For those who're beginning to discover blockchain know-how, chances are high the primary two names you'll come throughout are Bitcoin and Ethereum. Collectively, these two giants maintain nearly all of worth within the blockchain business.
Bitcoin, as essentially the most useful asset within the area, is constructed to guard that standing. Its community capabilities like SWIFT, offering a peer-to-peer system for transferring Bitcoin and sustaining an unchangeable file of BTC transactions. However whereas Bitcoin focuses on being a digital asset, Ethereum is constructed to be far more than only a token switch system.
A useful manner to consider Ethereum is to think about it as a worldwide laptop—just like the one you're utilizing proper now. Ethereum's protocol permits customers to run packages and carry out numerous operations, providing a platform for decentralized purposes (DApps) and sensible contracts. In actual fact, Ethereum's innovation on this space laid the inspiration for the rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), Actual World Belongings (RWAs), Decentralized Bodily Infrastructure Networks (DePINs), Non-Fungible Tokens, and nearly each different use case you possibly can think about inside Web3 at present.
Coin Bureau reviewed Ethereum again in 2021. Since then, the community has developed by means of main updates which have considerably shifted its capabilities. That’s why, we’re revisiting Ethereum to make sure the blockchain neighborhood, particularly newcomers, has a full understanding of what Ethereum represents at present.
👉 Purchase ETH through BloFin
👉 Purchase ETH through Bybit
What’s Ethereum?
Having a primary understanding of blockchain know-how and the Bitcoin community shall be extremely helpful as we delve into the ideas surrounding Ethereum. This foundational information will make it easier to grasp how Ethereum builds upon and differentiates itself from earlier blockchain applied sciences like Bitcoin.
At its most basic degree, Ethereum is a blockchain community. It operates as a public database that may be a huge community of computer systems, referred to as nodes, that updates and maintains collectively in actual time. Ethereum periodically information and updates this database's state in models referred to as blocks, every referencing its predecessor to kind a steady chain referred to as the blockchain. To make sure all nodes agree upon the state of the blockchain, Ethereum employs a consensus mechanism referred to as Proof of Stake (PoS).
Broad Use Instances of the Ethereum Community
A Peer-to-Peer Community and Decentralized Ledger
The Ethereum community options Ether (ETH) as its native cryptocurrency. Just like how Bitcoin operates, Ethereum allows peer-to-peer (P2P) transfers of Ether, permitting customers to ship and obtain worth with out intermediaries. The first position of the Ethereum protocol on this context is to facilitate these P2P transactions and keep the community by compensating nodes—validators—with ETH by means of its financial coverage. Ether's utility inside Ethereum mirrors Bitcoin's utility inside its personal community, serving as each a medium of trade and a reward for individuals who assist safe the community.
A Decentralized, Censorship-Resistant Laptop
Past easy worth transfers, the Ethereum community capabilities as a single, canonical laptop referred to as the Ethereum Digital Machine (EVM). Nodes can request the EVM to carry out arbitrary computations, which each taking part node executes to confirm the computation's correctness. The blocks include details about the operations carried out throughout their interval, and the consensus course of ensures each node has the identical copy of the outcomes, referred to as the frequent block state.
These computation requests devour assets and are paid for utilizing a metered system referred to as gasoline. Fuel charges are measured and paid in denominations of Ether. This mechanism ensures that the community stays environment friendly and prevents abuse of computational assets. Importantly, the complete operation is censorship-resistant; so long as you’ve got an web connection, nobody can stop you from interacting with the community. Cryptographic mechanisms make sure that as soon as transactions are verified as legitimate and added to the blockchain, they can’t be altered or tampered with later.
A Supply of Credible Block Area
Whereas Ethereum has at all times supplied block area for transactions and computations, it has not too long ago emerged as a monetized useful resource throughout the ecosystem. Ethereum's block area is taken into account one of the crucial credible, decentralized, and safe chunks of knowledge area out there, second solely to Bitcoin. This credibility stems from Ethereum's in depth validator community and its substantial financial assets, collectively guaranteeing its safety. The shortage of block area additionally ensures its optimum use.
Different blockchain networks can leverage Ethereum's credible block area to run their operations in a sandbox surroundings throughout the Ethereum community. This permits them to learn from Ethereum's safety and decentralization with out constructing and securing their very own networks from scratch.
Ethereum's Use Instances
These use instances spotlight the transformative potential of Ethereum, enabling:
- Censorship-Resistant Networking and Cash: Customers can transact and work together with out worry of interference or censorship from central authorities.
- An Open Web: Ethereum helps the event of decentralized purposes (DApps), fostering an Web the place information and providers are open and accessible.
- A Base for Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Ethereum's sensible contract capabilities underpin numerous monetary providers that function with out conventional intermediaries.
- Composable On-line Merchandise: Builders can construct modular purposes that interoperate seamlessly, encouraging innovation and collaboration throughout the ecosystem.
In essence, Ethereum is greater than only a cryptocurrency; it's a flexible platform that empowers customers and builders to create and take part in a decentralized digital financial system.
Elementary Ideas in Ethereum Protocol
Listed below are some foundational matters in regards to the Ethereum protocol that may assist construct important context for extra complicated discussions additional into the piece:
Ether (ETH)
Ether (ETH) serves because the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum protocol, very similar to Bitcoin (BTC) does for the Bitcoin community. Nonetheless, Ether's goal extends past being a retailer of worth; it powers an ecosystem of decentralized purposes, sensible contracts, and monetary devices.

Ether and Bitcoin: Related Foundations, Totally different Functions
Simply as Bitcoin maintains a canonical and immutable ledger of BTC transactions, Ethereum does the identical for Ether. "Canonicity" refers to the concept the blockchain's file of Ether transactions is the one true file, accepted throughout the complete community. As soon as a transaction is confirmed, it turns into a part of Ethereum’s immutable ledger, which means it can’t be altered or erased. This immutability is essential, because it ensures belief within the system, making certain that nobody can tamper with Ether transactions or manipulate balances.
For instance, think about a shared doc the place modifications can solely be added however by no means deleted or edited; everybody studying the doc can see the whole historical past. This high quality makes Ether transactions clear and immune to fraud, forming the spine of belief in Ethereum’s ecosystem.
Ether because the Medium of Trade inside Ethereum
On Ethereum, Ether is greater than only a foreign money—it’s additionally a community trade medium. To know this, think about Ethereum as a worldwide laptop, the Ethereum Digital Machine (EVM), which processes sensible contracts packages. Operating these packages requires computational energy, and identical to working any machine, it prices a payment, referred to as gasoline.
Fuel charges, which measure the computational work required for transactions, are paid to validators in Ether. These validators, the contributors who confirm and safe transactions on the community, earn ETH in return for his or her work. For instance, for those who provoke a transaction or work together with a sensible contract, a small quantity of Ether is paid as gasoline, compensating validators and making certain the community runs easily.
Ether’s Financial Coverage: Inflation and Burning
Ethereum’s financial coverage consists of each inflationary and deflationary components. When a brand new block is created, new models of Ether are minted, contributing to a managed inflation fee. Nonetheless, Ether additionally has a mechanism to counterbalance inflation—transaction charges, or a portion of gasoline charges, are "burned" or completely faraway from circulation.
"Burning" is a course of the place a certain quantity of Ether is destroyed by sending it to an handle and not using a non-public key. Relying on the quantity of community exercise, this burning mechanism can scale back the full provide of Ether over time. We’ll discover this burning mechanism additional in a later part, the place we’ll cowl its long-term impression on Ethereum’s financial system.
Ether as a Software for Community Safety
Securing the Ethereum community requires contributors to pledge a few of their Ether as a stake within the community, which acts as a deterrent towards malicious habits. Validators should lock up a specific amount of Ether in a course of referred to as staking. By doing so, they’ve a vested curiosity within the community’s success and integrity, as they danger shedding their staked Ether in the event that they act dishonestly or try to disrupt the community.
Consider it as a deposit in a high-stakes recreation; contributors danger shedding their deposit in the event that they play unfairly. This staking mannequin is key to Ethereum’s Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus, which we’ll discover in additional element later.
Denominations of Ether: Wei and Gwei
Ether will be divided into smaller models, permitting for exact transactions even when coping with fractions of ETH. Two frequent denominations are:
- Wei: The smallest unit of Ether, equal to 1 quintillionth (10^-18) of an ETH. If we examine Ether to a greenback, Wei can be like a single cent however on a a lot smaller scale.
- Gwei: Usually used for gasoline charges, Gwei represents one billion Wei or 10^-9 ETH. Once you see gasoline costs quoted, they’re sometimes expressed in Gwei for comfort. As an illustration, if the gasoline payment for a transaction is 20 Gwei, it’s really referring to twenty billion Wei.
These denominations make it attainable to handle even very small values effectively, a sensible function given Ethereum’s position in executing high-volume, low-cost transactions.
Ethereum Accounts
Non-public Keys and Public Keys: The Cryptographic Basis
On the coronary heart of each Ethereum account lies a non-public and public key, that are important to safe transactions. These keys are created utilizing the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) cryptography, particularly the secp256k1 curve. Right here’s a simplified view of the way it works:
- Non-public Key: This can be a randomly generated 256-bit quantity, which serves as a novel digital signature. A personal secret’s stored secret and must not ever be shared.
Instance of a personal key: 0x9c1c77ab91d10d71012d61dcb7b12aef8d509a2d13ed7c54f1e347b89720dc40 - Public Key: The non-public secret’s mathematically reworked utilizing ECDSA to create a corresponding public key. The ECDSA transformation course of makes it virtually inconceivable to reverse engineer the non-public key from the general public key, which is essential for safety.
As a result of the cryptographic algorithms used are one-way capabilities (referred to as hashing), public keys will be freely shared with out exposing the non-public key. To place it in perspective, reversing a personal key from a public key would require extra computational energy than exists on the earth, making Ethereum accounts safe.
Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs) and Key Pairs
Most customers work together with Ethereum utilizing Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs), which depend on key pairs. Every EOA is managed by a personal key, which gives unique entry to the account’s funds and transaction skills. Together with the non-public key, an EOA has a public handle—a simplified type of the general public key that represents the account.
A public handle is basically the general public face of an account, the place others can ship Ether or tokens. For instance, if Alice needs to ship Bob some Ether, she would use Bob’s public handle because the vacation spot. The non-public key allows Bob to authorize transactions from his account, making certain he can solely spend his funds.
Wallets: A Sensible Interface for EOAs
A pockets is a software program or {hardware} interface that enables customers to work together with Ethereum and handle their EOAs. Wallets retailer and handle the non-public and public keys, enabling customers to ship, obtain, and think about their property with out dealing with uncooked cryptographic particulars.
Scorching Wallets and Chilly Wallets
There are two main varieties of wallets:
- Scorching Wallets: These are related to the web, making them handy for frequent transactions. Examples of sizzling pockets suppliers embrace MetaMask and Belief Pockets. Nonetheless, sizzling wallets are extra prone to on-line assaults, so they’re typically really helpful for smaller quantities.
- Chilly Wallets: These are offline wallets, which retailer non-public keys on {hardware} gadgets or paper, offering enhanced safety. Fashionable chilly wallets embrace Ledger and Trezor, preferrred for long-term storage of considerable funds since they’re offline and subsequently extra immune to hacking.
