Bitcoin and Ethereum have become the most popular projects of the Blockchain movement. They aim to replace our current financial, trading and economic systems with a more decentralized, secure system.
In the belief that these networks will dominate a digital world decentralized, millions have invested their time and money in them.
These networks, however, are plagued with the fundamental problem that scalability, even though they have a combined market capital of over $200billion.
Many well-funded and community-backed blockchains are still in beta or alpha mode due to a lack of scalability. The coins are bought to hold as speculative investments because they are not able to be traded for goods or services.
The value that these Blockchains’ are promising cannot be realized at scale due to what is called the ‘Trilemma’.
Blockchain Trilemma
The ‘Scalability Trilemma’ is a term coined by Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin that addresses the problem of how to develop a blockchain technology that offers scalability, decentralization and security, without compromising either one.
Vitalik believes, at a basic level, Blockchains only can achieve 2 of the 3 traits at one time.
- Decentralization This is defined as the ability of the system to run when each participant has only access to O(c). (a laptop or small VPS is sufficient)
- Scalability (defined as being able to process O(n) > O(c) transactions)
- The Security of Your Own Home (defined as being able to defend against attackers using up to O(n+1) resources)
C stands for the computational resources available (including computation, storage, and bandwidth) to each node. n Refers to the ecosystem’s size in an abstract sense. We assume that the transaction load, the state size and market cap of crypto currencies are all proportional. n.)
Why is it important to have these components?
Decentralisation
This is the core of a Blockchain system. Decentralization allows networks to be permissionless and censorship-resistant, giving anyone the power to use and build on them.
Decentralization alone isn't scalable because decentralized systems operate on consensus, which means decisions (such as verifying transactions) are made by a group of nodes as opposed to an individual node.
Consensus is more likely than individual decisions to produce high-quality decisions, whereas individual decisions are likely to be quick and resist backlog.
Security
It is only on a decentralized network that immutability and peak security can be achieved, because what better place to store sensitive data that on a network that has no single ‘central’ point of failure.
Scalability
It is important to note that without the ability to increase the size and speed of a Blockchain, we cannot hope to have a significant impact on more than a small number of people. Bitcoin and Ethereum’s combined market cap is over $200 billion, but this was only possible because they were promised mainstream adoption one day.
This would mean that Bitcoin could match or exceed Visa’s current 24,000 transactions per seconds (as opposed its 7 transactions), and Ethereum as the technology behind the most successful and largest Dapps.
To move from a bootstrapped network into a major player in the world stage, the consensus process must become more efficient and faster without becoming less secure or centralized.
How do We Solve It?
Many solutions are still being developed or are currently on the market to try and solve the problem of scalability.
Alternative Coins
Bitcoin and Ethereum transactions are extremely slow. They average around 7 and 15 transactions a second, respectively.
Other cryptocurrencies with higher throughput rates are available. Litecoin was one of the first Bitcoin alternatives. LTC transactions can be completed in 56 tps by using a hashing algorithm that is different.
Ripple (XRP), Stellar Lumens, and other cryptocurrencies have transaction times between 1,500 tps (transactions per second) and 1,000 tps (transactions per second).
Lightning Network (Bitcoin)
The lightning network is called a ‘layer 2′ solution. Its main purpose is to increase the capacity of Blockchains, so that transactions are cheaper and more frequent.
Smaller, less significant transactions are stored ‘off chain’, and are essentially bundled up and validated independently by small communities before being sent back to the main Blockchain, where they can be processed as one single transaction.
