Studying about blockchain expertise may be overwhelming. A blockchain is a end result of a number of applied sciences and networking processes that occur like clockwork and networked worldwide by way of the web. Don't fear, we'll break that down and simplify the important thing elements.
This text is a newbie’s information to understanding blockchain expertise. In case you are eager on studying about Web3, that is the primary academic piece it is best to consult with. This text will assist you to construct the muse for blockchain expertise with relatable ideas, so let's start.
Introduction: The Medici and Beginning of Trendy Bookkeeping
In the course of the Renaissance, a robust household in Florence, Italy, rose to prominence by way of their patronage of the humanities and a revolutionary strategy to finance. The Medici household, identified for his or her banking prowess, launched one thing that might change the world of commerce endlessly: the double-entry bookkeeping system. This technique, which meticulously recorded debits and credit, ensured their monetary dealings have been clear and accountable, decreasing errors and fraud. It was a game-changer, offering newfound belief in transactions.
The Medici's innovation laid the groundwork for contemporary monetary techniques, establishing the significance of a dependable ledger for recording transactions. However what if the Medici had entry to a ledger that was not simply dependable however incorruptible, one which could possibly be considered by any individual concerned within the transaction(or anybody, interval) and but safe from tampering? What if this ledger didn't simply exist in a single place however was distributed throughout an unlimited community of unbiased record-keepers?

Quick ahead to the twenty first century, and that is not a hypothetical situation. The Medici's ledger has advanced into what we now name blockchain expertise. Blockchain takes the ideas of the double-entry ledger to an entire new stage, utilizing superior cryptography and decentralization. It's a system the place transactions aren’t simply recorded but in addition verified by an unlimited community of computer systems, making a clear, immutable report that's nearly impervious to fraud. That is the essence of blockchain, a expertise poised to revolutionize how we take into consideration and deal with digital transactions, very like the Medici household did for banking throughout the Renaissance.
From Double-Entry Bookkeeping to Blockchain Know-how
The Medici household’s double-entry bookkeeping system was one of many first evolutionary milestones in finance. It was the primary concept that laid down a systemic strategy to monitoring the possession and switch of property. The Medici bookkeeping techniques have been mixed with numerous applied sciences and refined over time with a number of sensible and conceptual improvements that led to the start of blockchain expertise. Right here’s a timeline of this evolution:
- Double-Entry Bookkeeping (14th-Fifteenth Century): The Medici household, amongst others in Renaissance Italy, adopted the double-entry bookkeeping system, which information every transaction in two accounts: debits in a single and credit in one other. This technique offered a transparent, organized methodology to trace the cash stream and helped cut back errors and fraud.
- The Creation of Computer systems (twentieth Century): With the invention of computer systems, accounting techniques have been digitized, permitting for quicker processing, storage, and retrieval of economic transactions. This was the primary main step in transferring away from bodily ledgers to digital ones.
- Cryptography (Nineteen Seventies-Eighties): The event of uneven cryptography, or public-key cryptography, allowed for safe communication over insecure channels and gave rise to digital signatures. This meant that transactions could possibly be securely verified while not having bodily presence or belief in a government.
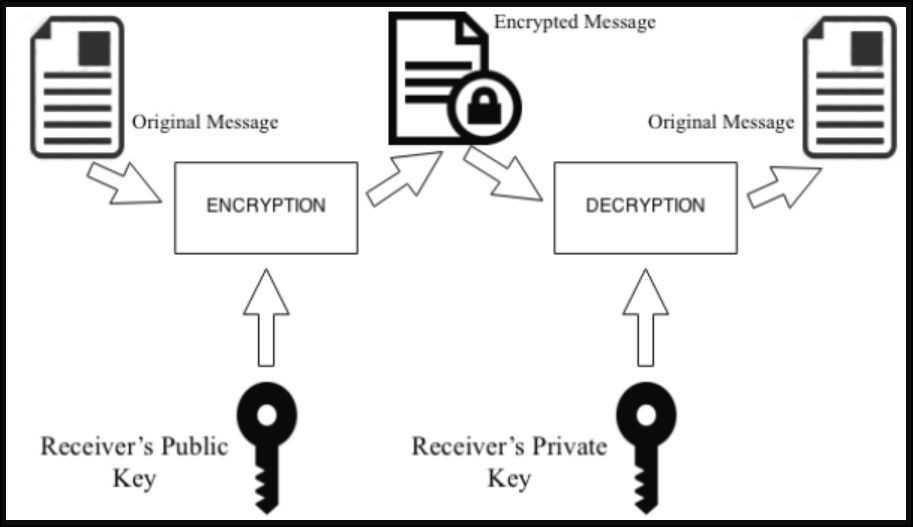
- The Web (Nineteen Nineties): The widespread adoption of the Web reworked the best way information was shared and communicated, setting the stage for international, immediate, and interconnected techniques of commerce and communication.
