Bitcoin captured the public's attention in 2017 when the price rocketed to almost $20,000 at the end of the year. Suddenly, people who'd never considered Bitcoin a serious investment were mortgaging their houses to buy it. That was a mistake for some, as Bitcoin's price and every other cryptocurrency plummeted in 2018.
Bitcoin, however, recovered. By the end of 2020, Bitcoin's price was around $28,000, and in April 2021, Bitcoin's price topped a staggering $64,000.
Bitcoin has stayed in the media's headlights and remains the number one cryptocurrency listed by market capitalization.
We can help you if the jargon of the crypto industry is confusing to you. Blockchain technology isn't as complex as you might think, and once you understand how Bitcoin works, you will have a clearer picture of whether you want to join the loyal Bitcoin community of fans.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin (BTC) is a digital currency and the first cryptocurrency created using blockchain technology for Bitcoin transactions. Bitcoin started in 2009, as a form of decentralized money and a transactional medium.
Bitcoin's primary purpose is to enable peer-to-peer transactions without relying on a central authority, eliminating the requirement for intermediaries like financial exchanges.
Bitcoins (BTC) are rewarded for validating a transaction in the Bitcoin network. Users can purchase Bitcoins on various exchange platforms. They mine Bitcoin using computing power.
Bitcoin is different from any other currency you have ever used. You can send Bitcoin to anyone on the global network. Your BTC assets are stored in a digital Bitcoin Wallet on your computer or mobile. Your assets will be stored safely in the Bitcoin ledger. You can access your assets with a public/private key pair.
If you are new to crypto and would like to learn more, you might feel confused by reading complicated explanations of Bitcoin. "what is Bitcoin?"Bitcoin Transactions and How Bitcoin Works
Don't worry. This article is intended to give you a detailed overview of Bitcoin, its network, and Bitcoin miner. We will remove the technical jargon to explain. “What is Bitcoin?” Simple, easy to understand language. Learn how to buy Bitcoin, sell Bitcoin, and the best Bitcoin exchanges recommended by Bitcoin users.
Bitcoin advocates are quick and easy to mention some ways in which Bitcoins are superior to other assets. This is not difficult to dispute. Bitcoin users praise its key features, including:
- A maximum of 21 million units with an inflation mechanism that is guaranteed by code – this means money printing and inflation runaway cannot occur.
- Send anywhere in the world within seconds or minutes at a fraction of what it costs to use fiat.
- Bitcoin is decentralized. Bitcoin does not have to conform to the needs or policies of third parties or governments. Bitcoin and Bitcoin transactions are not controlled or stopped by anyone.
- The current global payment networks are complex, inefficient, expensive, and slow.
- Bitcoin is more transparent and secure.
- Bitcoin’s network is owned by no one, which creates a level playing field among countries, corporations, or individuals.
- Bitcoins in the millions of dollars’ worth can be carried around on small devices like USBs or mobile phones, making them ultra-portable. It is not possible to say the same about gold or cash.
- Bitcoin can be used to do so much more. It is not just a currency. There are countless ways that the Bitcoin network could be used.
