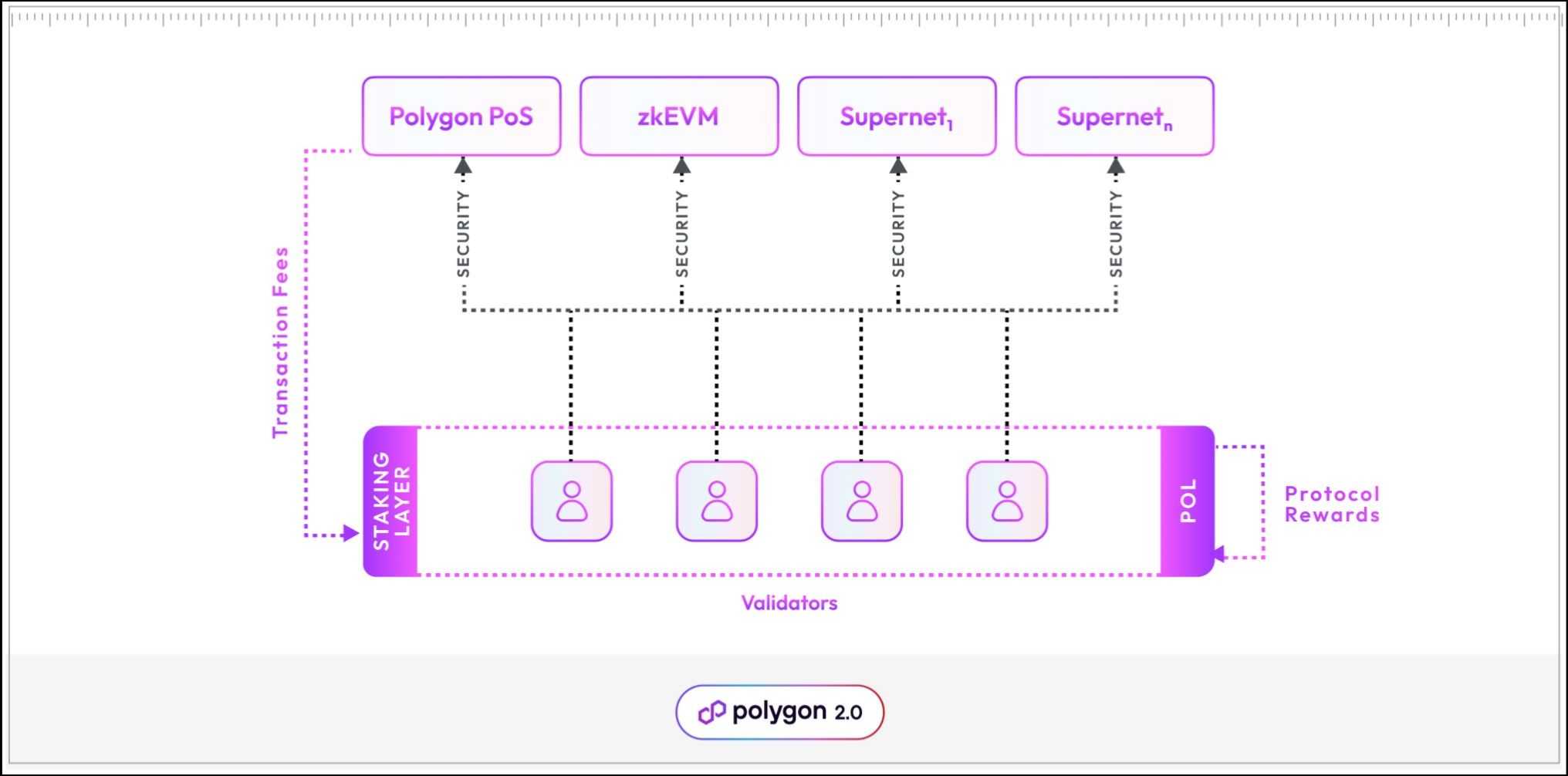
This mannequin creates a free marketplace for safety, the place validators observe incentives to safe the layer 2 networks on Polygon, making certain all networks obtain enough validators to make sure their particular person safety. It’s noteworthy that Polygon staking validators carry out broader duties than a typical POS validator.