Study deeper insights into what a pockets handle is, or take a look at Coin Bureau’s checklist of the Finest Ethereum Wallets!
Contract Accounts: Extending Ethereum’s Utility
Past EOAs, Ethereum has contract accounts. Not like EOAs, contract accounts do not need non-public keys; as an alternative, they’re managed by code referred to as sensible contracts.
- Creation and Perform: Contract accounts are created when customers deploy sensible contracts to the Ethereum blockchain. As soon as created, these accounts function independently, following predefined guidelines encoded within the contract.
- Limitations: Contract accounts can not provoke transactions independently—they should be triggered by an EOA. This design ensures that contract accounts solely act when exterior enter is supplied, stopping unauthorized actions.
Sensible Contracts: The Core of Contract Accounts
Sensible contracts are basically packages deployed on the Ethereum blockchain. When a sensible contract is deployed, it turns into a contract account with a novel handle, enabling others to work together with it. For instance, a decentralized trade (DEX) contract account might execute trades routinely based mostly on the situations set in its code.
As a result of contract accounts are managed by code, they’ve particular capabilities and limitations. They can not maintain non-public keys or provoke transactions, which means all operations should be triggered externally, usually by EOAs.
Triggering Sensible Contracts: Instance of an EOA-Contract Interplay
Think about Alice needs to swap Ether for a token utilizing a DEX sensible contract. Right here’s how this interplay unfolds:
- Alice’s EOA initiates the transaction by sending a message to the DEX’s contract account, specifying the swap particulars, and attaching the required Ether.
- The DEX contract account receives Alice’s request, executes the predefined swap operate, and sends again the token to Alice’s account.
- State Modifications and Closing Block State: This transaction updates the stability of Ether and tokens in Alice’s account and the DEX’s contract account, finalizing the blockchain’s state.
Every step on this course of requires computational assets, referred to as gasoline. Fuel is spent processing the contract code and updating the community’s state. The extra complicated the operation, the extra gasoline is required, which Alice pays in Ether as compensation for validators.
Solidity: The Language of Sensible Contracts
Sensible contracts on Ethereum are written in Solidity, a programming language designed particularly for the platform. Solidity permits builders to put in writing code figuring out how a contract account will behave, defining capabilities, storage, and guidelines.
As an illustration, a crowdfunding contract written in Solidity may embrace capabilities to simply accept funds, examine funding targets, and return funds if the goal isn’t met. Solidity's syntax is just like JavaScript, making it accessible to many builders. With Solidity, the Ethereum community has grow to be a versatile platform for builders to create decentralized purposes (DApps) throughout industries.
Ethereum Token Requirements: Enabling Versatile Digital Belongings
Ethereum has given rise to numerous token requirements, every designed to assist completely different digital property and purposes. Token requirements are like templates that outline the foundations for creating and managing tokens on the Ethereum community. Let’s have a look at the most well-liked requirements and the way they’re used.
ERC-20 Tokens: The Commonplace for Fungible Tokens
ERC-20 is the most typical token normal on Ethereum and is used to create fungible tokens—similar and interchangeable tokens. Every ERC-20 token operates on the identical primary ideas, making them straightforward to switch, retailer, and trade throughout wallets and platforms that assist the usual. ERC-20 tokens comply with a set of standardized capabilities, similar to switch and approve, making certain compatibility throughout numerous Ethereum-based purposes.
Some well-known examples of ERC-20 tokens embrace:
- USDT (Tether): A stablecoin pegged to the U.S. greenback, used broadly for buying and selling and funds.
- LINK (Chainlink): A token for the Chainlink community, supporting decentralized oracles.
- UNI (Uniswap): A governance token for the Uniswap decentralized trade.
ERC-20 tokens have grow to be the spine of decentralized finance (DeFi), powering buying and selling, lending, and staking purposes on Ethereum.
ERC-721 Tokens: The Non-Fungible Token Commonplace
The ERC-721 normal is designed for non-fungible tokens (NFTs)—distinctive digital property that can not be interchanged one-to-one like ERC-20 tokens. Every ERC-721 token has a novel identifier, permitting it to characterize particular person possession of a particular asset. This normal has been pivotal within the rise of digital collectibles, art work, and different property that profit from distinctive, verifiable blockchain possession. There are devoted markets the place you possibly can commerce NFTs. Here’s a checklist of the highest NFT Marketplaces.
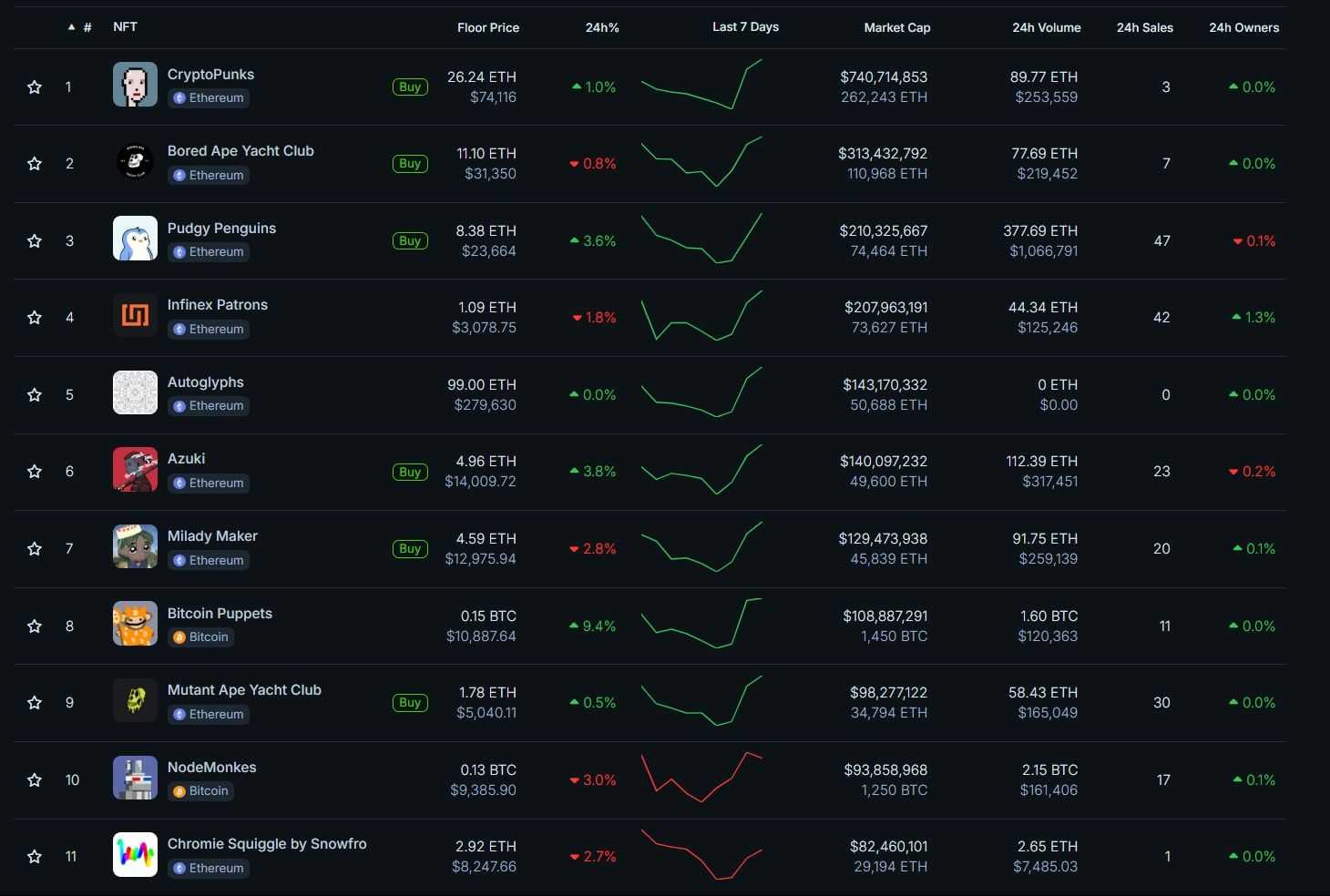
Examples of fashionable ERC-721 NFTs embrace:
- CryptoKitties: One of many earliest NFT initiatives, the place customers breed and commerce digital cats, every with distinctive traits.
- Bored Ape Yacht Membership: A set of distinctive, hand-drawn ape characters which have grow to be extremely collectible.
- Decentraland LAND: Digital actual property parcels within the Decentraland metaverse, every with its personal coordinates and distinctive properties.
ERC-721 tokens have introduced a brand new degree of individuality and possession to digital property, enabling new types of worth in artwork, gaming, and digital actual property.
ERC-1155 Tokens: The Multi-Token Commonplace
ERC-1155 combines options of each ERC-20 and ERC-721, making it preferrred for creating collections that include fungible and non-fungible tokens. This normal was developed for gaming and different use instances the place customers may want a number of varieties of property inside a single contract. For instance, in a online game, a participant may maintain each in-game foreign money (fungible) and distinctive weapons or armor (non-fungible), all managed by means of a single ERC-1155 contract.
Examples of ERC-1155 tokens embrace:
- Enjin Coin (ENJ): A gaming platform that enables customers to create fungible and non-fungible recreation property.
- Gods Unchained: A blockchain-based card recreation the place gamers personal distinctive playing cards (non-fungible) alongside in-game property like tokens (fungible).
By permitting a number of property in a single contract, ERC-1155 reduces the required contracts, making transactions extra environment friendly and less expensive.
Tokens as Token Contracts
Tokens on Ethereum are literally token contracts, that are particular varieties of sensible contracts. Every token is a separate contract that maintains its personal ledger of transactions and balances. For instance, whenever you purchase an ERC-20 token, you aren’t immediately holding it in your pockets; as an alternative, the token contract updates its ledger to replicate your possession. On this manner, tokens are particular varieties of sensible contracts that function as decentralized databases for monitoring token balances.
Once you switch an ERC-20 token, the token contract updates its inside ledger to lower your stability and improve the recipient’s. This method ensures all token-related transactions on the blockchain are clear and verifiable.
Is Ether an ERC-20 Token? Clearing Up a Frequent False impression
One frequent false impression is that Ether (ETH) is an ERC-20 token. Nonetheless, this isn’t the case. The ERC-20 normal allowed builders to design new tokens on Ethereum’s community. Alternatively, Ether is Ethereum’s native foreign money, and Ethereum natively tracks Ether transactions. This makes Ether distinctive—it doesn’t want a sensible contract to handle transactions, because the Ethereum protocol itself does.
As a result of Ether exists outdoors of any token contract, it isn’t an ERC-20 token. As an alternative, ERC-20 tokens are merely further property created on Ethereum utilizing sensible contracts, whereas Ether is the foreign money that fuels the complete Ethereum ecosystem.
Ethereum Blocks: The Constructing Blocks of the Blockchain
Ethereum blocks are basic to the construction of the Ethereum blockchain. They include batches of transactions, important information, and references to earlier blocks, making a steady and verifiable data chain. Let’s discover what Ethereum blocks are, how they’re made, and the elements they include.
Blocks as Batches of Transactions
An Ethereum block is basically a bundle of transactions grouped and confirmed collectively. Every block comprises a hash of the earlier block, which hyperlinks it to the chain, forming an unbroken sequence again to the very first block (the genesis block). This construction ensures that each block is related, making it inconceivable to switch a single block with out altering the complete chain.