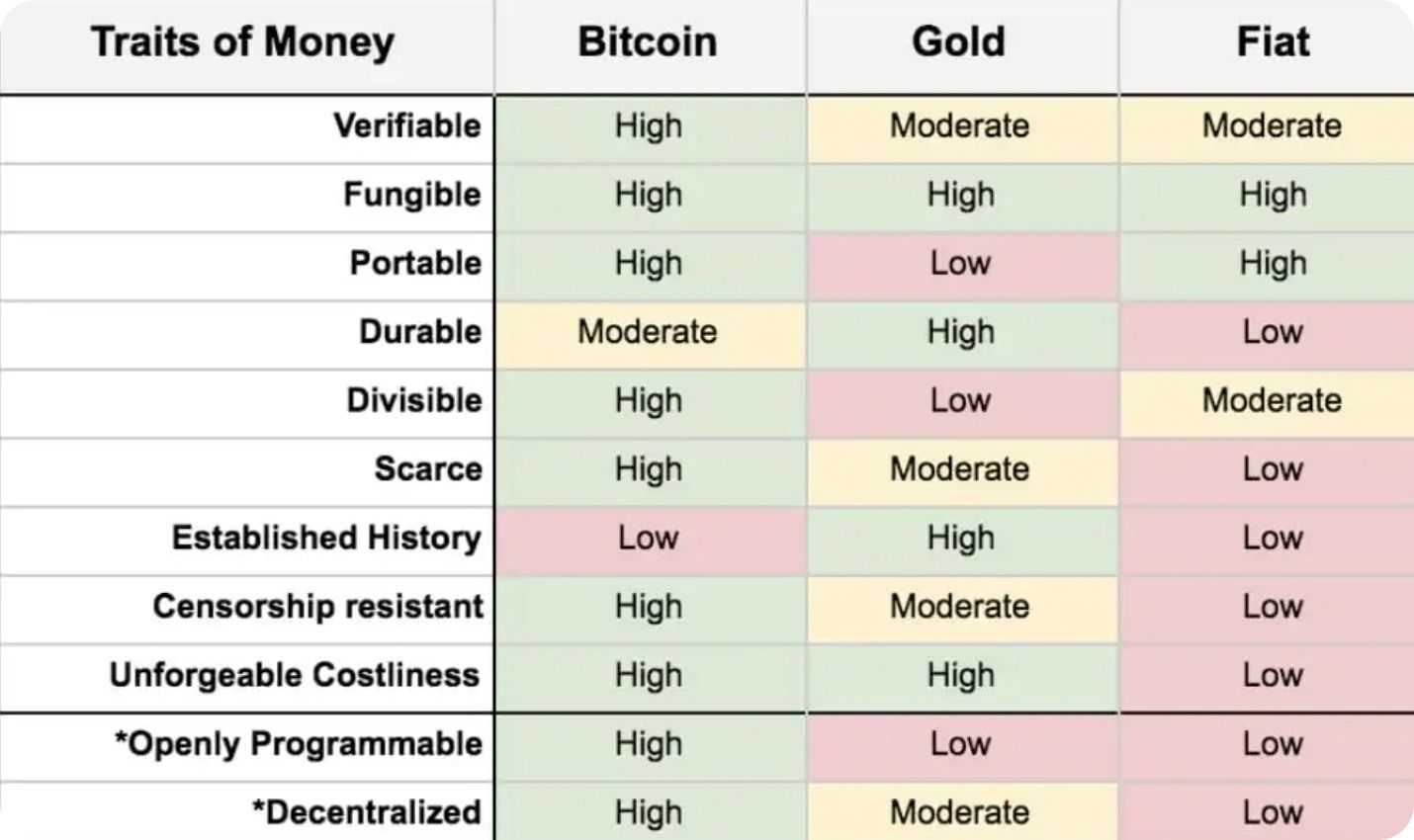
To be a valuable and viable asset, a currency must meet well-defined criteria. The criteria for a successful currency are:
- Durable
- When you are ready, download
- Divisible
- Uniform
- Scarce
It is easy to understand why Bitcoin is considered to be the superior currency when we compare it to other currencies.
Who Invented Bitcoin?
Search for "Who created Bitcoin?" you'll receive a mix of answers, so it's tricky to factually answer who created this digital currency and launched the Bitcoin Network.
Wikipedia says: "Satoshi Nakamoto (born 5 April 1975) is the name used by the presumed pseudonymous person or persons who developed Bitcoin, authored the Bitcoin white paper, and created and deployed Bitcoin's original reference implementation. As part of the implementation, Nakamoto also devised the first blockchain database. Nakamoto was active in the development of Bitcoin up until December 2010.
"There has been widespread speculation about Satoshi Nakamoto's true identity, with a variety of people posited as the person or persons behind the name. Though Nakamoto's name is Japanese, and he stated in 2012 that he was a man living in Japan, most of the speculation has involved software and cryptography experts in the United States or Europe."
(Source: Wikipedia)
Nobody truly knows Bitcoin's creator. Still, no matter who started Bitcoin, it's undisputedly a massive global network with a loyal Bitcoin community that believes in the future of Bitcoin and prioritizes freedom, self-sovereignty, and decentralized access to a monetary system that lives outside of authoritarian control. Since its inception, Bitcoin has attracted not only retail users but also institutional investors buying Bitcoin as the new digital gold.
If you are ready to buy Bitcoin and find out "What is Bitcoin?" let's dig in and find out more about Bitcoin.

As you are diving down the Bitcoin rabbit hole, you may consider further reading interesting:
- Can Bitcoin Become the World Reserve Currency?