Aside from requirements consensus operations, validators fill in different chain-specific roles, the place they may additionally generate zero-knowledge proofs or take part in Information Availability Committees on the Polygon chains. DACs independently calculate the state of the ZK-Rollups utilizing transaction information to safe the community (see the method described above).
Interop Layer
The Interop layer makes the entire Polygon ecosystem work like a single unit. The cross-chain connectivity throughout EVM chains as of late could be very fragmented. Cross-chain bridges are constructed between two chains on a necessity foundation, making the community fragmented. Moreover, Polygon can’t depend on relaying each cross-chain message by Ethereum due to its excessive charges and sluggish community time, making seamless connectivity unattainable.
To deal with these challenges, the Polygon crew developed the Interop Layer, which abstracts the complexity of cross-chain communication for all the Polygon ecosystem. It permits the next:
- A shared bridge to Ethereum permits seamless cross-chain transfers with out minting artificial belongings.
- It may well help quick atomic cross-chain transactions, a vital infrastructure for cross-chain functions.
How Does The Interop Layer Work?
Each Polygon chain maintains a neighborhood queue of outbound messages referred to as Message Queues, that are included within the ZK proofs that the chain generates. As soon as a specific message queue is secured by consensus in Ethereum, any recipient Polygon chain can safely devour its cross-chain messages.
To make sure the programmable scalability of the Polygon ecosystem, the Ethereum layer mustn't be burdened by having to simply accept an growing variety of ZK-proofs from a rising variety of Polygon chains.
The scenario above is mitigated through Aggregators. Aggregators are the distributed community of Polygon validators on Ethereum from the validator pool within the Staking Layer. Aggregators present two important providers:
- Accepting ZK proofs and message queues from the Polygon chains.
- Mixture the ZK-proofs right into a single ZK-proof and submit it to Ethereum for verification.
Aggregating ZK proofs ensures that the cumulative weight of the proofs stays the identical, irrespective of what number of ZK-proofs are aggregated to create a single ZK-proof, decreasing the fuel consumption considerably. As soon as the Aggregator accepts the proofs, the recipient chain begins to optimistically settle for inbound messages, understanding that Ethereum ensures international consistency. This course of is how the Interop Later facilitates seamless cross-chain interactions throughout the Polygon ecosystem.
Execution Layer
The Execution layer is the place the Polygon Community layer 2s execute their sensible contracts, calculate state transitions, and produce a sequenced batch of blocks. The Execution layer contains a number of parts, equivalent to:
- P2P layer – Permits community operators to find each other and talk.
- Consensus – Permits validators to succeed in an settlement on a single order of transactions.
- Mempool – Collects transactions submitted by customers and synchs them with all of the validators.
- Database – Shops transaction historical past.
- Witness generator – Generates witness information required by ZK provers.
Proving Layer
The proving layer is a ZK proving protocol that generates proofs for all transactions for each Polygon chain. This layer is important for ZK-proof era and verification, proof aggregation, implementation of ZK state machines, and environment friendly cross-chain communication. The Proving layer contains the next parts:
- Widespread Prover: A polygon-developed ZK prover designed to help arbitrary transaction sorts. Utilizing a single prover makes proof aggregation and verification easy and environment friendly.
- State machine constructor: A framework for outlining state machines. Builders can use the constructors to outline their very own state machines. State machines are the execution environments on the blockchain. As an example, the Ethereum state machine is named the Ethereum Digital Machine (EVM)
- State machine: Polygon gives two state machine implementations – zkEVM and MidenVM.
The up to date Polygon design abstracts the core blockchain structure into distinct layers. The zkEVM rollup, for example, is an execution layer 2 that leverages the proving layer to show ZK-Proofs. Then, the Interop layer relays any cross-chain requests from zkEVM to different rollups and combines the ZK-proofs from all rollups to undergo the staking layer. The Polygon Community stack works with the assistance of unbiased layers that carry out fundamental capabilities to facilitate a unified community.