- Cryptographic Hash Features and Merkle Timber (Late twentieth Century): These applied sciences offered the means to confirm massive units of knowledge effectively and securely. Merkle bushes, specifically, allowed for fast information verification inside massive datasets, which might turn out to be a crucial part of blockchain expertise.
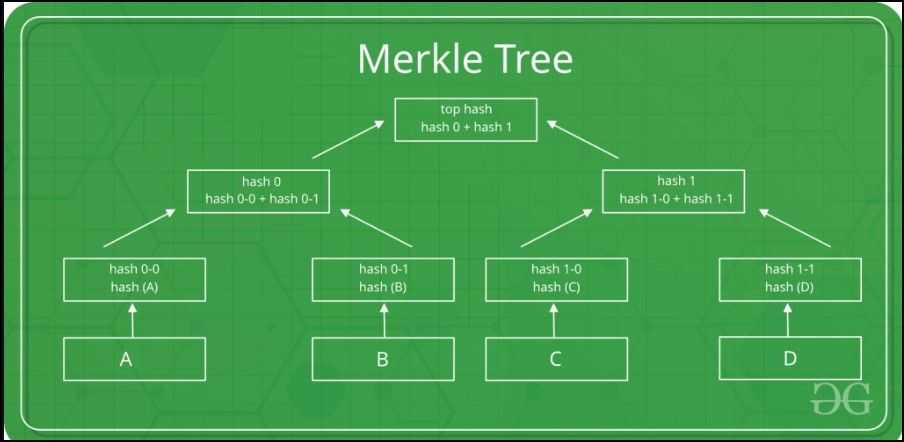
- Peer-to-Peer Networks (Late twentieth Century): The event of P2P networks for file sharing, like Napster and BitTorrent, demonstrated that distributed techniques may function with out centralized management, with every node within the community appearing as each a consumer and a server.
- Digital Foreign money Experiments (Nineteen Nineties-2000s): Numerous makes an attempt at creating digital currencies, equivalent to b-money and Bit Gold, launched ideas of making, distributing, and verifying digital cash with no central issuing authority. These techniques, nevertheless, didn’t resolve the double-spending drawback.
What’s the Double Spending Downside?
The double-spending drawback is a big problem with digital currencies. Not like bodily cash, which is tangible and can’t be simply duplicated, anybody can copy digital tokens. In a digital foreign money system, if safeguards aren’t in place, the identical digital token could possibly be copied and utilized in a number of transactions, undermining the belief and integrity of the foreign money.