- Bitcoin vs Gold: Which is Best?
How Does Bitcoin Work?
What made Bitcoin genuinely unique was its decentralised nature. Bitcoin is not controlled or overseen by any governing bodies or intermediaries. It is distributed across a peer-to-peer network of computers. Bitcoin transactions are private and anonymous between participants.
There are no bank accounts linked to an individual's name. Some people think Bitcoin transactions' anonymity is fantastic. Others, like governments, worry about criminal activity because individual identities cannot be tracked.
Bitcoin has revolutionised how people think about money and assets and was the foundation for the public becoming interested in cryptocurrencies. Today, Bitcoin transactions are commonplace. What was once a nascent idea considered a unique but useless hobby has gradually transformed the global financial system.
Many people worldwide believe that Bitcoin will do to finance what the internet did to the information system.
If you want to buy Bitcoin or sell Bitcoin, it may seem complicated if you are new to how Bitcoin works. Many organisations accept Bitcoin payments, and cryptocurrency transactions are becoming commonplace now.
What is Bitcoin supposed to do for finance, and how will it drive financial change in the future? These are tricky questions to answer because nobody can predict the future of blockchain technology or whether it could ever replace fiat currency.
Bitcoin's price has been an exciting roller coaster since it began in 2009. Today, as many cryptocurrencies have collapsed and failed beneath the ever-changing price volatility of the crypto market, Bitcoin is still the number one listed cryptocurrency.
Cryptocurrency and Digital Assets
Although Bitcoin is called a digital currency, that could seem slightly confusing because Bitcoin is not an asset in the traditional sense. It's not even a digital asset or file on your computer. OK. So what is a Bitcoin transaction? In simple terms, Bitcoin is a transaction record showing that someone sent you something of value. It's like a digital ledger.
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency that uses a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. That means Bitcoin is “mined” by a computer that devotes resources (electricity and processing power) to solve a complicated cryptographic problem called a "Hash Problem"
What is Proof of Work?
Bitcoin uses a Proof of Work Consensus model, meaning the Bitcoin network requires Bitcoin miners to spend their computational resources to validate transactions, construct Bitcoin blocks, and mine new units of Bitcoin. Miners are node operators using computational power to solve the hash problem.
"Proof of Work (PoW), also known as cryptographic proof, is a method of cryptographic verification in which a party (the prover), proves to another (the verifiers), that a particular amount of computational effort was expended. "
"Verifiers are able to confirm the expenditure with little effort. Moni Naor, Cynthia Dwork and others invented the concept in 1993 to prevent denial-of service attacks and other abuses of services such as spam."
"The term "proof of work" The term was coined by Markus Jakobsson in 1999 and formalized therein." (Source: Wikipedia)
If Wikipedia's explanation sounds too complicated, read our in-depth guide to the Proof of Work and Proof of Stakes concepts.
Alternatively, if you prefer, watch the video on the subject.
When Bitcoin began, it was easy for Bitcoin miners to validate a Bitcoin transaction and earn rewards. The Hash difficulty was 1, so Bob could set up a basic computer system with an internet connection in his garage and make a good living without frying his brain or PC.
Today, the hash difficulty is in the trillions. For example, in April 2023, the hash problem was almost 50 trillion.
The Bitcoin mining process is such that miners do not have to get the EXACT solution to the hash problem. The Bitcoin miner who gets closest to the solution receives a Bitcoin block reward. However, as the difficulty increases, so does the computational power requirements. Bob can no longer work in his garage on his PC because Bitcoin mining requires expensive, superior-quality CPU or ASIC computing.
Bitcoin is not a tangible asset, so it is tricky for many people to understand how to buy Bitcoin when it isn't a physical product. However, Bitcoin has undeniable value and can therefore be used as a currency. Like traditional currencies, you can send Bitcoin (BTC) to anyone worldwide.
If you want to send Bitcoin payments, there are some Bitcoin basics. You must first buy Bitcoin and transfer it to your secure Bitcoin wallet. Make sure you set up your digital wallet before starting.
If you are going to be buying Bitcoin, or any cryptocurrency, be sure you are using a reputable exchange. If you are looking for a step-by-step guide, we have a guide on How to Buy Bitcoin on Binance.