The Redesigned PoS Chain
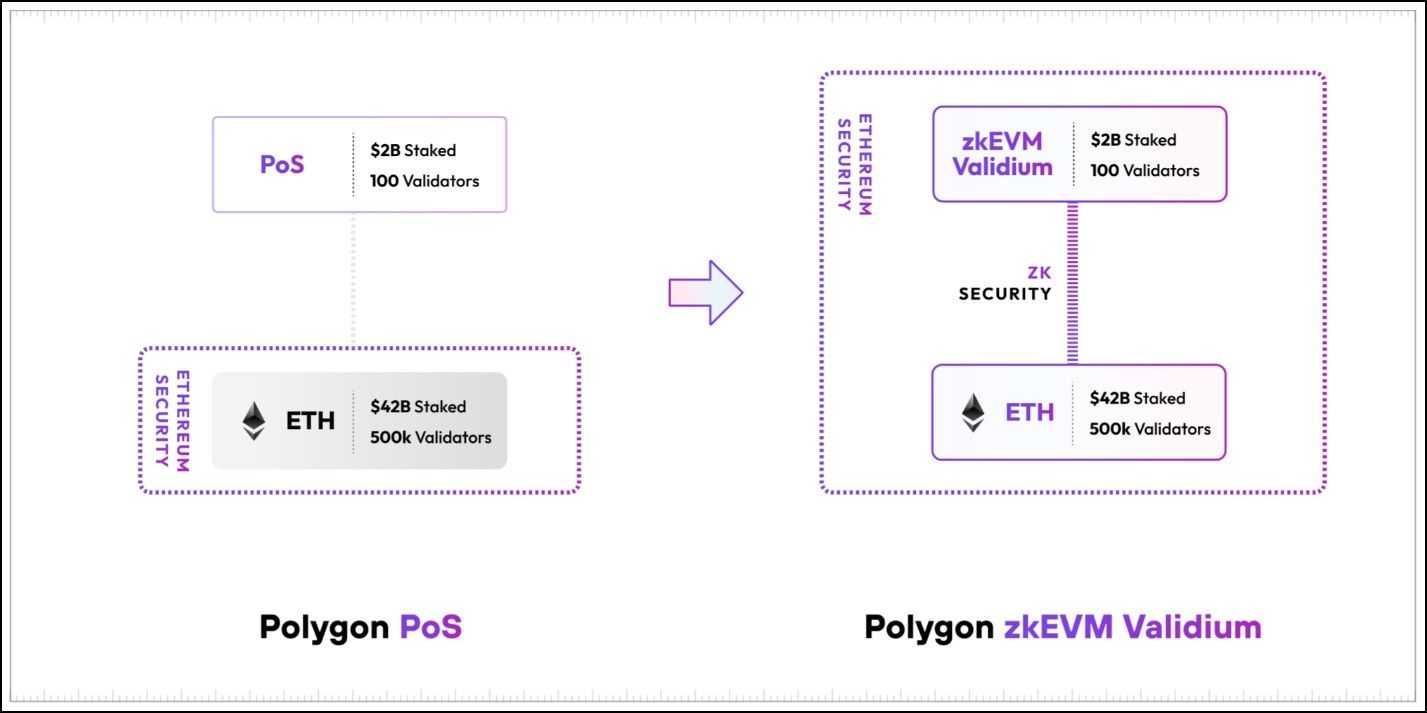
The Polygon POS chain was the Polygon crew’s first scaling resolution within the Ethereum ecosystem. The POS Chain labored on a expertise referred to as Sidechains. The replace will redesign the POS chain to implement the zkEVM Validium mannequin to align the POS chain with the Polygon 2.0 narrative. Allow us to break this replace down.
The Unique Polygon PoS Chain Design
The Polygon PoS Community contains three important layers:
- The Ethereum layer – A set of sensible contracts on Ethereum for validator report holding.
- Heimdall layer – A set of Proof of Stake nodes working parallel to Ethereum that commit Polygon Community checkpoints to the mainnet.
- Bor layer – A set of block-producing nodes shuffled by Heimdall nodes.
Right here is an outline of the block propagation course of behind Polygon PoS:
- A subset of energetic polygon validators creates blocks and broadcasts them to different validators.
- A particular block proposer from the Heimdall layer is liable for gathering all signatures for a specific checkpoint and committing the checkpoint to the Ethereum mainnet. Each checkpoint contains a number of blocks.
- The accountability of making blocks and proposing checkpoints varies on the validator’s stake ratio on the general validator pool.
The community additionally helps a two-way bridge between the PoS chain and Ethereum, permitting customers to maneuver belongings like POL (beforehand MATIC) and ETH between the networks.