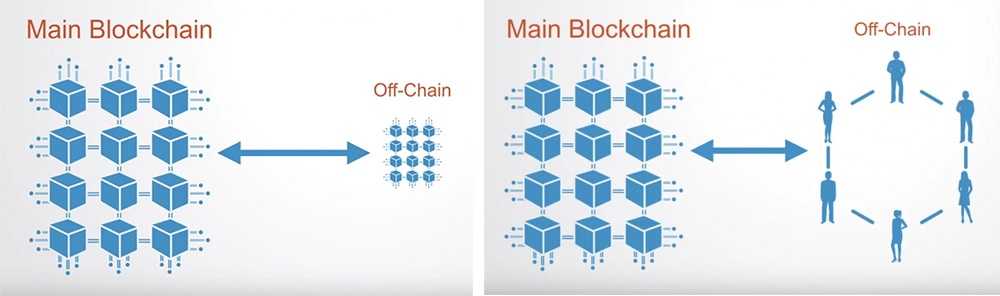
There are small communities that allow transactions to take place without registering them on the main Blockchain
It’s easier to think of this as a monthly grocery tab. All your purchases will be recorded and at the end, the cashier will accept a single payment.
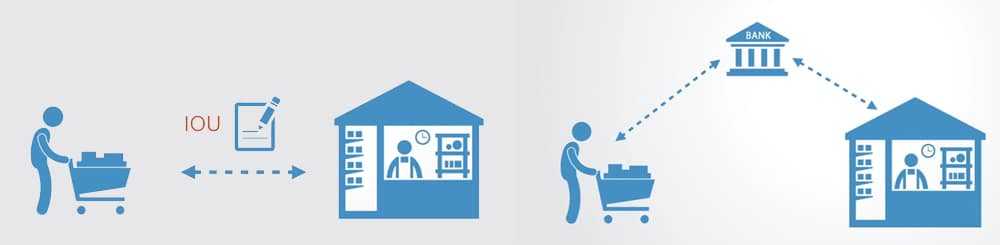
The bank will then acknowledge the final payment of the IOU for Groceries.
This means that we can reduce the number transactions from multiple to only two on the main Blockchain: one to open and close the transaction between main Blockchain and off-chain;
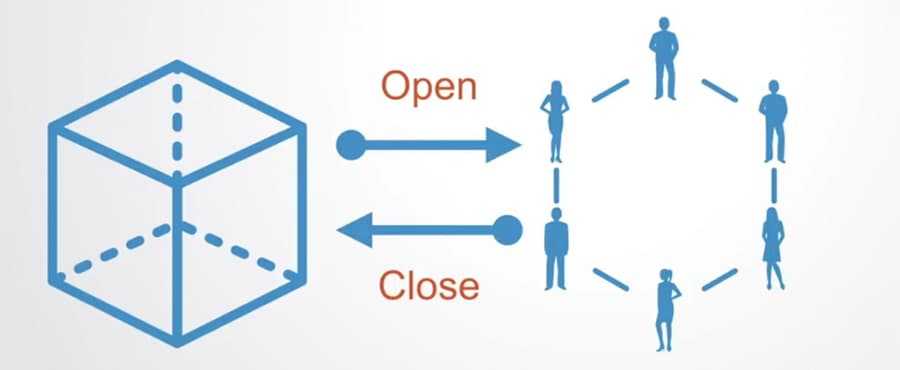
Offchain State Closure Image Sources
The lightening Network is the most promising solution to scalability for the Bitcoin Blockchain. Over the last 6 months, the number of Bitcoin transactions per day has dropped from 500k in Decembre to 200k by May. Meanwhile, the cost of each transaction has increased 50% since February 5.
The cost of a transaction should decrease as the volume of transactions increases in developed financial markets (we can see this pattern on the Internet; as the number users increased, we saw the cost of transferring money, information etc. drop dramatically).
Lightening is expected to replicate these patterns.
Plasma (Ethereum).
It is a layer 2 solution similar to Lightning Network that was created by Buterin, along with Joseph Poon who is the co-creator of Bitcoin Lightning Network.
With Plasma, ‘child chains’ are created on the Ethereum Blockchain (main chain), with there own validators. A company can create a child chain of plasma on top the main blockchain with agreements (or rules), using a smart contract.