Some Bitcoin exchanges, such as Binance, Gate.io, and Coinbase, have self-custody wallets, or you could use a cold storage wallet like Trezor, one of the most popular offline wallets.
Once you have Bitcoin, You can send it to someone else by instigating a transaction from your wallet and public address to the recipient's wallet. This transaction is then confirmed by the miners and placed onto the Bitcoin blockchain.

The Bitcoin Blockchain
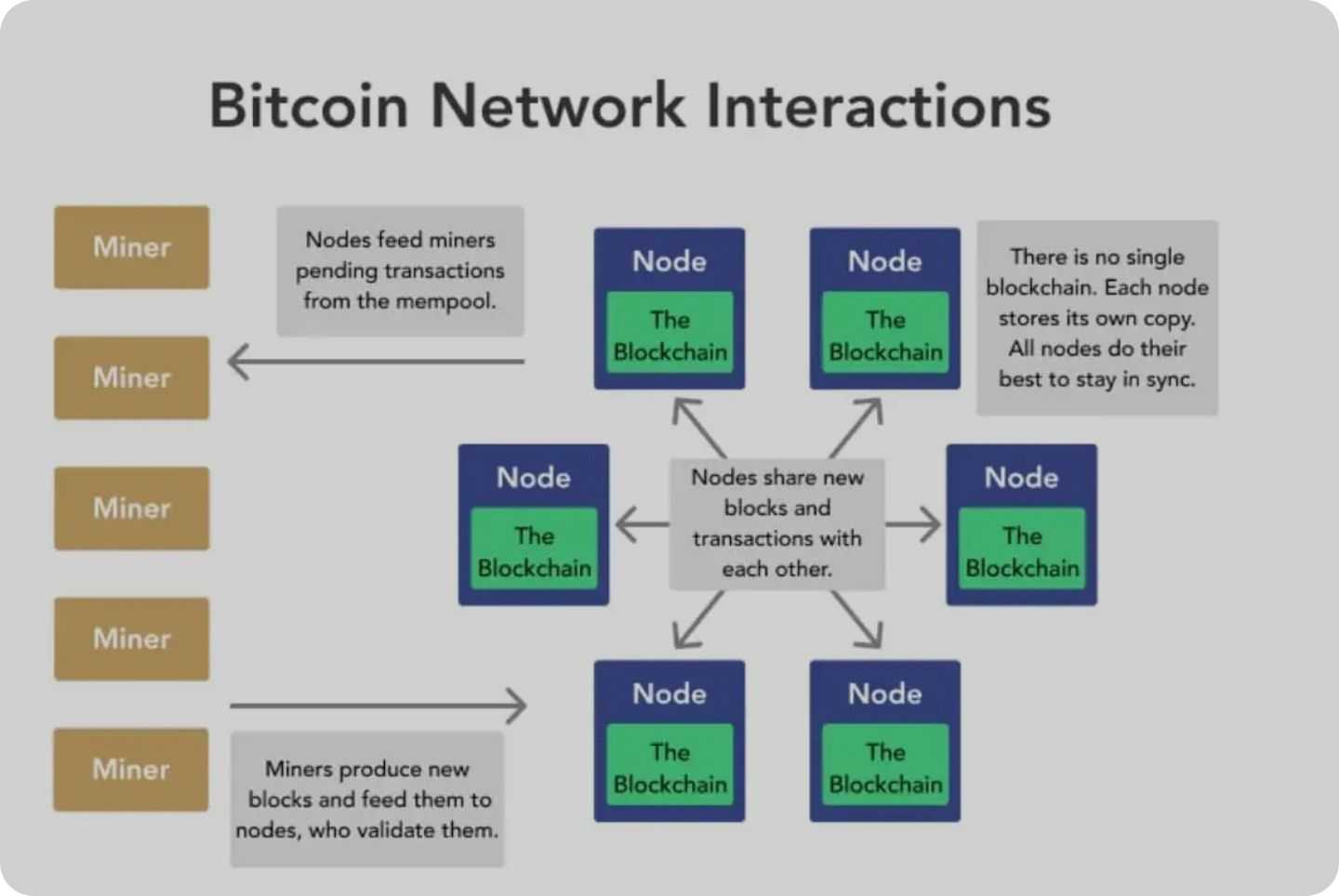
The Bitcoin blockchain is a decentralised ledger containing all transactions on the Bitcoin network since the beginning of time. Consider it as a sizeable accounting book with numerous debits and credits. Every single transaction on the Bitcoin network can be traced on the blockchain.