The Polygon PoS community does inherit minimal safety from Ethereum. The safety stems from the checkpoints that Polygon nodes periodically decide to Ethereum. The community can fork to the final synced checkpoint in a breach and slash the colluding validators.
Polygon PoS Adopts zkEVM Validium
As intimidating because the title ‘zkEVM Validium’ might sound, we’ve got already lined the background to know this blockchain design. A Validium is a better throughput, decrease price model of ordinary ZK-Rollups. Validium trades off some safety ensures supplied by ZK-Rollups to realize a better throughput. To shortly recap, customary ZK-Rollup makes the next information obtainable to the validators of the Ethereum community:
- ZK-proofs of all of the transactions included within the rollup state.
- A state dedication of the rollup state.
- Related transaction information to calculate the rollup state.
The Ethereum validators can reconstruct the rollup state with this data, which permits them to confirm if the brand new state was calculated appropriately, right here’s the way it works:
- The ZK-proofs are checked towards the state dedication to confirm if all of the transactions for which the proof was offered are certainly part of the brand new state.
- Subsequent, they use the offered transaction information to reconstruct the rollup state to substantiate the validity of the state dedication itself.
- Due to this fact, Ethereum mainnet validators are capable of confirm rollup blocks with no belief assumptions, as they’ve entry to all related information required for the verification.
The distinction between customary ZK-Rollups and Validium lies within the final step. It seems that the transaction information, the puzzle piece important for calculating the rollup state, is kind of memory-heavy, making up the majority of the ZK-Rollups information on Ethereum.
A Validium mannequin works like a typical ZK-Rollup however skips sharing transaction information with Ethereum. The Ethereum validators nonetheless have entry to zk-proofs and state commitments, enabling them to show if all transactions have been appropriately included within the rollup state. Nonetheless, they can not confirm the validity of the rollup state, a scenario referred to as lack of information availability.
An Ethereum node should confirm three essential facets of any layer 2 block:
- All transactions included are right and provable through zk-proofs.
- The brand new rollup state contains all right transactions, provable through zk-proofs and rollup state.
- The validity of the rollup state is verified by reconstructing the state with the transactions in the best order.