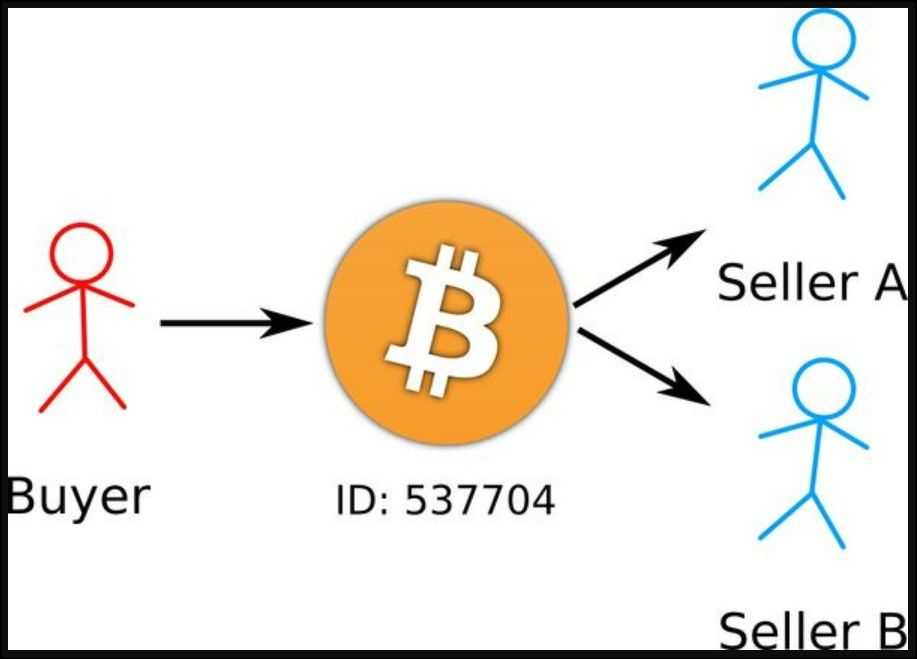
In conventional banking techniques, central authorities (like a financial institution) mitigate this situation. They preserve a ledger of account balances and transactions. This central authority verifies every transaction to make sure that the identical cash isn't spent greater than as soon as. For a decentralized foreign money like Bitcoin, the place there isn’t any central authority to confirm transactions, fixing the double-spending drawback is extra advanced. The system wants a method to agree on the validity and order of transactions to make sure that every unit of the foreign money is simply spent as soon as.
Proof-of-Work/Consensus Algorithms (2000s)
The idea of proof-of-work, initially proposed to discourage spam emails, was tailored to create a consensus mechanism that would safe a decentralized community and resolve the double-spending drawback by guaranteeing that every transaction is simply counted as soon as.
Bitcoin: The First Blockchain (2008)
Satoshi Nakamoto mixed these improvements to create Bitcoin, which encompasses a safe, decentralized ledger of transactions. This ledger, or blockchain, was maintained throughout a number of nodes in a community with no central authority. It was a breakthrough in recording, verifying, and trusting monetary transactions.
The Bitcoin Community is a distributed ledger the place all transactions are recorded chronologically and publicly. Transactions are grouped into blocks, and every block is linked to the earlier one, creating a series. Blockchain community members (miners) resolve advanced mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain. As soon as a block is added, altering it turns into computationally impractical, securing the ledger in opposition to double-spending.
With the Bitcoin community, a decentralized ledger may lastly help irreversible transactions. As soon as a transaction is confirmed and added to the blockchain, it turns into irreversible. This immutability ensures that after a digital token is spent, it can’t be spent once more, successfully fixing the double-spending drawback in a decentralized setting. If you wish to study extra about Bitcoin, you should definitely take a look at our in-depth Bitcoin 101 Information.
What’s a Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that information transactions throughout a number of computer systems(nodes) in a method that ensures safety, transparency, and immutability. It employs cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms, equivalent to Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, to take care of information integrity and forestall unauthorized alterations. Every report, or 'block,' is linked to earlier ones, forming a chain, thereby making the historical past of all transactions completely seen and verifiable by all members.