This hash-based linkage varieties the core of Ethereum’s safety and transparency. As a result of every block is determined by the earlier one, any try to tamper with a previous transaction can be instantly obvious. Every participant on the community can confirm the complete historical past of transactions, making certain that every one nodes within the community agree on Ethereum’s exact transaction historical past and state.
Making certain Synchronization and Consensus
Blocks are the mechanism by which all community contributors keep a synchronized state of Ethereum. When a brand new block is added, it updates the complete community with the most recent set of confirmed transactions. This synchronization is essential, because it ensures each node on Ethereum shares a constant view of account balances, sensible contract states, and transaction historical past.
By way of this course of, Ethereum’s blockchain achieves consensus—settlement amongst all nodes within the community’s present state. This consensus is important for sustaining belief and stopping fraudulent or conflicting information.
Making a Block: The Function of Validators
In Ethereum’s Proof of Stake (PoS) system, validators create new blocks. Relatively than utilizing energy-intensive mining, Ethereum selects a validator at random to suggest every new block. This validator assembles pending transactions right into a block, attaches the required data (such because the earlier block’s hash), and broadcasts it to the community for verification.
As soon as the block is proposed, different validators on the community confirm its contents, making certain that every one transactions are reputable and that the block conforms to Ethereum’s guidelines. When greater than 2/third of the validators agree, the block is added to the chain, and the validator who proposed it’s rewarded with transaction charges and newly minted Ether.
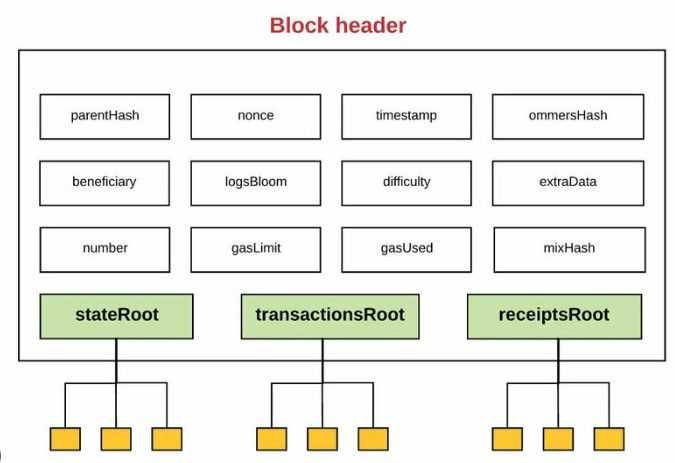
Inside an Ethereum Block: Key Parts
Ethereum blocks include a number of important items of knowledge:
- Transaction Information: That is the primary content material of the block, recording all transactions included within the block. Every transaction comprises particulars such because the sender and receiver’s addresses, the quantity of Ether or token being transferred, and the gasoline charges paid.
- State Information: Ethereum’s distinctive account-based mannequin signifies that every block additionally comprises state information, which tracks the balances of each account and the standing of sensible contracts. This state information represents the cumulative impact of all previous transactions on Ethereum, together with updates to token balances and sensible contract variables.
- Block Header: The block header is a compact piece of metadata summarizing the block’s key properties. It consists of:
- Mother or father Hash: The hash of the earlier block, linking the brand new block to its predecessor and forming the blockchain.
- State Root: A cryptographic root that summarizes the state of all accounts and contracts after the block’s transactions are utilized.
- Transactions Root: A root hash summarizing all transactions within the block, making certain their integrity.
- Receipts Root: A root that shops metadata for every transaction, like gasoline used and logs produced, serving to to trace outcomes of contract executions.
- Issue and Nonce (in older PoW blocks): Though now largely out of date below PoS, these fields point out the block's problem degree below Ethereum’s former Proof of Work (PoW) mannequin.
These elements enable every Ethereum block to behave as a self-contained file of transactions and updates to the community’s state. Each node can validate a block by checking its hashes and verifying that its transactions and state modifications align with Ethereum’s guidelines.
In abstract, blocks function each transaction containers and checkpoints for consensus, enabling Ethereum’s decentralized community to take care of a constant and tamper-resistant historical past. By analyzing these blocks, any participant can confirm the complete chain’s integrity and belief that Ethereum’s state is correct and safe.
Proof of Stake: Ethereum’s Transition to Vitality-Environment friendly Consensus
Initially, Ethereum operated on a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mannequin, just like Bitcoin. This method required miners to resolve complicated cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. Nonetheless, the vitality calls for of PoW, together with scalability issues, led to a big improve referred to as the Beacon Chain onerous fork, which transitioned Ethereum to Proof of Stake (PoS) in September 2022. This shift aimed to make Ethereum extra sustainable, safe, and environment friendly.
Understanding Proof of Stake and the Function of Validators
In Ethereum’s PoS system, contributors who need to assist safe the community grow to be validators fairly than miners. To affix as validators, contributors should "stake" a minimal of 32 ETH—a dedication that acts as a deposit, signaling that they’re trusted community members.
Validators play a key position within the PoS course of:
- They’re chargeable for proposing and validating new blocks.
- Validators additionally take part within the finalization course of, solidifying Ethereum’s state and securing its transaction historical past.
If a validator is chosen to suggest a block, they arrange pending transactions, create a brand new block, and broadcast it to the community. Different validators confirm the brand new block’s contents to verify its legitimacy, making a safe and decentralized consensus. Coin Bureau’s information on Ethereum Staking might help you get began with taking part within the Ethereum community.
Key Metrics of Ethereum’s PoS System
A number of core metrics outline Ethereum’s PoS course of:
- Block Time: In Ethereum’s present community, every PoS block is created roughly each 12 seconds. This interval ensures that transactions are processed effectively and gives a gradual stream of recent blocks, which retains the community responsive.
- Finality: Ethereum’s PoS mannequin features a idea referred to as finality, which marks some extent at which transactions are thought of everlasting and can’t be reversed. Finality happens each 32 slots, a slot being a 12-second interval by which a block will be proposed. Which means that each 6.4 minutes, Ethereum reaches a finalized state, solidifying the blockchain and making certain that latest transactions are unchangeable.
- Slashing: Ethereum employs slashing to take care of safety and forestall malicious habits. Suppose a validator acts dishonestly or fails to carry out their duties (similar to trying to suggest conflicting blocks). In that case, they danger having a portion of their staked ETH "slashed" or completely eliminated. This penalty is a deterrent, selling sincere participation and making certain Ethereum’s cryptoeconomic safety.
Liquid Staking and the Rise of LST Tasks
Whereas conventional staking requires validators to lock up their ETH, liquid staking permits stakers to retain liquidity on their property. In liquid staking, customers obtain Liquid Staked Tokens (LSTs) representing their staked ETH, permitting them to make use of these tokens in different elements of the Ethereum ecosystem (e.g., DeFi) whereas their authentic ETH stays staked.
Though liquid staking just isn’t part of Ethereum’s core protocol, it has grow to be extraordinarily fashionable, with a considerable portion of all staked ETH flowing by means of liquid staking initiatives. High liquid staking suppliers embrace:
- Lido: The biggest liquid staking protocol, the place customers obtain stETH, a tokenized model of staked ETH.
- Rocket Pool: A decentralized staking service providing rETH as a liquid token, permitting customers to stake in smaller quantities or as node operators.
- Puffer finance: A more moderen liquid staking supplier that goals to supply extra accessible staking choices with high-security options.
These initiatives supply flexibility and liquidity for stakers, making staking extra accessible to the broader Ethereum neighborhood whereas strengthening Ethereum’s safety by encouraging extra staking participation.
Decentralized Functions (DApps) and DeFi
Constructing upon our earlier dialogue of sensible contracts, Decentralized Functions (DApps) function on the Ethereum blockchain, leveraging its decentralized infrastructure to offer providers with out centralized management.
- Execution within the EVM: DApps run throughout the Ethereum Digital Machine (EVM), Ethereum's world computational surroundings. The EVM processes sensible contracts, making certain that DApps execute constantly throughout all community nodes.
- Programmability through Sensible Contracts: DApps are programmable by means of sensible contracts written in Solidity, Ethereum's main programming language. These contracts outline the logic and guidelines governing the DApp's operations, enabling numerous functionalities.
- Turing Completeness: The EVM is Turing full, which means it could possibly carry out any computation given sufficient assets. This functionality permits builders to create complicated and versatile DApps. Nonetheless, to forestall infinite loops and extreme useful resource consumption, Ethereum requires gasoline charges for computations. With out such a mechanism, a non-terminating course of might devour infinite gasoline, resulting in community congestion and potential abuse.
Outstanding Classes of DApps within the Ethereum Ecosystem:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Platforms providing monetary providers like lending, borrowing, and buying and selling with out intermediaries.
- Actual-World Belongings (RWAs): DApps that tokenize bodily property, similar to actual property or commodities, enabling on-chain possession and buying and selling.
- Decentralized Bodily Infrastructures (DePINs): Tasks that decentralize bodily infrastructure providers, like networking or storage, by means of blockchain know-how.
- Sport Finance (GameFi): Integrates gaming with monetary incentives, permitting gamers to earn cryptocurrency by means of gameplay.
- Social Finance (SocialFi): Combines social networking with monetary components, enabling customers to monetize content material and interactions.
- Liquid Staking: Companies that enable customers to stake cryptocurrencies whereas sustaining liquidity by means of tokenized representations of staked property.
- Restaking: Mechanisms enabling customers to stake property throughout a number of protocols, enhancing yield alternatives.
- Yield-Bearing Stablecoins: Stablecoins that supply curiosity or yield, offering passive earnings whereas sustaining a steady worth.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Platforms for creating, shopping for, and promoting distinctive digital property representing possession of particular objects or content material.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Platforms facilitating peer-to-peer cryptocurrency buying and selling with out centralized intermediaries.
Here’s a checklist of the High DApps within the Ethereum community.
What’s Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) refers to a broad ecosystem of monetary purposes constructed on blockchain networks, primarily Ethereum, that function with out conventional intermediaries like banks or brokers. DeFi goals to create an open, permissionless, and clear monetary system accessible to anybody with an web connection.
Significance of DeFi:
- Distinction with Centralized Finance: Conventional monetary methods are sometimes characterised by centralized management, restricted accessibility, and potential inefficiencies. DeFi addresses these points by offering decentralized alternate options which might be extra inclusive and immune to censorship.
- Stablecoins in DeFi: Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to steady property, similar to fiat currencies, to attenuate worth volatility. They’re integral to the DeFi area, serving as a steady medium of trade and a unit of account inside numerous protocols. Stablecoins facilitate lending, borrowing, and buying and selling actions by offering a constant worth reference.
As of November 2024, the full worth locked (TVL) in Ethereum's DeFi ecosystem has reached roughly $192 billion, marking the very best degree in 15 months and signaling renewed development within the sector.
This substantial valuation underscores DeFi's increasing position within the monetary panorama, providing progressive options and alternatives past the constraints of conventional finance. Try the Finest DeFi Tasks by Coin Bureau.
Blockchain Explorers: Home windows into the Blockchain
One of many distinctive options of blockchain know-how is its full transparency. Each transaction on the Ethereum community is seen to the general public, creating an open ledger the place all actions are recorded and verifiable by anybody. Not solely are transactions clear, however sensible contract information on Ethereum can be open-source, permitting customers to view the contract’s code and confirm its performance. This openness allows contributors to belief the community with no need a centralized authority.