The blockchain is decentralised which means that it is not stored in one particular location. True to the nature of Bitcoin, the network nodes (computers) maintain the blockchain in the Bitcoin ecosystem. That means the blockchain is public, so anyone can view transactions on the network.
You can view the latest Bitcoin ledger on a blockchain explorer like blockchain.info
The decentralised ledger is called a “chain” because all newly created blocks link to previous blocks. Using advanced cryptographic principles, each block contains data about the prior blocks. That makes Bitcoin transactions immutable, a concept that eliminates the possibility of double spending.
Bitcoin Public Addresses
As mentioned previously, Bitcoin is anonymous. There are no Bitcoin accounts where you keep your money. No one can see the identity of an individual sending or receiving money. One person can send Bitcoin to someone else on the entire network by using their public Bitcoin address.
A Bitcoin address is a string of letters and numbers generated automatically from a wallet. An example is this 1PzNiHPM9iVRd2fBpqcMv78m5pgQsag3pn
Bitcoin addresses come in several formats, but they all identify a destination for Bitcoin transactions. The most common format for Bitcoin addresses is Base58, which begins with a "1" and consists of a string of letters and numbers. Bech32 is another format that starts with "bc1" and is designed to be more efficient and error-resistant than Base58. Alternatively, there is the Pay-to-Script-Hash (P2SH) format, which starts with "3" and is used for more complex transactions.
A digital wallet is a collection of files providing access to public addresses. It is unique to each wallet you have and can be used continuously or discarded once a payment is received. When this address is created, it generates a “cryptographic key pair” composed of a private key and a public key.
The private key is known to only you, and the public key is known to the whole network (your unique public address).
To simplify further, consider your public address as your mobile phone number. You happily give that number to your contacts. However, giving your private key address would be like giving someone your login details to your bank account.
Store your private keys address safe because if someone gained access to your virtual wallet, they could transfer your digital assets to their wallets, and you would not be able to recover the losses.
You will have different private and public keys for each wallet if you have more than one Bitcoin or virtual wallet.
When you send Bitcoin to someone else, the transaction needs to be cryptographically “signed” by your private key. The public key allows the network and the miners to verify the message is signed with the correct private key.
It is important to note that no one can forge your private key. It is linked to your public key using asymmetric cryptography and hash functions. The exact explanation is beyond this initial introduction, but all you need to understand is that it's impossible to replicate the private key. Even a small change to a factor in the private key will result in a completely different public key.
Similarly, the hash function that produces the public key from the private key is a one-way function. That means you can calculate the public from the private key, but there is no way of calculating it the other way.
One more stage of algorithmic hashing occurs on your public key before it is created into a human-readable Bitcoin address. The hashing function used in Bitcoin is an SHA 256 algorithm.
If it interests you, read more about cryptographic hash functions.
Bitcoin Security: How Safe is BTC?
One of the many concerns for new Bitcoin adopters is whether the blockchain is secure. What is to stop someone from double-spending their Bitcoins? What prevents a hacker from changing a transaction in the blockchain and assigning themselves more money?

Of course, security and trust go hand in hand. You cannot have a decentralised currency without all participants having 100% confidence in the network. Theoretically, the blockchain is entirely tamper-proof unless one party gains control of 51% of the network. This “rule of 51” is central to the Bitcoin protocol and was addressed in the original whitepaper by Satoshi.
In essence, if there is a disagreement about the structure of the blockchain, the network will override and choose the chain presented by the majority of the miners on the network.
With regards to a hacker being able to change a prior transaction and assign more Bitcoin to themselves, it is impossible due to the immutability of the blockchain. All blocks with transactions link to the previous blocks. This link uses a similar hashing function for the private and public keys.
Even a tiny change to a transaction in a previous block would result in a completely different blockchain than the established one. Hence, the miners would immediately notice that it's an incorrect blockchain and then revert to the one that most agree on.
People often wonder, “Is Bitcoin Safe?” We cannot predict Bitcoin's price, so we cannot know for sure from a price standpoint how future Bitcoin adoption will go. Another thing we have no control over is how safe Bitcoin will be from regulatory scrutiny. Virtual currencies like Bitcoin challenge the traditional financial system.