A Validium lacks the important final element, transaction information required to confirm the state, however why does that matter?
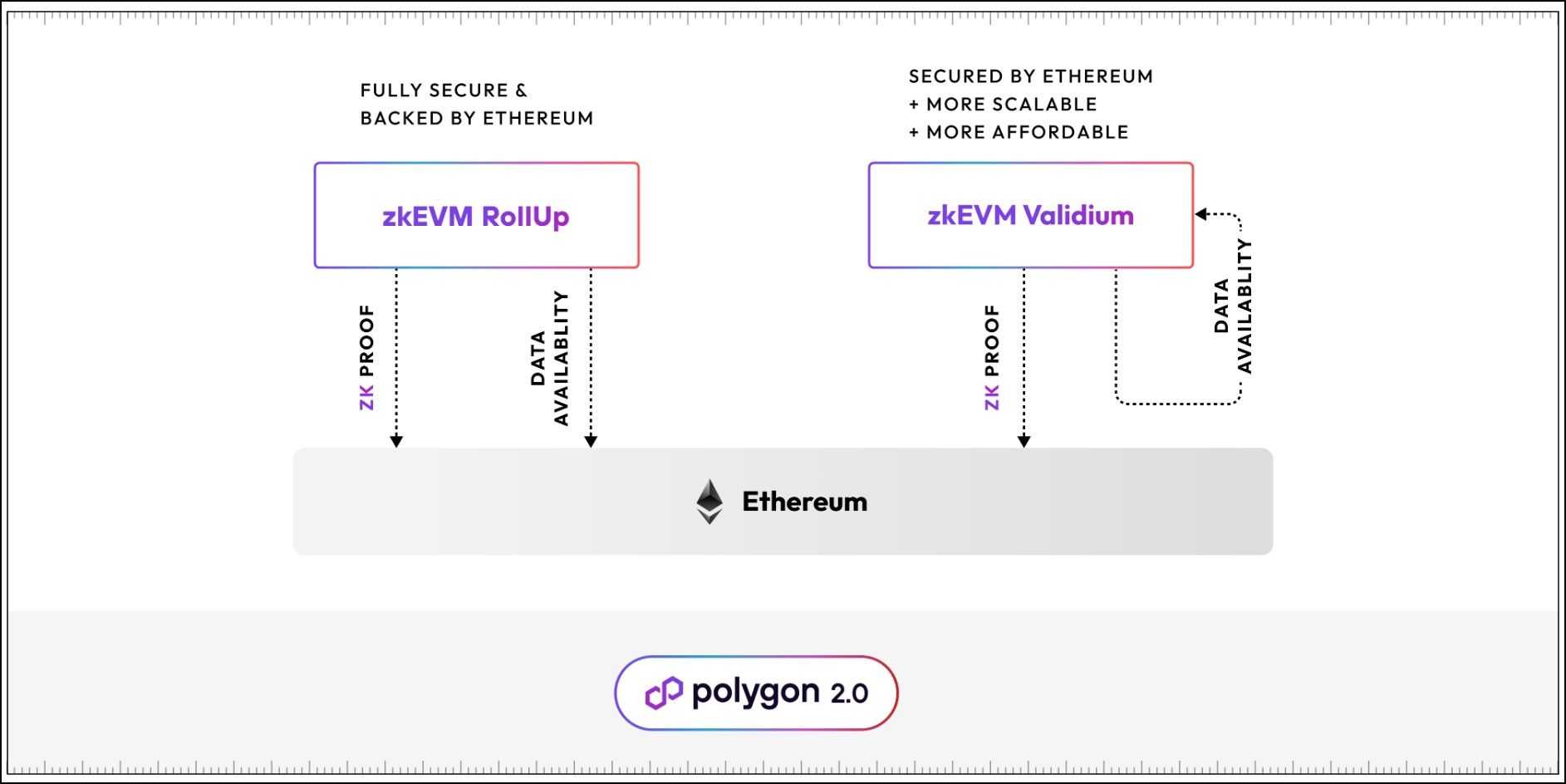
Probably the most essential factor of a blockchain consensus course of is agreeing upon the best order of transactions. A scarcity of consensus concerning the order may yield vastly totally different block states for a similar pool of transactions. In Validium, the order assure is secured by the validators in layer 2, that are the prevailing validators of the PoS chain.
Polygon zkEVM Validium Design Abstract
Let's summarize this part with some situations the place sacrificing safety in Valudium could also be virtually possible:
- Low-value transactions have minimal impact on slippage, decreasing the inducement of tampering with transaction ordering. Validium is useful for such on a regular basis transactions.
- Additionally it is helpful in enterprise networks the place privateness is most well-liked. Hiding transaction information in these settings is extra essential for privateness than safety and decentralization.
Due to this fact, with the Validium chain and the usual zkEVM rollup, Polygon addresses each person demand for scalability and safety.
Polygon Chain Improvement Package
Polygon CDK (Chain Improvement Package) is an open-source, modular codebase to assist builders launch ZK-powered Ethereum layer 2 chains that plug into the Polygon Community for interoperability. Builders that use the CDK to deploy new chains will routinely launch a ZK-powered layer 2 on Ethereum, interoperable with the remainder of the Polygon Community through the Interop Layer by default.
With the CDK, builders can deploy customized layer 2 chains tailored for his or her use case. They might select a number of parts to construct their chains. A few of them are:
- Information Availability – Rollup or Validium designs
- Execution setting – zkEVM or MidenVM
- Token – Native or customized fuel token
- Sequencers – Centralized or Decentralized
Most important options of the Polygon CDK:
- Modularity and Customizability – The flexibility to decide on between totally different infrastructural parts.
- Interoperability and shared liquidity – Shared liquidity and interoperability with the remainder of the Polygon ecosystem.
- Entry to Polygon’s ZK expertise – Entry to Polygon’s ZK-powered proof programs.
Listed below are some initiatives constructing within the Polygon ecosystem with the assistance of the Polygon CDK:
- Immutable – Constructing Web3 video games on Ethereum.
- Astar Community – A sensible contract platform on Polygon.
- Palm Basis – Democratizing Artwork with the Palm Community on Polygon.
- Acentrik – Enterprise Web3 options.