Blockchain Explorers: Browsers for On-Chain Information
To make this information simply accessible, blockchain explorers act like net browsers for the blockchain. As you utilize a search engine to seek out web sites, a blockchain explorer helps you to search and think about on-chain information, together with transaction particulars, account balances, and sensible contract data.
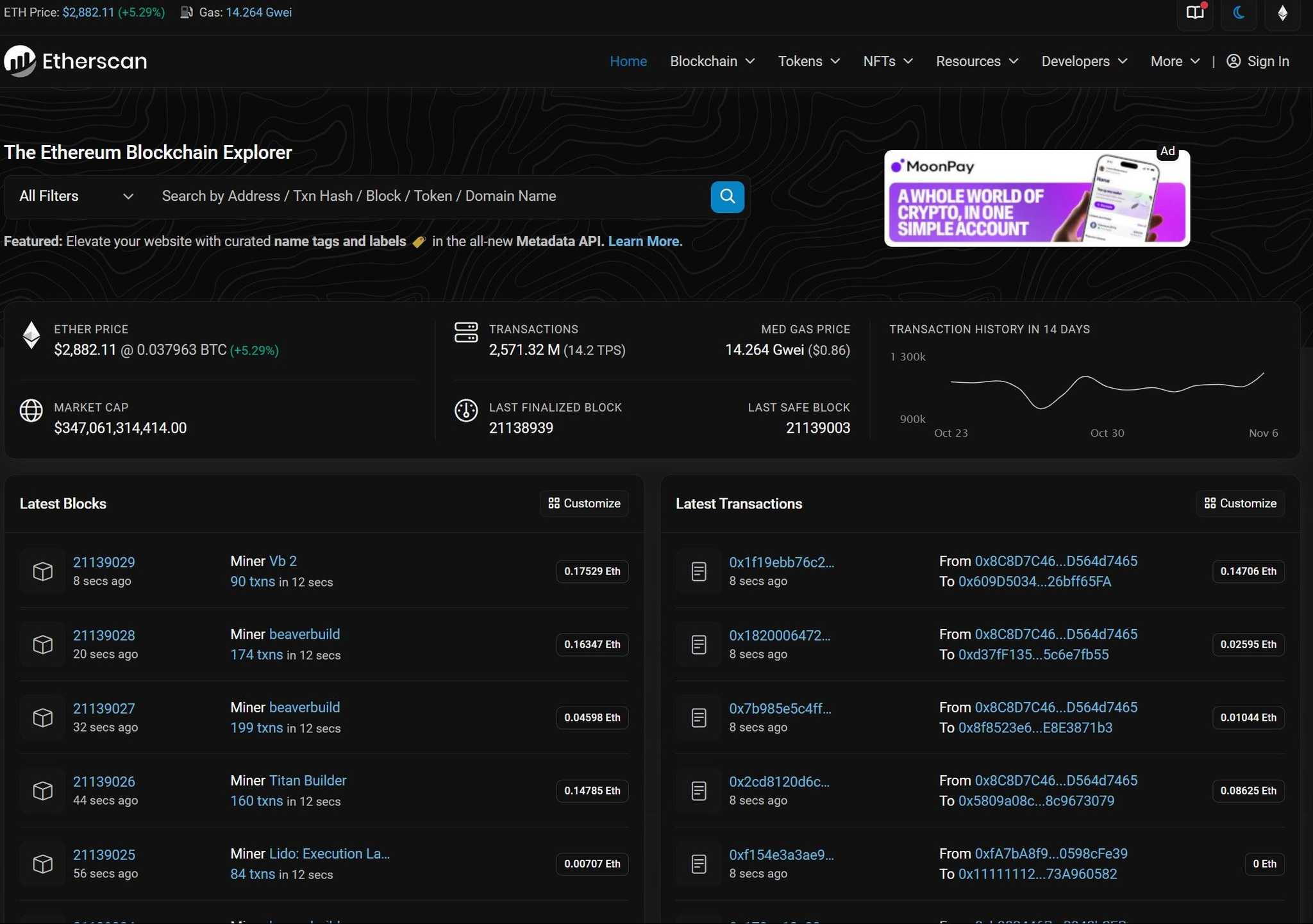
Etherscan is essentially the most broadly used blockchain explorer for Ethereum. It gives a user-friendly interface for navigating Ethereum’s blockchain, making it attainable to trace transactions, examine contract particulars, and analyze on-chain metrics. Right here’s a have a look at some key capabilities that Etherscan gives:
- Observe Transaction Trails: Etherscan permits customers to enter any Ethereum handle or transaction hash to view the complete transaction historical past. You may hint the trail of tokens, Ether transfers, and different actions, offering perception into how property have moved throughout the community.
- Confirm Transfers: Customers can confirm transfers of Ether and tokens, making certain that funds or transfers have been accomplished efficiently. Every transaction entry consists of particulars like sender and receiver addresses, transaction quantities, and timestamps, all recorded on the blockchain.
- Audit Sensible Contracts: Since Ethereum sensible contracts are open-source, customers can view their code immediately on Etherscan. This makes it attainable to audit contracts, examine for potential dangers, and perceive the performance of fashionable decentralized purposes (DApps). Auditing sensible contracts permits customers to evaluate whether or not a contract is reliable earlier than interacting.
- Test Contract Balances: Etherscan lets customers examine the balances of each EOAs (Externally Owned Accounts) and contract accounts. This function helps observe the holdings of decentralized purposes, liquidity swimming pools, or different DeFi initiatives, offering transparency about the place funds are saved and the way they’re managed.
- View On-Chain Metrics: Etherscan gives insights into community metrics, similar to gasoline costs, block occasions, and the variety of lively validators. Customers also can view details about community exercise, together with transaction volumes and developments over time. These metrics give customers a deeper understanding of Ethereum’s community well being and utilization.
Blockchain explorers like Etherscan are important instruments for anybody interacting with Ethereum, as they provide a clear view into the blockchain’s operations. By making all transaction and contract information simply accessible, they uphold Ethereum’s ideas of openness and safety, empowering customers to confirm and discover the community independently.
Understanding Ether Financial Coverage
Ethereum’s method to its native foreign money, Ether (ETH), is exclusive. Ethereum is programmed with an infinite provide mannequin, in contrast to Bitcoin, which has a capped provide. Nonetheless, to forestall an overflow of ETH in circulation, Ethereum carried out a basic improve referred to as EIP-1559, which launched a stability between new ETH coming into the system and older ETH being eliminated.
Ethereum Blocks and Provide Management
With Ethereum’s transition to Proof of Stake (PoS), the availability of ETH is now influenced by community demand and gasoline charges. Validators who change miners in PoS create blocks in response to consumer transaction demand. Every block adjusts the general ETH provide relying on the gasoline charges customers pays and the protocol’s dynamic gasoline administration.
What’s Fuel?
On Ethereum, gasoline measures the computational assets required to execute on-chain transactions. Each motion—sending ETH, interacting with a sensible contract, or deploying a brand new DApp—consumes gasoline. Fuel charges are decided by the models of gasoline consumed in a transaction, multiplied by the present gasoline worth (measured in gwei, the place 1 gwei = 10^-9 ETH).
EIP-1559 launched a brand new gasoline payment construction, with every transaction’s gasoline payment cut up into two elements:
- Base Price: That is the minimal gasoline payment required for a sound transaction. The bottom payment is decided by the community and fluctuates relying on transaction quantity and community demand. Upon profitable transaction execution, it’s burned out of Ethereum’s provide.
- Precedence Price: Customers can add a tip above the bottom payment, referred to as the precedence payment, to incentivize validators to incorporate their transactions within the subsequent block. The upper the precedence payment, the faster the transaction shall be processed.
Most Ethereum wallets enable customers to set a gasoline restrict, which caps the precedence payment they’re prepared to pay. This protects customers from extreme charges, as setting a gasoline restrict prevents their transactions from endlessly consuming funds. If community demand is excessive, customers might place a better precedence payment to keep away from delays. Nonetheless, if the transaction fails or is omitted, any gasoline spent on processing the request is not going to be refunded.
Ethereum Block Breakdown and Fuel Administration
Ethereum blocks are measured by the full gasoline consumed inside them. Each 12 seconds, the community randomly selects a validator to suggest a brand new block, focusing on a block dimension of 15 million gasoline however permitting as much as a most restrict of 30 million gasoline.
To stop transaction prices and community storage calls for from hovering, Ethereum dynamically adjusts the base payment based mostly on its proximity to the goal block dimension:
- Goal Block Measurement: The perfect block dimension is 15 million gasoline.
- Base Price Adjustment: If blocks devour greater than 15 million gasoline in two consecutive blocks, the bottom payment will increase by 12.5% for every block. This adjustment continues till a block consumes lower than 15 million gasoline, at which level the bottom payment decreases by 12.5% for every block.
EIP-1559’s gasoline mannequin goals to not make gasoline charges cheaper however extra predictable. By adjusting the bottom payment based mostly on block utilization, Ethereum ensures smoother pricing, decreasing sudden fluctuations that beforehand made transaction prices risky.
Insights into ETH Inflation and Deflation
One in all EIP-1559's key impacts has been its impact on ETH provide dynamics. Every new block mints a small quantity of recent ETH, including to the full provide. Nonetheless, the protocol additionally burns the bottom payment—the portion of gasoline charges paid by customers—successfully eradicating ETH from circulation.
This burn mechanism has led many to explain ETH as a deflationary foreign money, however that is solely partly correct. Ethereum turns into deflationary solely when the quantity of ETH burned exceeds the quantity minted, which happens in periods of excessive demand when base charges spike. If demand drops, the speed of ETH burning slows, permitting the full provide to develop.
The result’s a novel stability between inflation and deflation, managed by the community’s demand and utilization. Throughout peak occasions, ETH provide contracts as extra ETH is burned, whereas decrease demand results in net-positive minting. This mechanism helps preserve Ethereum’s provide extra balanced and conscious of market situations.
Ethereum Blockchain Layers: The Basis of the Ethereum Community
Ethereum’s mainnet is organized into three core layers, every serving a particular operate to make the blockchain safe, purposeful, and decentralized. These layers—Information Availability Layer, Consensus Layer, and Execution Layer (EVM)—are important for Ethereum’s operation. Collectively, they kind a whole blockchain however are separated based mostly on duties, not bodily boundaries. Every layer is contained inside Ethereum’s validator nodes, making a unified but modular structure.
Information Availability Layer
The Information Availability Layer makes transaction information accessible to all contributors. When customers work together with Ethereum, each transaction and sensible contract interplay generates information that should be broadcast to the community. This layer ensures that this information is obtainable to validators and nodes, permitting them to confirm transactions and synchronize Ethereum’s state.
Information availability is important as a result of it ensures that every one nodes see the identical information, sustaining transparency and stopping information from being withheld or hidden by malicious actors. This layer is essential to preserving the community’s liveness and making certain that each validator can independently confirm the chain’s state.
Consensus Layer
The Consensus Layer is the spine of Ethereum’s safety. It coordinates Ethereum’s Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, the place validators agree on the present state of the blockchain. The layer is chargeable for validating transactions, including new blocks, and making certain all nodes comply with the identical guidelines.