Let’s break down every highlighted key phrase:
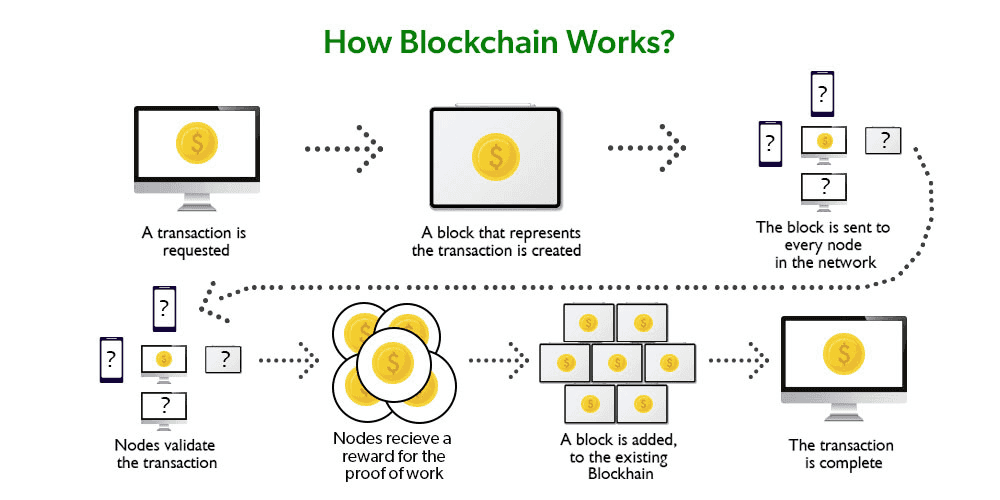
- Blockchain: A blockchain is a system of recording info in a method that makes it tough or inconceivable to alter, hack, or cheat the system. It’s a digital ledger of transactions that’s duplicated and distributed throughout the whole community of laptop techniques on the blockchain.
- Decentralized: Within the context of blockchain, decentralization refers back to the switch of management and decision-making from a centralized entity (particular person, group, or group thereof) to a distributed community. This ensures that no single entity has full management over the whole community.
- Distributed Ledger Know-how (DLT): This can be a digital system for recording the transaction of property during which the transactions and their particulars are recorded in a number of locations concurrently. Not like conventional databases, distributed ledgers haven’t any central information retailer or administration performance.
- Transactions: In blockchain, transactions are the actions carried out in a blockchain community, such because the switch of worth, info, or rights. These transactions are grouped and recorded in blocks.
- Nodes: A node refers to a pc related to the blockchain community. Every node has a replica of the whole blockchain ledger and participates within the community's propagation. Nodes are accountable for validating and relaying transactions, contributing to the consensus course of, and sustaining the integrity and safety of the blockchain. They make sure the decentralization of the community, as every node operates independently and has equal authority to confirm and report transactions.
- Safety: Within the blockchain context, safety refers back to the numerous cryptographic methods and blockchain structure used to make sure that transactions are securely recorded on the blockchain and the community is immune to hacking and fraud.
- Transparency: Transparency in blockchain expertise implies that each transaction is publicly recorded within the ledger and may be seen by all community members, making every part within the blockchain traceable and auditable.
- Immutability: Immutability within the blockchain implies that as soon as a transaction has been recorded within the distributed ledger, it can’t be altered or deleted. This can be a elementary function that ensures the integrity of the blockchain and the permanence of the information recorded.
- Cryptographic Hashing: This can be a course of by which a selected algorithm transforms enter information of any dimension right into a fixed-size string of characters, which is normally a sequence of numbers. This hash is exclusive to the particular information enter, making it a safe method of representing transactions on the blockchain.
- Consensus Mechanisms: These protocols guarantee all nodes are synchronized with one another and agree on the true state of the distributed ledger. Examples embody Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
- Proof of Work (PoW): A consensus mechanism that requires a participant node to unravel a tough computational drawback with a purpose to add a brand new block to the blockchain. This mechanism is used to verify transactions and produce new digital currencies.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): An alternative choice to Proof of Work, this consensus mechanism permits an individual to validate block transactions primarily based on the variety of cash the participant holds. Which means that the extra cash owned by a miner, the extra mining energy they’ve.
- Knowledge Integrity: Within the blockchain, this refers back to the accuracy and consistency of knowledge over its lifecycle. It ensures that information shouldn’t be altered or tampered with.
- Block: A block, within the context of blockchain, is a set of recorded transactions which might be mixed right into a single, cryptographically safe unit.
- Chain: In blockchain, a series refers to a sequence of blocks in a selected order. Every block incorporates a reference to the earlier block, linking them collectively in a chronological and unbreakable chain.