- OKX- Introduced they are going to be launching their Layer 2 on Polygon
The POL (Matic) Token
POL (previously MATIC) is the native token within the Polygon ecosystem. It’s the default mode of paying fuel for transactions within the PoS chain. It additionally fuels safety ensures of layer 2 networks on Polygon that deploy Polygon stakers of their infrastructure. POL can also be the governing token within the ecosystem, important for the democratic implementation of enchancment proposals within the ecosystem.
POL house owners may also stake their holdings to assist safe the Polygon POS chain and earn rewards. Staking POL (Matic) by Ledger is among the most secure methods to take action because it combines the safety of a {hardware} pockets with the pliability to decide on your individual validator. Yow will discover different staking tokens in our Prime Staking Tokens article.
Migration to POL:
The POL token will change MATIC to turn out to be the main software for coordinating and rising the Polygon ecosystem. POL makes two “game-changing” enhancements, as Polygon put it:
- Validators can validate a number of chains, i.e. as many chains as they need.
- Each chain can supply a number of roles (and corresponding rewards) to validators.
Important options of the POL token embody:
- Restaking: POL stakers will safe the community and obtain rewards. After staking a specified quantity of POL tokens to run a validator node, the consensus algorithm affirms the validator's dedication to defending the community, and as an incentivization system, validators will probably be rewarded with POL tokens. Restaking refers back to the POL token powering the safety of different chains that function underneath the Polygon Supernet construction as effectively. Validators on the Polygon community may even be capable to validate different chains, incomes rewards from transaction charges generated on the secondary networks.
- Ecosystem safety: The decentralized pool of Proof-of-Stake validators can safe the Polygon chain.
- Parallel scalability: The validators of the staking layer can theoretically safe an infinite variety of layer 2 chains with the identical POL liquidity.
- Group possession: With decentralization as its core worth, Polygon is supposed to be ruled by its group. POL needs to be enabled to carry governance rights, i.e., be utilized in governance frameworks.
- Each Polygon chain’s group can determine which token their chain will use for fuel charges.
The improve to POL from MATIC would require a easy technical motion, sending MATIC to the improve sensible contract, routinely returning the equal quantity of POL. Token holders could be given ample time to improve, equivalent to 4 years or extra. Nonetheless, if the group consensus is gathered supporting this proposal, the migration may begin inside months. If it piques your curiosity, you possibly can try the POL whitepaper.
The place to Purchase Matic/POL
Exchanges are nonetheless providing the Matic model of the token as POL is rolled out, however as Polygon is among the crypto trade's main initiatives, it’s obtainable on most respected exchanges. We suggest SwissBorg, Kraken, OKX, Bybit, Crypto.com , and so on.
Man has a couple of centralized exchanges to suggest if you wish to purchase it with money. There are additionally decentralized exchanges, however you will want some type of cryptocurrency to alternate for it. The most typical sorts used are stablecoins.
The place to Retailer MATIC Tokens
Many of the wallets out there can retailer your MATIC tokens safely. Sizzling wallets equivalent to MetaMask, Exodus and Belief Pockets are common choices for ease of use. In the event you plan to carry on to them for some time, then chilly wallets aka {hardware} wallets are your finest guess. Ledger, Trezor, and Ellipal are stable chilly pockets decisions for the storage of MATIC.
Is Polygon good for Ethereum?
Polygon is helpful for Ethereum as a result of it accentuates essentially the most important factor of the Ethereum blockchain – safety and decentralization. Polygon might profit Ethereum in two broad methods:
- Selling the EVM ecosystem – As extra providers are constructed on EVM and extra customers enter the ecosystem, it reduces the inducement to construct on non-EVM ecosystems.
- By growing fuel use – Elevated on-chain exercise results in extra demand for ETH to pay for fuel.
In the end, Polygon advantages Ethereum organically by contracting the provision of ETH and burning extra fuel, deflating ETH provide and probably growing its worth.
Does the Ethereum Roadmap Make Polygon Out of date?
The reply to this query is extra nuanced than a easy sure or no. The Ethereum 2.0 improve transitioned the protocol consensus to Proof of Stake and launched fuel administration efficiencies to the community. All layer 2 networks obtain finality on the Ethereum blockchain by paying to have their transactions included within the mainnet. Due to this fact, enhancing the bottom layer effectivity improves efficiency on the above layers.