By way of this layer, Ethereum achieves consensus on reputable transactions and finalized, making it immune to double-spending assaults and community manipulation. The Consensus Layer retains Ethereum decentralized, as validators work collectively to take care of and safe the chain.
Execution Layer (EVM)
The Execution Layer, also called the Ethereum Digital Machine (EVM), is the place the precise execution of sensible contracts and transactions happens. This layer processes computations, manages sensible contract logic, and updates account balances. Consider it as Ethereum’s computational engine, dealing with the whole lot from token transfers to DeFi protocols.
The EVM permits Ethereum to operate as a programmable blockchain able to working decentralized purposes (DApps) and complicated contract logic. By separating execution from information availability and consensus, Ethereum can give attention to every job effectively with out overwhelming the community.
How These Layers Create the Ethereum Mainnet
Collectively, these layers mix to kind the Ethereum mainnet. They exist inside every validator node, offering distinct functionalities whereas remaining interconnected inside its structure. This separation of duties makes the Ethereum community extra resilient, as every layer independently manages a core blockchain operate, permitting validators to take care of a constant and verified ledger throughout the community.
The Scalability Trilemma
Like most blockchains, Ethereum faces the scalability trilemma—the problem of concurrently attaining scalability, safety, and decentralization. When all duties of the blockchain layers (information availability, consensus, and execution) are carried out by the identical community of nodes, they create a bottleneck that restricts scalability. Right here’s how every pillar of the trilemma is affected:
- Safety: Ethereum maintains sturdy safety requirements by prioritizing the consensus layer. Nonetheless, rising community safety usually includes sacrificing velocity.
- Decentralization: Decentralization requires validators to share duties, stopping one celebration from controlling the community. Nonetheless, with all layers performing duties collectively on every node, it turns into tough to scale with out sacrificing some degree of decentralization.
- Scalability: For Ethereum to course of extra transactions rapidly, the community wants to extend throughput. Nonetheless, with all layers mixed, larger transaction volumes put strain on every layer, particularly the Execution Layer, resulting in slower processing occasions.
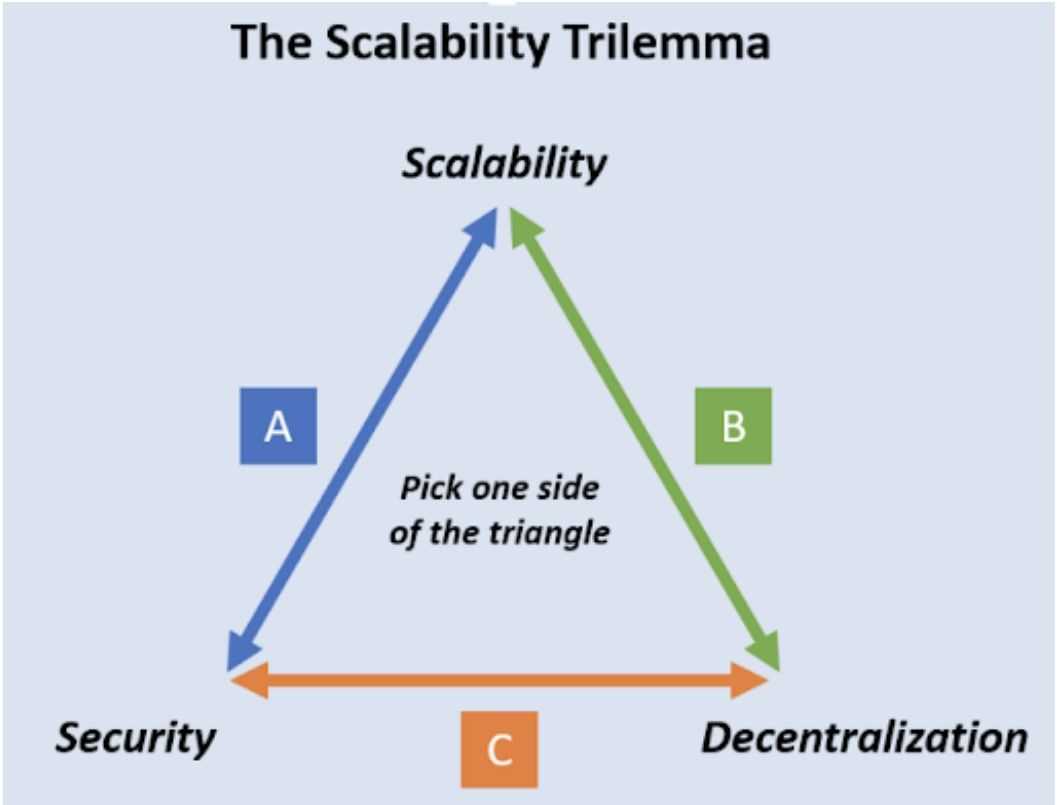
Ethereum’s trilemma lies in balancing these three targets, as any emphasis on one can pressure the others. The necessity to scale with out compromising safety or decentralization led Ethereum to undertake a Rollup-centric roadmap.
Rollup-Centric Roadmap: Ethereum’s Answer to the Trilemma
To beat the trilemma, Ethereum adopted a rollup-centric roadmap that offloads scalability capabilities to a brand new layer whereas sustaining a safe and decentralized mainnet.
- Concentrate on Safety and Decentralization: Below this roadmap, Ethereum’s mainnet is optimized to deal with Information Availability and Consensus layers, whereas the Execution Layer is partially offloaded to a separate layer. By specializing in safety and decentralization, Ethereum can keep the integrity of the community whereas attaining higher scalability by means of exterior options.
- Introduction of Layer 2 Options: This roadmap led to growing Layer 2 (L2) options, or “rollups.” Layer 2 protocols are specialised execution environments that deal with many transactions outdoors the primary Ethereum chain however periodically report again to the Ethereum mainnet. Rollups deal with execution off-chain, then bundle and submit the transaction information to Ethereum’s mainnet for safety and finalization.
This rollup-centric method addresses Ethereum’s scalability points by distributing the workload. The mainnet ensures information availability and consensus, whereas Layer 2 ecosystems present environment friendly transaction processing. As Layer 2 networks proceed to develop, Ethereum’s ecosystem has grow to be extra able to dealing with excessive demand whereas sustaining its safety and decentralization.
Scaling the Ethereum Ecosystem: The Rollup-Centric Roadmap
Within the earlier part, we mentioned the completely different layers of the Ethereum mainnet and launched the concept of a rollup-centric roadmap. Let's dive deeper into this matter to know Ethereum's evolution and the way it addresses scalability challenges.
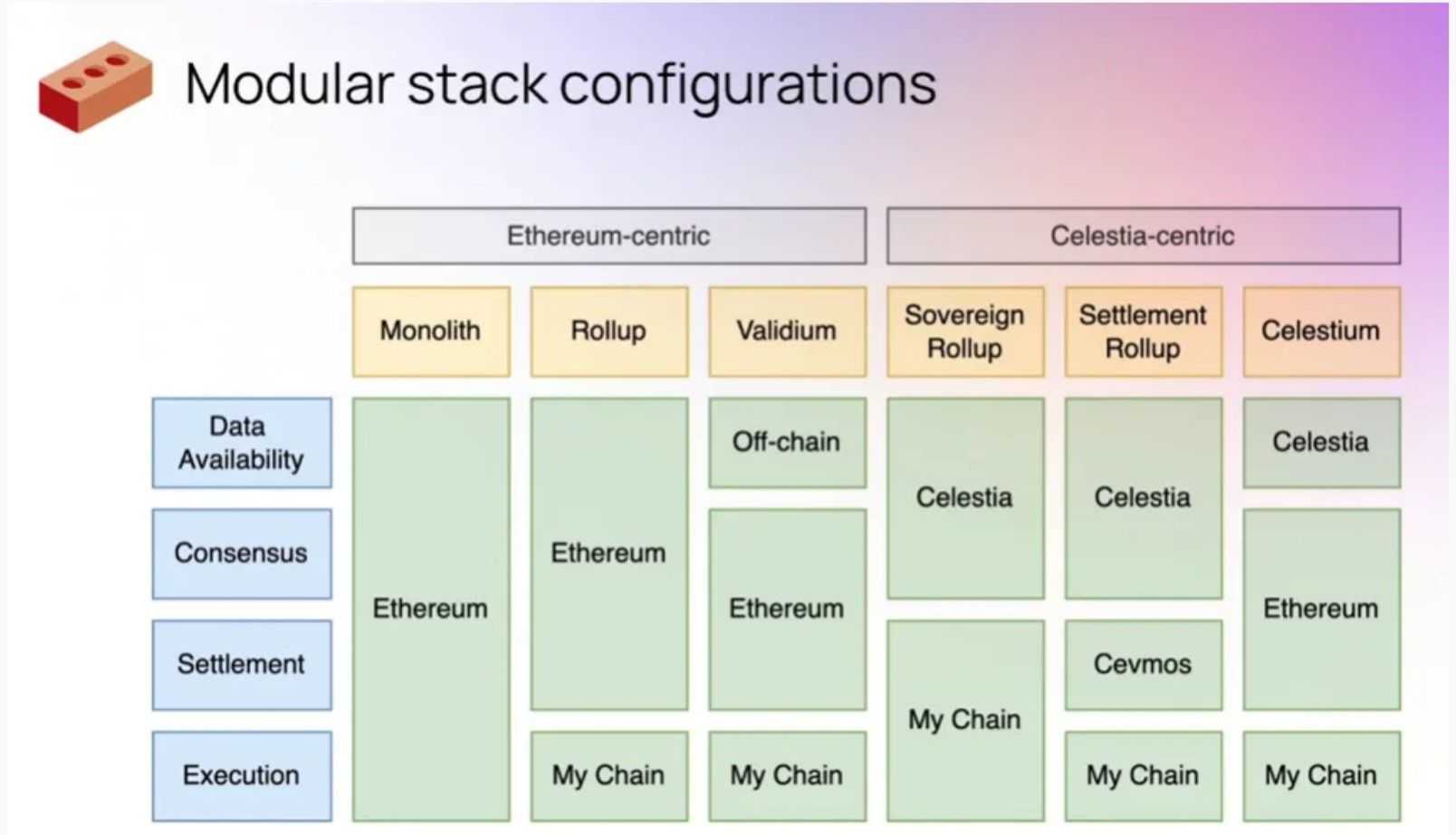
Blockchain Modularity: Splitting the Chain for Increased Scalability
Blockchain modularity includes separating a blockchain's core capabilities—Information Availability (DA), consensus, and execution—into distinct layers. By modularizing these elements, Ethereum goals to attain larger scalability whereas sustaining a cohesive ecosystem. Every layer makes a speciality of its particular job:
- Information Availability Layer: Ensures that transaction information is accessible to all community contributors.
- Consensus Layer: Maintains community safety by verifying and agreeing on the state of the blockchain.
- Execution Layer (EVM): Handles the computation and execution of sensible contracts.
The Ethereum neighborhood acknowledged that scaling the ecosystem with out shedding safety and decentralization was solely attainable by modularizing Ethereum. By delegating particular capabilities to devoted layers, the community can deal with elevated demand extra effectively with out overloading any single part.
Ethereum's Core Energy: Supply of Credible Block Area
Because the Ethereum ecosystem grew, it turned essentially the most decentralized blockchain community on account of its in depth community of validators. Ethereum's core power isn't simply that almost all purposes and DeFi initiatives are constructed on it; fairly, it gives essentially the most safe blockchain community by means of its Information Availability layer upheld by validators.