- Verifiable: This means that the information recorded within the blockchain may be independently verified by any participant of the community, guaranteeing belief and accuracy within the recorded info.
Well-liked Proof of Work (PoW) blockchains embody likes of Bitcoin, Monero, Litecoin and others, whereas examples of notable Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchains are Solana, NEAR, Avalanche, Ethereum and Cardano. Now we have an article explaining Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake intimately if you want to study extra.
A Bitcoin Community Cycle
The Bitcoin community employs the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. Right here's an in depth step-by-step rundown of the method:
- Transaction Initiation: Customers provoke transactions by sending Bitcoin to a different person's pockets handle. Every transaction incorporates the sender's and receiver's pockets addresses, the quantity of Bitcoin being transferred, and a digital signature created by the sender’s personal key.
- Transaction Broadcast: As soon as created, the transaction is broadcast to the Bitcoin community. Nodes within the community (any laptop with the Bitcoin software program and the whole copy of the blockchain) obtain and confirm the transaction. They test the digital signature and make sure the sender has enough steadiness.
- Transaction Pooling: Verified transactions are pooled collectively within the reminiscence pool (mempool). The mempool is a kind of holding space for transactions awaiting inclusion in a block.
- Block Formation: Miners (particular nodes) choose transactions from the mempool to kind a brand new block. Miners usually prioritize transactions with increased charges. Every block has a hard and fast capability, so not all transactions within the mempool could also be included within the subsequent block.
- Proof of Work: So as to add a block to the blockchain, miners should resolve a fancy mathematical drawback (PoW). This includes discovering a hash (consider it as the answer to the mathematical drawback that must be correct as much as sure decimal locations) that’s beneath a selected goal worth. The method is computationally intensive and requires important processing energy.
- Block Verification: As soon as a miner efficiently solves the PoW drawback, the brand new block is broadcast to the community. Different nodes within the community confirm the answer and the validity of the transactions within the block (e.g., guaranteeing no double-spending).
- Including the Block to the Blockchain: After verification, the brand new block is added to the present blockchain. Every block incorporates a reference to the hash of the previous block, creating a series of blocks. This linkage ensures the safety and immutability of the blockchain.
- Rewarding the Miner: The miner who efficiently provides a block to the blockchain is rewarded with newly created Bitcoins (block reward) and transaction charges. This incentivizes miners to contribute their computational energy to the community.
- Community Replace: As soon as the block is added, the up to date model of the blockchain is propagated all through the community. Every node updates its copy of the blockchain, sustaining the community’s consistency and integrity.
- Continuation: The method repeats for the creation of each new block, roughly each 10 minutes. Miners repeatedly choose new transactions from the mempool, and the cycle of fixing the PoW, block verification, and addition to the blockchain continues.
This consensus course of ensures that each one transactions on the Bitcoin community are verified and recorded securely, sustaining the decentralized, clear, and immutable nature of the blockchain.
From Bitcoin to Web3
Bitcoin is essentially a peer-to-peer (P2P) community. Its main function is to facilitate BTC transactions between events whereas sustaining decentralization and permissionlessness. Because the Bitcoin blockchain is designed for fundamental monetary transactions, it doesn’t inherently help a system of advanced programmable logic, or good contracts.
A programmable logic would let customers create transactions which might fulfil solely when sure predetermined circumstances are met, permitting them to program when a transaction will get executed. Bitcoin, subsequently, doesn't align straight with the idea of "Web3". Whereas it launched the thought of decentralized transactions and impressed the event of blockchain expertise, it doesn’t embody the broader functionalities related to Web3.
Inspiration for Sensible Contracts and Web3
Web3, sometimes called the third era of the web, is a imaginative and prescient of a decentralized on-line ecosystem primarily based on blockchain. Not like the present web (Web2), the place information and content material are largely managed by centralized entities (like large tech firms), Web3 envisions a user-centric web with decentralization, openness, and better person utility and management.