Governments worldwide may dislike the decentralised nature of Bitcoin transactions, and even the SEC (the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission) is continually trying to find loopholes to make digital assets like Bitcoin reclassified as a financial security. Should that happen, it could change everything.
From a technical perspective, we know that Bitcoin is the safest and most secure asset humanity has ever created. The code that runs the Bitcoin blockchain is “set in stone,” so to speak, and with the Bitcoin mining hash rate hitting all-time highs in 2022, the unbreakable code is infallible. As the saying goes, “code is law”, and Bitcoin's code is about as trustworthy as the laws of physics or thermodynamics.
You can learn more about crypto safety and, most importantly, how to use crypto securely in our Crypto Safety 101 article.
Bitcoin Mining Process
Bitcoin acts as digital gold for some, being a store of value, while others use it as a currency, as a way to transfer value like traditional currencies. People view Bitcoin as a safe haven asset and inflation hedge that is limited in supply and hence will always be in demand.
Like gold, Bitcoin must be mined to be created. However, Bitcoin mining is done by computers that solve complicated mathematical problems using brute-force computing. Once a Bitcoin mining computer or ASIC miner has solved the hash problem, they receive a Bitcoin block reward. This point is where new Bitcoins enter the supply.
It is also important to note that the Bitcoin supply has a maximum limit, capped at 21m BTC. Hence, Bitcoin is naturally deflationary. The network can also regulate the amount of Bitcoin being mined by adjusting the computational difficulty of the problems. As it gets more complex, it becomes more expensive to solve the hash problems and mine the Bitcoin.
You can understand that Bitcoin mining is comparable to mining for a natural resource. For example, when first mining gold, it is at the surface and easy to pull up. As miners dig for more gold, digging deeper is necessary, which adds costs. Eventually, gold supplied to the market will begin to slow down. Only a finite amount of gold on planet Earth can be mined.
Understanding Bitcoin: What is Inside the Block?
We have mentioned the Bitcoin blocks in the blockchain without explaining how the blocks are comprised. Bitcoin blocks hold all of the transaction information for a particular period. They also contain other data, such as a timestamp (identifying when a miner picked up the transaction) and a hash of the block before. Each block has a size limit of 1MB
Given that the current block has a hash of the block before, it is inextricably linked to that block. Hence, there can be no changes to the blocks prior without changing the structure of the entire hash function.
You may also wonder how the block can contain information about all prior blocks and remain within the size limits. It works through a cryptographic discipline called Merkle trees. This subject is beyond the scope of this post, but it can effectively hash together all transactions and efficiently store them within limits.
When a Bitcoin miner validates transactions and completes a block, they receive payment in Bitcoin for solving the problem and get the transaction fees for all transactions. It is important to note that these are Bitcoin already in circulation and won't impact Bitcoin supply.
The Costs of Using Bitcoin
Whenever you want to send funds on the Bitcoin network, you must pay a fee to incentivise the miner to confirm the transactions. However, this fee is normally quite low, especially when using Bitcoin's Lightning Network. Bitcoin transactions can be sent for fractions of the cost as we see from traditional banking systems and online payment processors.
When sending money online with an online merchant such as PayPal, your fees are usually about 2-3% of the transaction amount. With Bitcoin, when you send coins, you are typically charged about 0.1mBTC (1 thousandth of a Bitcoin) per 1,000 bytes.
Considering the average Bitcoin transaction size and number of transactions, you can get an idea of the total percentage of all volume paid in fees. Bitcoin fees for using the network are about 0.760%, much lower than fiat currency transactions with PayPal (May 2023).
You may be interested in the question of international payments abroad. If you've ever had to make a SWIFT payment, you will know how long it could take and how much it costs. Usually, a range of intermediary banks can facilitate the transactions.
Payments can take anywhere from 3-4 business days. In comparison, on the Bitcoin network, average confirmation times take minutes or even fractions of a second on the Lightning Network.

How Do You Buy Bitcoin?
Step #1: Choose a Reputable Cryptocurrency Exchange
When you are ready to buy Bitcoin (BTC), it's essential to choose a secure, established crypto exchange and one that has a user-friendly interface.
As a beginner, opting for a crypto exchange with a user-friendly interface, low fees, and robust security measures is advisable. For example, some leading platforms are Binance, Gemini, Coinbase, Kraken, and OKX.