What’s Credible Block Area?
Credible block area refers back to the safe and dependable area on the blockchain the place transactions and information are saved and verified. Within the context of Ethereum, this credible block area is underpinned by the Information Availability layer. Ethereum's validators collectively facilitate essentially the most safe block area in Web3.
What makes Ethereum's block area significantly useful is its arbitrary usability. This implies the block area isn't restricted to securing solely Ethereum transactions; different networks can hire it to safe their networks as sandboxed environments inside Ethereum. This "sandboxed environment" analogy illustrates how different protocols can leverage Ethereum's sturdy safety with out interfering with the mainnet's operations.
By providing credible block area, Ethereum gives a basis for different initiatives to construct securely, benefiting from the community's decentralization and consensus mechanisms.
What’s the Rollup-Centric Roadmap?
Constructing on these insights, the rollup-centric roadmap represents Ethereum's developed give attention to making its credible block area extra scalable and accessible. The roadmap outlines a method the place Ethereum's mainnet specializes within the Information Availability and Consensus layers. In distinction, the Execution layer is shifted to a brand new layer dealt with by Layer 2 options, referred to as rollups.
Rollups are scaling options that course of transactions off the primary Ethereum chain however return transaction information to the mainnet for safety and consensus. By doing so, they:
- Enhance Scalability: Offloading execution to rollups reduces congestion on the mainnet, permitting for larger transaction throughput.
- Keep Safety and Decentralization: Since rollups depend on Ethereum's credible block area for safety, they inherit the mainnet's sturdy security measures.
- Improve Accessibility: Rollups make it extra inexpensive and environment friendly for customers to work together with the Ethereum ecosystem by decreasing gasoline charges and rising transaction speeds.
The rollup-centric roadmap permits Ethereum to give attention to its strengths—offering safe and decentralized block area—whereas rollups deal with scalability. This division of labor allows Ethereum to develop sustainably with out compromising its foundational ideas.
Within the subsequent part, I’ll clarify how credible block area motivated the rise of the Ethereum Layer 2 ecosystem.
The Ethereum Layer 2 Ecosystem
Ethereum's Layer 2 options (or L2s) are separate blockchain networks that work alongside Ethereum to execute transactions effectively whereas leveraging Ethereum for safety and information availability. These L2s present a scalable framework that enables excessive transaction throughput, decrease prices, and enhanced consumer expertise, all whereas inheriting Ethereum's safety and decentralization.
How Ethereum Layer 2s Work
An Ethereum Layer 2 is designed as an impartial blockchain community that processes giant transactions off the primary Ethereum chain. Nonetheless, as an alternative of functioning independently, it depends on Ethereum’s Information Availability (DA) and Consensus layers for safety and finality. Right here’s how the method works:
- Sequencer Nodes: Layer 2s makes use of a specialised node referred to as a sequencer to gather, validate, and execute transactions in excessive volumes. This sequencer node performs a vital position by ordering and bundling transactions into giant batches, optimizing throughput, and decreasing congestion.
- Batching Transactions and Validity Proofs: As soon as the sequencer processes a batch of transactions, it constructs a mixed validity proof that represents the integrity of the complete batch. Some Layer 2s, referred to as zk-rollups, make the most of zero-knowledge proofs (ZK proofs) to create a succinct validity proofs. ZK proofs enable these rollups to verify that the transactions in a batch are legitimate with out revealing detailed details about every transaction, which reinforces privateness and effectivity.
- Posting Batches to Ethereum: After the sequencer creates the validity proof, the rollup posts the bundled transactions and the proof on Ethereum as a single transaction. This transaction is dealt with by a rollup sensible contract deployed on Ethereum, which verifies the validity of the batch based mostly on the proof submitted.
- Leveraging Ethereum’s Credible Block Area: As soon as posted, the Ethereum DA layer shops copies of the rollup’s information throughout the community, successfully vouching for the rollup by guaranteeing information availability. This design permits the rollup to leverage Ethereum’s credible block area, making certain that even when Layer 2 encounters points, the info stays accessible on Ethereum, and customers retain the power to recuperate their transactions.
- Price Effectivity and Safety: By batching a number of transactions right into a single proof, the price of posting information to Ethereum is split throughout all transactions throughout the batch. This dramatically reduces the fee per transaction, permitting Layer 2s to supply low charges whereas inheriting Ethereum’s safety, liveness, and decentralization.
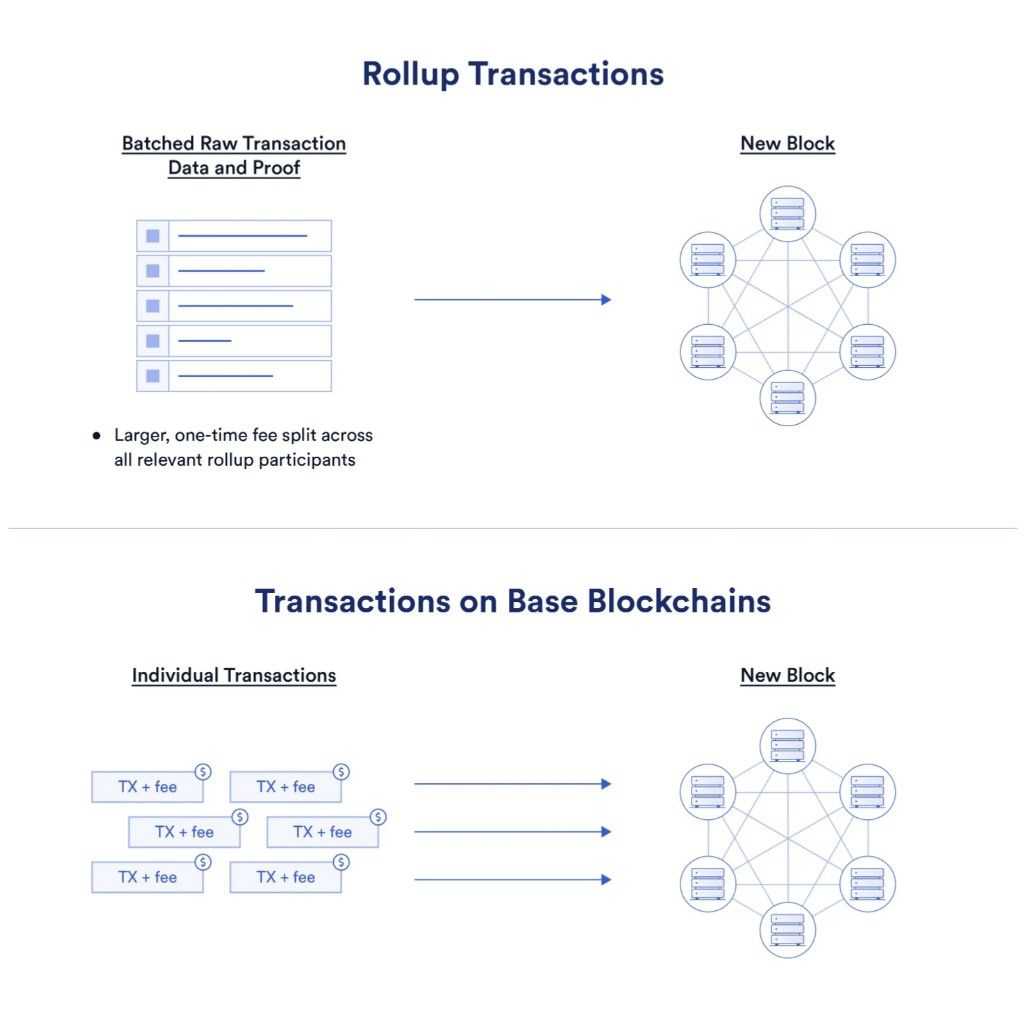
In abstract, Ethereum Layer 2s, like zk-rollups improve scalability by offloading transaction execution whereas counting on Ethereum to safe the community’s information and integrity. Ethereum can scale sustainably by means of this symbiotic relationship with out sacrificing safety or decentralization.
Proto-Danksharding: Making Credible Block Area Cheaper
In March 2024, Ethereum carried out the Dencun improve, which launched EIP-4844, referred to as Proto-Danksharding. This important enhancement decreased the price of credible block area for Layer 2 options by almost 90%, fostering higher scalability and effectivity throughout the Ethereum ecosystem.
Understanding the Improve By way of a Laptop Analogy
To understand the impression of this improve, let's revisit our earlier analogy of Ethereum as a pc:
- Earlier than the Improve: Layer 2 options saved their transaction information in Ethereum's RAM. In computing, RAM is the place lively processing happens; it's restricted in capability and comparatively costly. In Ethereum, this corresponds to CALLDATA, the area the place transaction information is processed and saved. Storing giant quantities of knowledge in CALLDATA was expensive and constrained by area limitations.
- After the Improve: With the Dencun improve, Layer 2 options saved their information in Ethereum's ROM. ROM is used for storage that doesn't require fixed processing, providing bigger capability and decrease prices. In Ethereum, this new storage technique known as BLOB DATA (Binary Massive Objects Information). By shifting information storage from CALLDATA to BLOB DATA, Layer 2s can retailer data extra effectively and affordably.
Introducing Blob Information and Blob Fuel
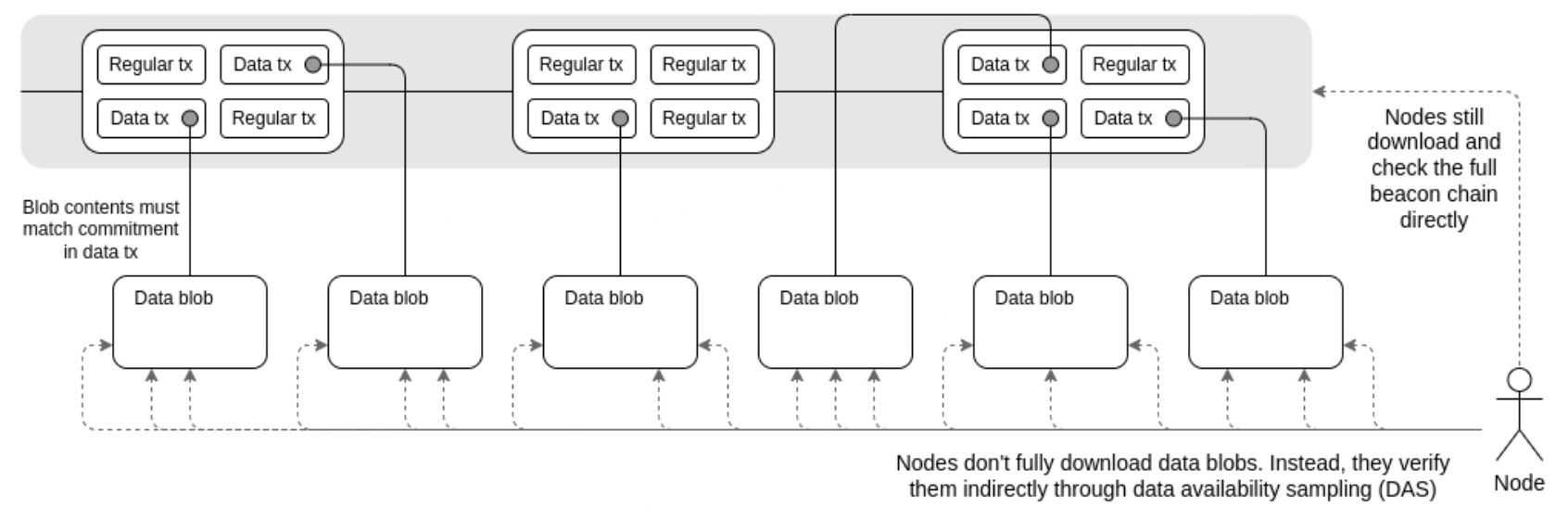
The Dencun improve supplied a brand new storage format and launched a separate gasoline mechanism referred to as Blob Fuel. This method operates parallel to the present gasoline mechanism, sustaining an analogous construction however at a considerably decrease value. By using Blob Fuel, BLOB DATA transactions grow to be extra economical, decreasing the general bills for Layer 2 operations.