Ethereum, created by Vitalik Buterin and others, prolonged the blockchain idea past Bitcoin’s scope. It launched a platform the place builders can construct decentralized purposes (DApps) and good contracts, setting the stage for extra advanced interactions than simply cryptocurrency transactions. The success of Ethereum confirmed that blockchain expertise has purposes far past monetary transactions. It may be used for decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), and extra, embodying the ethos of Web3.
Sensible contracts have been pivotal on this evolution. They permit advanced agreements and automatic, trustless interactions in a decentralized setting, that are crucial for the varied functionalities envisioned in Web3.
Sensible Contracts and Ethereum
A wise contract is a self-executing contract with the phrases of the settlement between purchaser and vendor being straight written into traces of code. The code and the agreements contained therein exist throughout a distributed, decentralized blockchain community. The important thing traits and functionalities of good contracts embody:
- Automated Execution: Sensible contracts routinely execute, management, or doc related occasions and actions in response to the phrases of a contract. The code triggers the execution of the contract's clauses when pre-defined circumstances are met.
- Decentralization: Since they’re deployed on a blockchain, good contracts inherit the properties of the expertise, together with decentralization. This implies no single celebration has management over the execution of the contract, decreasing the chance of manipulation, fraud, or interference.
- Transparency and Immutability: As soon as a wise contract is created, it’s clear to all events concerned and can’t be modified (immutable). This transparency ensures that each one events perceive the contract phrases and can’t dispute the programmed actions as soon as triggered.
- Safety: Sensible contracts use cryptographic safety inherent in blockchain expertise, making them safe and tamper-proof. That is essential for belief in transactions and agreements.
- Effectivity and Velocity: They will considerably cut back the effort and time concerned in conventional contract processes, eliminating the necessity for intermediaries and decreasing paperwork.
- Price-Efficient: Sensible contracts take away the necessity for intermediaries, equivalent to legal professionals and banks, doubtlessly decreasing transaction prices.
- Accuracy: By automating processes and decreasing handbook intervention, good contracts decrease the chance of errors which might be frequent in conventional contract processing.
Sensible contracts have a variety of purposes, together with in finance (like automated loans or insurance coverage contracts), provide chain administration, digital identification, authorized processes, and extra. Pc scientist Nick Szabo first proposed the idea within the Nineteen Nineties, but it surely was the event and implementation of blockchain platforms like Ethereum that introduced good contracts into sensible use.
Sensible contracts are thought-about revolutionary as, for the primary time in human historical past, people have the flexibility to enter into an settlement that doesn’t require belief within the opposing celebration nor require any third-party intermediaries to facilitate the method. This ends in contract fulfilment being much more environment friendly, cheaper, and eliminates the necessity to belief the events concerned as execution is autonomous. This reduces the chance of unhealthy actors and fraudulent contractual agreements.
Ethereum
Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain system that includes good contract performance. Launched in 2015, it extends past Bitcoin's main perform as a digital foreign money, offering a platform for constructing decentralized purposes (DApps). Ethereum's native cryptocurrency is Ether (ETH). It revolutionizes blockchain capabilities by providing a versatile setting for growing a variety of purposes, leveraging the safety and decentralization of blockchain expertise. Key improvements of Ethereum over Bitcoin are:
- Sensible Contract-Powered EVM: Ethereum operates utilizing the Ethereum Digital Machine (EVM), a robust, decentralized computational engine. The EVM interprets and executes good contracts. The EVM setting permits builders to create all kinds of decentralized purposes (DApps) on Ethereum’s platform, from monetary providers and video games to advanced information administration techniques. Sensible contracts on Ethereum are extremely programmable, autonomous, and work together seamlessly with different contracts and DApps.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Ethereum has transitioned to a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, referred to as Ethereum 2.0. Not like Proof of Work (PoW), utilized in Bitcoin, PoS doesn't require energy-intensive mining. Validators are chosen to create new blocks and validate transactions primarily based on the quantity of cryptocurrency they maintain and are keen to "stake" as collateral. PoS provides elevated power effectivity, quicker transaction processing, and enhanced scalability in comparison with PoW.