Choose an exchange with an integrated Bitcoin wallet or open a separate digital wallet to store your Bitcoin.
There are also peer-to-peer Bitcoin platforms and non-custodial exchanges if you don't want to sign up for a centralized exchange.
Step #2: Choose a Secure Storage Solution
Many crypto exchanges offer integrated Bitcoin wallets or recommend trusted partners where you can securely store your Bitcoin. However, as most crypto exchanges are centralised, they have access to your wallet addresses by default. Therefore, you may prefer a cold storage solution, an offline digital wallet, for greater security.
To learn more about cold storage wallets, read "How do hardware wallets work?"
Step 3: Select Your Payment Method
You must first fund your account with a crypto exchange before you can purchase Bitcoin. The majority of platforms offer payment options, such as:
- Debit card
- Bank transfer
- Cryptocurrency
- Apple Pay or Google Pay
- Skrill & Neteller
Step #4: Place an Order for Bitcoin (BTC).
After you’ve transferred money to your account, and created a digital wallet you can purchase Bitcoin (BTC). Firstly, check Bitcoin's price with the crypto exchange and then look for the ticker symbol BTC.
You don't have to purchase one Bitcoin. You can select a monetary amount instead. For example, let’s say you have $180 available to spend and Bitcoin (BTC), which is worth $18,000, is the currency of choice. It’s no problem. If you buy $180 worth of Bitcoin (BTC), then you will own 1% of a Bitcoin.
It's easy to find how to buy Bitcoin on most crypto exchanges as there is usually a drop-down menu for cryptocurrencies. You select Bitcoin (BTC) then transfer it to the wallet address.
Step #5: Transfer Bitcoins to your digital wallet
The final step in acquiring Bitcoin (BTC) is to move it into a safe crypto wallet. Your Bitcoin (BTC), once you have followed the transfer instructions, will appear in your wallet.
What does the future hold for Bitcoin
It is fascinating to see how a global, self-governing currency decentralised by the government can transform our worldview. In the future, perhaps there won’t be any banks charging exorbitant charges. There may be no central banks that can devalue someone's money with inflation and quantitative easing.
But when it comes down to global disruption, blockchain technology can change the world. Many companies have already started using a decentralised blockchain to manage supply chain, raise money through crowdfunding, improve the security of their systems, etc.
There have also been many other cryptocurrency projects that have greatly improved upon the Bitcoin protocol and include more focus on privacy, like Monero, or smart contract technology like Ethereum.
Many Bitcoin enthusiasts feel that Bitcoin may someday become the world reserve currency and the ultimate hedge against inflation and store of value. In 2023, Bitcoin developers introduced Bitcoin Ordinals. This was the biggest event in cryptocurrency since the invention of Bitcoin.
What are the risks and benefits of investing in Bitcoin?
Bitcoin Investment: What are the risks?
- Volatility: Bitcoin’s high volatility is well-known. The value of Bitcoin can be subject to significant fluctuations in the short term. Bitcoin can be a risky investment because of its volatility, especially for inexperienced and conservative investors.
- Uncertainty in the regulatory environment: Changes in government regulations and policies may impact Bitcoin’s legality, acceptance, taxation or taxation. This could affect its value or investment prospects.
- Security concerns Bitcoin is a secure network, but individual investors may be susceptible to cyber attacks or phishing scams. To mitigate these risks, it is important to use reputable exchanges and wallets as well as safeguard your private keys.
- Absence of intrinsic value Market demand and investor sentiment determine Bitcoin's price. Bitcoin is not a traditional asset like stocks or real estate, as it does not have any underlying assets.
Bitcoin Investment Benefits:
- High-return potential: Bitcoin has shown the ability to generate substantial returns. Early investors made significant gains as Bitcoin's price increased over time. However, Bitcoin's historical price performance does not guarantee future returns.
- Decentralisation: Bitcoin is based on a blockchain, which is a decentralised system that cannot be controlled by a government or central authority. Decentralisation bypasses conventional banking systems, enabling borderless transactions.
- Portfolio diversification: Bitcoin's low correlation with traditional asset classes makes it an attractive option for diversifying investment portfolios.
- Accessibility worldwide: Bitcoin enables individuals to participate in the financial world without restrictions. It allows for cross-border payments with lower fees and quicker settlement times than traditional bank systems.