Influence on the Ethereum Ecosystem
By enabling BLOB DATA and Blob Fuel, Ethereum has made its credible block area extra accessible and inexpensive. This development promotes the expansion of the Layer 2 ecosystem, permitting for larger transaction throughput and decrease charges. Consequently, Ethereum has solidified its place as the biggest community of interconnected chains in Web3, providing a scalable and safe platform for decentralized purposes.
For a deeper understanding of Ethereum Layer 2 options, readers can discover extra assets on Coin Bureau.
The Ethereum Roadmap: Historical past and Way forward for Upgrades
Ethereum’s evolution is guided by a sequence of community-driven proposals referred to as Ethereum Enchancment Proposals (EIPs). EIPs function a formalized course of for proposing, discussing, and implementing modifications to the Ethereum community. They vary from small technical changes to main community upgrades and are important for refining Ethereum’s performance, scalability, and safety.
What Are EIPs?
An EIP is a doc that proposes a brand new function, course of, or enchancment to the Ethereum community. Every EIP outlines the motivation behind the proposed change, the technical particulars, and the anticipated impression on the community. EIPs comply with a structured lifecycle, together with neighborhood discussions, testing, and closing approval or rejection. As soon as accepted, an EIP could also be included right into a future improve, serving to Ethereum adapt to new challenges and enhance its general effectivity.
The Course of Behind Ethereum Upgrades
The Ethereum neighborhood has established a tough system for researching and growing upgrades:
- Concept and Draft Stage: Builders, researchers, or neighborhood members suggest new concepts based mostly on noticed wants, business developments, or progressive analysis. These concepts are sometimes debated throughout the neighborhood to guage their potential impression.
- EIP Proposal: If an thought positive factors assist, it strikes to the formal EIP stage, the place it’s documented intimately. The proposal explains the issue being addressed, outlines the answer, and consists of technical specs.
- Overview and Dialogue: The Ethereum neighborhood, together with core builders and stakeholders, evaluations the EIP. This open course of permits for suggestions, enhancements, and modifications based mostly on neighborhood enter.
- Testing and Growth: Promising EIPs enter the testing section. Right here, builders simulate the proposed modifications on take a look at networks to guage their effectiveness, examine for bugs, and guarantee compatibility with present options.
- Incorporation into Community Upgrades: If testing is profitable, the EIP is scheduled for inclusion in an upcoming Ethereum improve. These upgrades, usually named after cities or ideas (e.g., “Dencun” or “Shanghai”), are deliberate to introduce a number of EIPs in a coordinated launch, regularly enhancing the community.
This structured course of ensures that Ethereum stays a collaborative, community-driven challenge, with EIPs forming the idea for steady enchancment. Within the following sections, we’ll discover particular upgrades within the Ethereum roadmap which might be set to advance the community considerably. Listed below are a number of the foundational EIPs handed within the community:
- Frontier – July 30, 2015: This was the preliminary launch of the Ethereum community, a barebones implementation meant for builders.
- Frontier Thawing – September 7, 2015: This replace lifted the gasoline restrict per block, permitting for transactions to be processed and making ready for future upgrades.
- Homestead – March 14, 2016: This improve launched protocol and networking modifications, enhancing the community's capabilities and paving the best way for future upgrades.
- DAO Fork – July 20, 2016: In response to a hack of The DAO, a decentralized autonomous group, this fork moved funds from the compromised contract to a brand new one, permitting customers to withdraw their ETH.
- Tangerine Whistle – October 18, 2016: This fork addressed community well being points associated to underpriced operation codes, mitigating denial-of-service assaults.
- Spurious Dragon – November 22, 2016: An additional response to DoS assaults, this improve tuned opcode pricing, enabled blockchain state "debloat," and added replay assault safety.
- Byzantium – October 16, 2017: This improve decreased block rewards, delayed the "difficulty bomb," and added options like non-state-changing calls and cryptography strategies for layer 2 scaling.
- Constantinople – February 28, 2019: This improve decreased block rewards, ensured the community's continued operation, optimized gasoline prices, and launched the power to work together with uncreated addresses.
- Istanbul – December 8, 2019: This improve optimized gasoline prices, improved resilience towards DoS assaults, enhanced the efficiency of layer 2 options, enabled interoperability with Zcash, and expanded contract performance.
- Muir Glacier – January 2, 2020: This improve delayed the "difficulty bomb," stopping degradation of community usability by mitigating rising block problem.
- Staking Deposit Contract Deployed – October 14, 2020: This launched staking to Ethereum, paving the best way for the Beacon Chain launch.
- Beacon Chain Genesis – December 1, 2020: This marked the launch of the Beacon Chain, a big step towards Ethereum's Proof-of-Stake imaginative and prescient.
- Berlin – April 15, 2020: This improve optimized gasoline prices and elevated assist for numerous transaction sorts.
- London – August 5, 2021: This improve launched EIP-1559, reforming the transaction payment marketplace for higher predictability and effectivity.
- Altair – October 27, 2021: This improve to the Beacon Chain added assist for "sync committees," facilitating mild purchasers, and elevated validator penalties.
- Arrow Glacier – December 9, 2021: This improve pushed again the "difficulty bomb," making certain clean community operation.
- Grey Glacier – June 30, 2022: Just like Arrow Glacier, this improve additional delayed the "difficulty bomb.”
- Bellatrix – September 6, 2022: This upgrade prepared the Beacon Chain for The Merge, adjusting validator penalties and fork choice rules.
- Paris (The Merge) – September 15, 2022: This monumental upgrade transitioned Ethereum from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake, marking a significant milestone in its history.
- Shanghai-Capella ("Shapella") – April 12, 2023: This upgrade enabled staking withdrawals from the Beacon Chain to the execution layer, a crucial feature for stakers.
- Cancun-Deneb ("Dencun") – March 13, 2024: This upgrade focuses on scalability, introducing EIP-4844 (Proto-Danksharding) to reduce data storage costs for layer 2 rollups, resulting in lower transaction fees for users.
Here are some of the most anticipated EIPs still under research in the Ethereum community:
Account Abstraction: Simplifying Ethereum User Interactions
One anticipated upgrade in Ethereum’s roadmap is Account Abstraction, a concept designed to make user interactions on Ethereum more flexible, efficient, and user-friendly. Traditionally, Ethereum has two types of accounts: externally owned accounts (EOAs) controlled by private keys and Contract Accounts governed by code. Account abstraction aims to blur this distinction, enabling all accounts to operate more like smart contracts and allowing custom transaction logic.
Account Abstraction essentially lets users customize their accounts by introducing programmable features, such as multi-signature requirements, social recovery mechanisms, and meta-transactions. This flexibility is useful for onboarding users unfamiliar with private key management, making Ethereum more accessible and secure.
Key EIPs Under Account Abstraction
Two primary EIPs contribute to Ethereum’s account abstraction: EIP-4337 and EIP-7702. Let’s look at each in detail.
EIP-4337: Decentralized Account Abstraction Without Consensus Changes
EIP-4337 proposes a system for implementing account abstraction without changing Ethereum’s core consensus. This is achieved by introducing a new type of "Person Operation" that operates independently of the standard Ethereum transaction model.
Here’s how it works:
- User Operations: EIP-4337 introduces a concept called "Person Operations," which is a way for users to interact with Ethereum without relying on traditional private key transactions. Instead, these operations are handled by a separate pool called the "Person Operation Mempool."
- Bundlers: Particular nodes, referred to as bundlers, combination a number of Person Operations and submit them as a single transaction to the Ethereum community. This permits for extra environment friendly processing of transactions, as customers can batch a number of operations into one.
- Sensible Contract Wallets: EIP-4337 allows all accounts to operate as sensible contract wallets, which means customers can embrace further logic, similar to every day spending limits or multi-sig necessities. This method enhances safety and consumer management, making Ethereum accounts extra versatile.
The most important good thing about EIP-4337 is that it permits for account abstraction with out altering Ethereum’s underlying consensus mechanism. This makes it simpler to implement whereas nonetheless attaining the advantages of customizable accounts and versatile transaction fashions.
EIP-7702: Non permanent Sensible Contract Code for EOAs
EIP-7702, co-authored by Vitalik Buterin, proposes a brand new transaction kind that enables Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs) to quickly set a sensible contract code executable solely in the course of the transaction. This method allows EOAs to entry account abstraction options with out completely migrating to sensible contract accounts or delegating transaction management to exterior contracts.
Key features of EIP-7702 embrace:
- Non permanent Contract Code: EOAs can embrace a contract_code area of their transactions, specifying code that’s lively solely in the course of that transaction.
- Enhanced Performance: This mechanism permits EOAs to carry out complicated operations similar to gasoline sponsorships, batch transactions, and customized execution logic with out altering their basic construction.
- Alignment with Account Abstraction Roadmap: By enabling short-term sensible contract capabilities, EIP-7702 aligns with Ethereum's broader aim of unifying account functionalities whereas preserving the simplicity of EOAs.
Collectively, EIP-4337 and EIP-7702 characterize important steps towards a extra versatile and user-friendly Ethereum ecosystem, permitting for enhanced account functionalities with out compromising the community's safety or requiring in depth structural modifications.
Proposer-Builder Separation (PBS): Enhancing Ethereum’s Safety and Scalability
Proposer-Builder Separation (PBS) is an upcoming improve that goals to enhance Ethereum’s safety and scalability by dividing the core duties of validators. At present, validators are chargeable for constructing and verifying blocks, creating potential inefficiencies and safety dangers. With PBS, these roles shall be cut up between two specialised contributors: block builders and proposers (Ethereum validators). PBS optimizes block area utilization by separating block development and verification and addresses safety issues similar to Maximal Extractable Worth (MEV).
What’s Maximal Extractable Worth (MEV), and Why is it a Safety Concern?
Maximal Extractable Worth (MEV) refers back to the most revenue a validator could make by reordering, together with, or excluding transactions inside a block. MEV arises as a result of particular transaction placements will be exploited to generate revenue, incentivizing validators to govern transaction orders.
A typical instance of MEV exploitation is the sandwich assault, usually seen in decentralized exchanges (DEXs). In a sandwich assault, a validator detects a big commerce about to occur and performs the next actions:
- The validator locations a commerce proper earlier than the big commerce to drive up the asset's worth.
- The massive commerce executes, additional elevating the asset’s worth.
- The validator then sells the asset instantly after the big commerce, making the most of the elevated worth.
This course of extracts worth from different customers and compromises community safety and equity. PBS goals to handle MEV by introducing a extra clear and controlled method.