Child-chains may spawn other child-chains. They can also spawn child-chains.
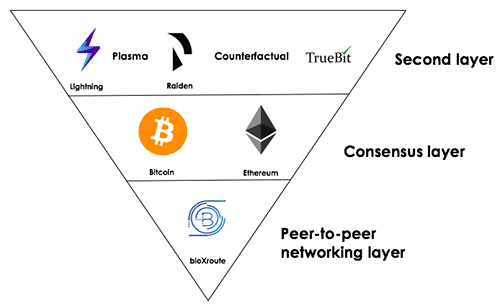
Scaling Solutions – Image Source
Plasma allows us to perform complex operations on the child-chain, running applications for thousands of users while only occasionally interacting with Ethereum’s main-chain. This would result in a higher number of transactions per second, and lower transaction costs.
There are other solutions that are being developed simultaneously to help with Ethereum's scaling issues. Raiden Network is one of the solutions being developed to help with scaling Ethereum.
Sharding is the other solution being implemented. This is the distribution of nodes to certain groups, so that nodes don't have to validate the whole Blockchains history before validating a new transaction.
BloXroute makes another interesting proposition. The above image shows another scalability option that allows crypto currencies and Blockchains scale up to thousands of transactions every second (TPS), without changing the protocol.
Scalability-focused solutions
We have mentioned a few crypto currencies that can be used to speed up transactions, but they only solve one part of the Trilemma. Other coins are being developed to specifically address the scaling issue.
EOS
EOS is an Ethereum competitor focused on providing a more scalable alternative using a method called ‘delegated proof of stake”.
With this method, the network nominates multiple “Witness nodes” as representatives who help to make certain high-level decisions more quickly without polling the entire network.
This is clearly a more centralized approach, handing control to about 100 witnesses who are voted in by the community. It’s easy to see how such a system could be influenced by internal politics and self-interest (people’s vote strength is determined by how many tokens thsey hold. This means that people who have more tokens will influence the network more than people who have very few tokens).
However, this (along with other system upgrades) has enabled EOS to run tests where they achieved 50,000 tps.
Cosmos
Cosmos aims to become an “Blockchains are the internet of Blockchains” that solves the problem of scalability and Interoperability (the ability for many Blockchains to communicate with each other).
With Cosmos, scalability is achieved through the vertical and horizontal approach:
Vertical scalability is the addition of resources to a single system node, such as a single computer or network station, which often results in additional CPUs or memory. Vertical scalability provides more shared resources for the operating system and applications.
Horizontal scalability is achieved by having multiple parallel chains running the same application and operated by a common validator set. This (in theory) makes Blockchains more scalable by enabling smart contracts and transaction processing to execute simultaneously.
Conclusion
Scalability is a problem that has many Blockchains fiercely competing to create a solution that will enable their network to reach mainstream adoption.
As these networks continue to progress, we may have to ask deeper questions about how we define decentralization, and how much decentralization is needed to satisfy a Blockchains ethos while achieving scalability.
Today this is determined by specific use cases, mainly, whether a Blockchain needs “sovereign grade” censorship resistance (in the case of Bitcoin) versus “”Platform grade” (in Ethereum’s case).
Sovereign grade refers the the need for decentralization so that a store (like Bitcoin), which has the highest security levels, cannot be manipulated by government or attacked (in other terms; is resistant to Government censorship).
Platform grade is a way to give developers assurances that a centralized stakeholder, such as Facebook, Google, or Apple cannot alter the rules of a platform to disrupt their ability continue to work on it.
According to your point of view, as a builder who wants to have maximum freedom, or currency holders who want maximum security, and autonomy, you should only support a degree of decentralization which allows you to achieve just the right level of censorship resistant needed.
I don’t think any single solution will be able to achieve the perfect balance in terms of scalability security and decentralization. It is fascinating to watch the way each network implements their unique solution to the Blockchain Trilemma.
Featured image via Fotolia