It's crucial to recognise that investing in Bitcoin carries risks. Its suitability as an investment option depends on an individual's risk tolerance, investment goals, and understanding of the cryptocurrency market.
It's advisable to conduct thorough research, seek professional financial advice, and invest only what you can afford to lose in such a volatile and evolving asset class.
How to store Bitcoin safely
Bitcoin owners should prioritize taking care of their Bitcoin. Here are some suggestions:
- Use a virtual wallet that is secure: You can store Bitcoin in a number of reputable digital wallets. Hardware wallets provide offline storage, and are considered to be the safest method.
- Protect your assets Use strong passwords, antivirus software and firewalls.
- Update your wallet software: Updates from wallet providers are often released to address vulnerabilities and enhance overall security.
- Keep your private key secure: Private keys will be crucial to accessing and controlling Bitcoin. Store them securely and offline.
- Avoid online storage Avoid storing large quantities of Bitcoins in online exchanges or wallets. Even the most reputable of exchanges may be susceptible to security breaches or hacking attempts.
- Consider using a multisignature wallet Additional security is provided by multiple signature wallets.
- Use the best practices outlined in our Crypto Safety 101 Article.
You can also read our conclusion.
You now hopefully understand Bitcoin (BTC), and how it operates. It may seem complicated initially, but armed with this new knowledge, you'll soon speak about Bitcoin like a pro.
Bitcoin has transformed the world we know. Bitcoin’s popularity continues to rise as traditional finance systems continue to collapse around the globe.
FAQs
How long does it take to mine one bitcoin?
The mining of one Bitcoin takes about 10 minutes.
Bitcoin – A Good Investment?
Only you know what makes a good investment. We do not act as financial advisors. Instead, we always advise you to seek independent investment advice.
Bitcoin investments have brought in a lot for many. Nevertheless, many people also lost a large amount of money.
What will $100 buy me in Bitcoins?
It depends on what the Bitcoin price is. Assume Bitcoin is $10,000. You could get 1% Bitcoin for $100.
How much should I invest in Bitcoin?
Bitcoins and other cryptocurrencies are high-risk investments. The golden rule when investing in any asset, is only to invest what you are comfortable with and what you’re willing to lose. Most investment managers suggest a portfolio that is diversified with an exposure of 1 to 5% in Bitcoin.
Wherever possible, always seek professional investment advice
Can You Turn Bitcoin into Cash?
Yes. Converting Bitcoin (BTC), into cash is much easier than it was a few short years ago. You can convert Bitcoin to “real” money. You can exchange it for fiat currency at some crypto-exchanges, through a Bitcoin ATM or via peer-to-peer transactions.
How do I buy Bitcoin?
- Select a Reputable Cryptocurrency exchange
- Select a Secure Storage Option
- Select Your Payment Option
- Place a Bitcoin Order (BTC).
- Transfer Bitcoins to your digital wallet
How can I store bitcoin safely?
Store your Bitcoins in a digital wallet that is secure. Transfer your BTC into a cold (offline), offline wallet.
What is Bitcoin Wallet? How do I create it?
Bitcoin wallets are virtual wallets that store your Bitcoin (BTC). Many reputable wallets such as Trust Wallet Exodus Ledger Nano Trezor Model T are available.
For more information, please read our article about the Best crypto wallets.
What is Bitcoin and other Cryptocurrencies difference?
Bitcoin has the biggest market share. The goal is to simplify and speed up transactions without any government restrictions.
There are more than 24,000 cryptocurrencies listed, but none has a market share as large as Bitcoin. They are known as altcoins which are Bitcoin’s alternatives.
Bitcoin is restricted to trading using BTC, but there are many other cryptocurrencies that can be used to make secure and low-cost trades. Most are used for more flexible purposes, such as purchasing goods and services.
Is Bitcoin Legal?
In most countries Bitcoin is legal, but not in all.
“The legal status of cryptocurrencies varies substantially from one jurisdiction to another and is still undefined or changing in many of them. Whereas in the majority of countries the usage of cryptocurrency isn’t in itself illegal, its status and usability as a means of payment (or a commodity) varies, with differing regulatory implications.
While some states have explicitly allowed its use and trade, others have banned or restricted it. Likewise, various government agencies, departments, and courts have classified cryptocurrencies differently. “(Source: Wikipedia)