How PBS Works
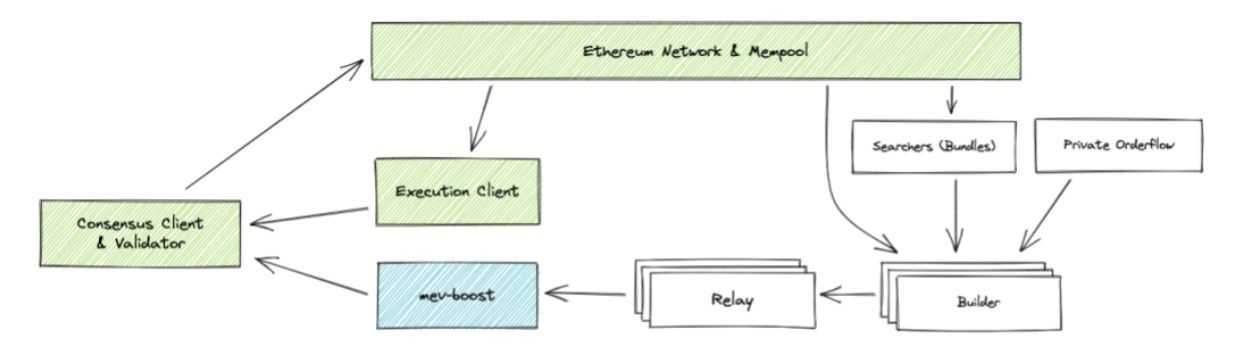
PBS will introduce a brand new community participant referred to as Block Builders, makes a speciality of establishing essentially the most environment friendly blocks. Right here’s a breakdown of the PBS course of:
- Block Constructing by Block Builders: Block builders gather transactions and use specialised algorithms to create environment friendly blocks that maximize community throughput whereas accounting for MEV. They produce blocks which might be optimized for the very best profitability with out compromising integrity.
- Block Public sale: As soon as block builders have created the blocks, they enter an public sale the place proposers (Ethereum validators) choose the block with the very best bid.
- Block Verification by Proposers: The proposers confirm the transactions throughout the chosen block, making certain they meet Ethereum’s requirements. If the block is legitimate, it’s accepted by the community. The successful bid is distributed among the many taking part builders and proposers, creating an incentive construction that rewards environment friendly block manufacturing.
How PBS Enhances Ethereum’s Safety and Scalability
- Environment friendly Block Area Utilization: With block builders optimizing the development of every block, Ethereum’s block area is used extra successfully, rising the variety of transactions processed per block and thus enhancing scalability.
- Clear MEV: PBS makes MEV public, integrating it into Ethereum’s consensus mechanism. This transparency permits MEV practices to be monitored and managed, decreasing the danger of malicious actions and enabling the Ethereum protocol to punish exploitative MEV ways.
- Diminished Danger of Collusion and Bias: Below the present system, validators deal with each block development and verification, permitting the potential for biased habits or collusion. PBS eliminates this danger by separating these duties, with proposers centered solely on verification. This ensures a impartial block choice course of and reduces alternatives for collusion.
PBS remains to be below lively analysis and growth throughout the Ethereum neighborhood as builders proceed to refine its design to maximise safety and scalability advantages.
Danksharding: Ethereum's Imaginative and prescient for Full Scalability
Danksharding represents the whole realization of Ethereum's scalability roadmap, constructing on the foundational work of Proto-Danksharding. Whereas Proto-Danksharding launched blob-carrying transactions—permitting rollups to retailer information effectively inside every block—Danksharding takes this idea to the following degree, additional enhancing the community’s capability to assist high-throughput purposes and scale back Layer 2 (L2) transaction prices.
From Proto-Danksharding to Danksharding
Proto-Danksharding, already reside on the Ethereum mainnet, permits every Ethereum block to hold as much as 6 blobs of knowledge. These blobs are information sections devoted to rollups, enabling high-volume transaction processing with out congesting the Ethereum mainnet. Blobs make information out there however don’t require each Ethereum node to execute the transactions, decreasing computational pressure.
If Proto-Danksharding proves profitable, full Danksharding will improve the blob restrict per block from 6 to 64, dramatically multiplying the community's capability for rollup information and decreasing transaction prices for Layer 2 options. With extra blobs per block, Ethereum can deal with even higher volumes of transactions off-chain, additional decreasing congestion and gasoline charges on the mainnet.
Managing Elevated Storage Necessities
As promising as Danksharding is, rising the blob restrict per block introduces important storage necessities for Ethereum nodes. Increased blob capability means extra information saved in every block, probably making it difficult for validators to take care of a full copy of the blockchain with out substantial will increase in storage.
One proposed answer to handle this problem is to prune blob information older than one month from the mainnet. Which means that blob information can be faraway from actively saved information on nodes after one month, liberating up area and making storage calls for extra manageable.
This answer is viable as a result of:
- Finalized Information: Blob information older than one month is finalized and immutable, which means it has been completely validated and may not be altered.
- Minimal Danger of Forks or Inconsistencies: After one month, the possibilities of community forks or inconsistencies affecting the integrity of outdated blob information are extraordinarily low, making pruning a protected and efficient solution to scale back storage overhead.
Danksharding thus gives Ethereum a scalable future, leveraging optimized information administration to assist the community’s development and cementing Ethereum as a pacesetter in Web3 scalability.
Pectra: The Ethereum Meta EIP
The Ethereum Pectra Improve is a big forthcoming enhancement to the Ethereum community aimed toward enhancing scalability, effectivity, and consumer expertise. Scheduled to roll out in two phases beginning in early 2025, Pectra combines two beforehand deliberate upgrades—Prague and Electra—right into a cohesive replace.

Key Options of the Pectra Improve:
- Account Abstraction: Pectra introduces account abstraction, permitting customers to pay gasoline charges with numerous tokens, not simply Ether (ETH). This flexibility enhances consumer comfort and broadens the usability of the Ethereum community.
- Sensible Contract Effectivity: The improve consists of enhancements to the Ethereum Digital Machine (EVM), making sensible contract execution extra environment friendly. This enhancement reduces prices and complexity for builders and customers interacting with decentralized purposes (DApps).
- Validator Staking Enhancements: Pectra will increase the utmost stake for validators from 32 ETH to 2,048 ETH, permitting for extra versatile staking choices. This transformation goals to optimize community safety and effectivity by accommodating bigger staking operations.
- Introduction of Verkle Bushes: The improve implements Verkle timber, an information construction that improves information storage and verification processes. This development enhances the community's scalability by decreasing the quantity of knowledge nodes have to retailer, resulting in sooner transaction processing and decrease prices.
- Assist for Layer 2 Options and PeerDAS: Pectra enhances Layer 2 options by introducing Peer Information Availability Sampling (PeerDAS), a know-how that facilitates information dealing with for these networks. This enchancment helps Ethereum's scalability by enabling extra environment friendly off-chain transaction processing.
By integrating these options, the Pectra Improve goals to make Ethereum extra accessible, environment friendly, and scalable, benefiting each on a regular basis customers and builders throughout the ecosystem.
What’s Ethereum: Closing Ideas
In revisiting Ethereum’s ecosystem, we acquire a brand new appreciation for the way huge and dynamic this community has grow to be. Over time, Ethereum has developed from a single-layer blockchain into a fancy ecosystem designed to accommodate the broadest vary of purposes, property, and customers.
What’s significantly placing is the irony of Ethereum’s structure. Ethereum has grow to be essentially the most intricate, deeply researched, and broadly adopted blockchain community, but its underlying ethos is to stay a generalized platform. Whereas different Layer 1 blockchain, like Solana with its give attention to scalability or Cosmos with its emphasis on interoperability, are purpose-built, Ethereum is designed to be essentially the most versatile and general-purpose answer. This adaptability has positioned Ethereum because the central platform for a lot of improvements, making it essentially the most complete blockchain in scope.
Furthermore, this revisited exploration underscores that we will not talk about Ethereum as a singular community. Right now, Ethereum is far nearer to embodying the construction of the Web itself—an unlimited, interconnected community of networks, encompassing various property, purposes, and communities. Ethereum has grown to be greater than only a blockchain; it’s a platform that underpins the broader Web3 ecosystem, reflecting its continued enlargement and profound affect on the digital world.
Often Requested Questions
What’s Ethereum?
Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform that capabilities as a worldwide laptop. It permits customers to run decentralized purposes (DApps) and execute sensible contracts, that are self-executing contracts with the phrases of the settlement immediately written into code. Not like Bitcoin, which primarily focuses on peer-to-peer transfers of worth, Ethereum gives a flexible ecosystem for builders to construct and deploy purposes with out intermediaries.
How does Ethereum differ from Bitcoin?
Whereas Bitcoin focuses on being a retailer of worth and a peer-to-peer cost system, Ethereum is designed to be a versatile platform for decentralized purposes. Bitcoin’s blockchain is optimized for recording BTC transactions, whereas Ethereum’s community helps complicated computations, decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and extra. Ethereum additionally transitioned to a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, making it extra energy-efficient than Bitcoin’s Proof of Work (PoW) system.
What’s Ether (ETH)?
Ether (ETH) is the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum community. It’s used to pay for transaction charges (gasoline), compensate validators who safe the community, and function a medium of trade throughout the ecosystem. Not like Bitcoin, which has a hard and fast provide, Ethereum has an infinite provide however employs mechanisms like payment burning to stability inflation.
What are Ethereum Layer 2 options?
Layer 2 (L2) options are impartial networks that run on high of Ethereum to extend scalability and scale back transaction prices. These options, like zk-rollups and optimistic rollups, offload transaction execution to a secondary layer whereas leveraging Ethereum’s mainnet for safety and information availability. L2 options enable Ethereum to deal with larger transaction volumes extra effectively.
What’s EIP-1559, and the way does it have an effect on Ethereum's financial coverage?
EIP-1559, carried out in August 2021, reformed Ethereum’s payment construction by introducing a base payment that’s burned, decreasing the full provide of ETH. This mechanism has a deflationary impact when community exercise is excessive, serving to to stability inflation by burning a portion of gasoline charges.
What’s Proto-Danksharding?
Proto-Danksharding, launched in March 2024, reduces the price of storing information on Ethereum by implementing a brand new kind of transaction referred to as blob-carrying transactions. This improve makes Layer 2 rollups extra environment friendly, decreasing transaction charges and rising scalability.
What’s Account Abstraction (EIP-4337)?
Account abstraction goals to make Ethereum accounts extra versatile by permitting customers to customise transaction logic, similar to enabling social restoration or gasoline funds with tokens apart from ETH. EIP-4337 introduces “User Operations” to attain this with out altering Ethereum’s core consensus, making wallets and accounts extra versatile.
What’s the way forward for Ethereum?
Ethereum’s future includes scaling by means of Layer 2 options, implementing full Danksharding, and introducing upgrades like account abstraction and proposer-builder separation (PBS). These enhancements purpose to make Ethereum extra scalable, safe, and user-friendly whereas decreasing transaction prices and rising throughput.
Is Ethereum safe?
Sure, Ethereum is very safe on account of its decentralized validator community and cryptographic mechanisms. Nonetheless, like every blockchain, sensible contracts deployed on Ethereum can include vulnerabilities if not correctly coded or audited. Customers are suggested to train warning when interacting with new initiatives and DApps.