After Ethereum 2.0, the rollup-centric roadmap can also be set to introduce Danksharding to the community, a novel scaling resolution dramatically decreasing dedication prices for layer 2 networks. Because it seems, the post-Danksharding design for the usual rollup is similar to Validium, however with fewer safety ensures. If customary rollup designs obtain near-Validium throughput however with comparatively larger safety, the replace may cut back the inducement to make use of the Polygon POS Validium chain.
Nonetheless, it’s value mentioning that a lot of the evaluation above is concept, because the applied sciences we’ve got in contrast haven’t but been carried out, and their results haven’t been realized absolutely, so so much stays to be seen.
Prime Initiatives on Polygon
Being the multipurpose chain that it’s, Polygon, lengthy recognized for being house to a few of the high DeFi dApps, can also be now referred to as the no. 2 gaming platform for Web3 video games. The rise in gaming ranks is attributed to the formation of Polygon Studios in July 2021. On this part, we briefly take a look at a few of the high dApps on the community simply to provide you an thought of the community’s capabilities.
- AAVE – A high DeFi protocol with one of many highest TVL, in response to DeFi Llama, is on Polygon.
- Aavegotchi – This undertaking was launched by AAVE, and options NFTs of ghosts, just like the AAVE ghost icon. These ghosts reside within the Gotchiverse, and could be procured in two methods: summoning an Aavegotchi or selecting one up on the Aavegotchi bazaar.
- Uniswap V3 – The highest decentralized alternate within the crypto house has been obtainable on Polygon by common consensus since December 2021. Buying and selling quantity for the alternate on the Polygon community is round $38 million, in response to CoinMarketCap, in comparison with the $99.88 million for the alternate throughout all of the networks.
- OpenSea – the highest NFT market, has a presence on the Polygon community. Low-cost fuel charges and quick transaction pace are a particular plus for NFT merchants.
- Decentraland – the undertaking that popularised the time period “Metaverse” has a footprint on Polygon.
Polygon 2.0 Assessment – Closing Ideas
Modularity, Composability, and Interoperability are important pillars of the Web. Modularity is the flexibility to summary totally different components of the tech stack. Composability is the flexibility to mix totally different modular parts in numerous configurations to construct new merchandise or programs effectively, and interoperability is the flexibility for such totally different programs to speak and work together with one another seamlessly and effectively. These talents facilitate Polygon’s Worth Layer of the Web.
Polygon 2.0 is a major transfer by a serious ecosystem in the direction of implementing international modularity, composability, and interoperability. In a really perfect world, Polygon’s Worth Layer will thrive not solely on Ethereum but in addition on different Layer 1 networks. The tech stack’s modularity could make this transition simpler than earlier than by solely updating the required parts relatively than constructing the stack once more from the bottom up.
Polygon 2.0 is essentially the most formidable experiment in layer 2. It makes huge bets on a number of novel applied sciences, together with zero-knowledge proofs, restaking, and the appchain thesis. If the experiment proves profitable and sustainable, it has the potential to determine itself because the gold customary for layer 2 structure.
Regularly Requested Questions
What’s Polygon (Matic)?
Polygon (previously referred to as Matic) is a collection of blockchain options. The Polygon Community is a multi-layered community that hosts a number of interoperable layer 2 blockchains, like zkEVM and akEVM Validium, in addition to a number of third-party networks. The Polygon ecosystem is related to Ethereum for safety and finality.
Is Polygon (Matic) nearly as good as Ethereum?
The reply depends upon the context. Ethereum is best at offering safety and finality ensures, owing to its huge and decentralized validator community and substantial capital staked to safe the community. Nonetheless, these capabilities make Ethereum sluggish and costly to make use of, which is the place Polygon shines. Due to this fact, they is perhaps higher than the others in sure contexts.
Does Polygon have a future?
The way forward for the Polygon community is trying very vivid with quite a few high-profile partnerships and the success of Polygon Studios, the gaming arm of the community. These partnerships straddle each side of the fence as common companies equivalent to Starbucks and Nike be a part of Web3 dApps like Uniswap and AAVE to supply their providers to customers.
The evolution to Polygon 2.0 additionally highlights the undertaking’s dedication to innovation and advancing the cryptocurrency house. Of all of the Ethereum layer 2s, Polygon is among the many leaders not simply as a scaling resolution, however in constructing out a whole zkEVM ecosystem.