- Subsequent-Gen Blockchain with Programmable Execution Layer: Ethereum represents a big evolution from Bitcoin, typically considered "Blockchain 2.0". Whereas Bitcoin's blockchain primarily information monetary transactions, Ethereum's blockchain capabilities as a programmable, execution layer. This layer is the place the good contracts function, providing a platform the place builders can write and deploy code that executes routinely underneath particular circumstances. This programmable layer, sitting atop the consensus mechanism, opens limitless prospects, reworking Ethereum right into a foundational expertise for decentralized purposes and future blockchain improvements.
It’s a crude comparability that isn't precisely correct and never everybody agrees, however to assist wrap your head across the variations between Bitcoin and Ethereum, many customers really feel it’s useful to think about Bitcoin as digital gold whereas Ethereum is extra akin to the web. Bitcoin is a retailer of worth and cost system, whereas Ethereum is trying to help the following evolution of the web. Some additionally consult with Etehreum as “digital oil” because it basically runs the Web3 world just like how oil runs the bodily machines and engines we use each day.
Parting Ideas
As we conclude this newbie's information to blockchain expertise, it’s necessary to acknowledge the monumental shift this innovation has introduced into the digital world. From Medici's double-entry bookkeeping to the subtle blockchain networks of as we speak, we’ve witnessed a exceptional evolution in how transactions and information are managed. Blockchain expertise, with its promise of decentralization, transparency, and safety, isn’t just a technological development; it’s a paradigm shift in how we understand belief and alternate worth within the digital age.
For freshmen getting into the world of blockchain, keep in mind that this journey is akin to exploring a brand new frontier. The ideas of cryptocurrencies, good contracts, and decentralized purposes are only the start. As blockchain expertise continues to evolve, it’ll undoubtedly current new alternatives and challenges. The potential for blockchain to revolutionize industries is immense, however so is the necessity for accountable and knowledgeable engagement with this expertise.
Your exploration of blockchain isn’t just about understanding a brand new expertise; it's about envisioning new methods during which we will construct a extra clear, environment friendly, and equitable digital future.
Loved this content material? If you wish to hear extra from us and get up-to-the-minute updates and behind-the-scenes content material, be happy to take a look at our socials channels, Discord, and Useful resource Hub.
Continuously Requested Questions
What’s Blockchain Know-how?
Blockchain expertise is a decentralized, distributed ledger that information transactions throughout a number of computer systems. This ensures that every transaction is safe, clear, and immutable. Using cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, blockchain maintains information integrity and prevents unauthorized alterations, making each transaction completely seen and verifiable by all community members.
How Does Blockchain Clear up the Double-Spending Downside?
Blockchain solves the double-spending drawback by way of its decentralized ledger and consensus mechanisms. Transactions are grouped into blocks, verified by community members, and added to the blockchain. As soon as a transaction is recorded, it is irreversible and can’t be duplicated, guaranteeing that digital tokens can solely be spent as soon as, sustaining the foreign money’s integrity.
What Makes Ethereum Totally different from Bitcoin?
Whereas Bitcoin is primarily a digital foreign money, Ethereum extends past this by offering a platform for decentralized purposes and good contracts. Ethereum’s blockchain capabilities as a programmable layer, permitting builders to create purposes that automate advanced processes. This positions Ethereum as a foundational expertise for a variety of decentralized options.
What are Sensible Contracts?
Sensible contracts are self-executing contracts with the phrases written straight into code on the blockchain. They routinely execute and management legally related actions or occasions in response to the contract phrases when predetermined circumstances are met. This automation provides a safe, clear, and environment friendly method to facilitate agreements with out intermediaries.
What’s the Significance of Proof of Stake in Blockchain?
Proof of Stake (PoS) is a consensus mechanism that selects validators to create new blocks and validate transactions primarily based on the quantity of cryptocurrency they maintain and stake. This methodology is extra energy-efficient than Proof of Work, utilized in Bitcoin, and permits for quicker transaction processing and enhanced scalability, making blockchain networks extra sustainable and environment friendly.